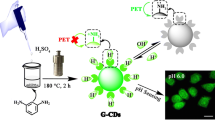
Abstract
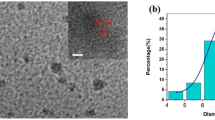
A near-infrared nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dot (N,S-CD)-based ratiometric fluorescent probe is proposed that is synthesized via hydrothermal approach using glutathione and formamide as precursor for sensing and imaging of Zn2+. The prepared N,S-CDs facilitate binding with Zn2+ owing to N and S atom doping. The ratio (I650/I680) of fluorescence intensity at 650 nm and 680 nm increased with the concentrations of Zn2+ when the excitation wavelength was 415 nm. The linearity range was 0.01 to 1.0 μM Zn2+with a detection limit of 5.0 nM Zn2+. The proposed probe was applied to label-free monitoring of Zn2+ in real samples and fluorescent imaging of Zn2+ in living cells, which confirmed its promising applications.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu L, Guo Q, Liu Y, Sun Q (2015) FRET-based ratiometric fluorescent probe for detection of Zn2+ using a dual-emission silica-coated quantum dots mixture. Anal Chem 87:5318–5323
Li Y, Shi J, Wu X, Luo Z, Wang F, Guo Q (2009) Tracing of intracellular zinc(II) fluorescence flux to monitor cell apoptosis by using fluozin-3AM. Cell Biochem Funct 27:417–423
Cuajungco M, Lees G (1997) Zinc metabolism in the brain: relevance to human neurodegenerative disorders. Neurobiol Dis 4:137–169
Chausmer A (1998) Zinc, insulin and diabetes. J Am Coll Nutr 17:109–115
Vasto S, Candore G, Listi F, Balistreri C, Colonna-Romano G, Malavolta M, Lio D, Nuzzo D, Mocchegiani E, Di Bona D, Caruso C (2008) Inflammation, genes and zinc in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res Rev 58:96–105
Rai A, Kumari N, Nair R, Singh K, Mishra L (2015) A new rhodamine derivative as a single optical probe for the recognition of Cu2+ and Zn2+ ions. RSC Adv 5:14382–14388
Nolan E, Lippard S (2009) Small-molecule fluorescent sensors for investigating zinc metalloneurochemistry. J Acc Chem Res 42:193–203
Ren H, Wu B, Jia-Tong Chen J, Yan X (2011) Silica-coated S2–enriched manganese-doped ZnS quantum dots as a photoluminescence probe for imaging intracellular Zn2+ ions. Anal Chem 83:8239–8244
Tomat E, Nolan E, Jaworski J, Lippard S (2008) Organelle-specific zinc detection using zinpyr-labeled fusion proteins in live cells. J Am Chem Soc 130:15776–15777
Xu Z, Yoon J, Spring D (2010) Fluorescent chemosensors for Zn2+. Chem Soc Rev 39:1996–2006
Wang B, Liang Z, Tan H, Duan W, Luo M (2020) Red-emission carbon dots-quercetin systems as ratiometric fluorescent nanoprobes towards Zn2+ and adenosine triphosphate. Microchim Acta 187:345–354
Ning P, Jiang J, Li L, Wang S, Yu H, Feng Y, Zhu M, Zhang B, Yin H, Guo Q, Meng X (2016) A mitochondria-targeted ratiometric two-photon fluorescent probe for biological zinc ions detection. Biosens Bioelectron 77:921–927
Han B, Peng T, Yu M, Chi C, Li Y, Hu X, He G (2018) One-pot synthesis of highly fluorescent Fe2+-doped carbon dots for a dual-emissive nanohybrid for the detection of zinc ions and histidine. New J Chem 42:13651–13659
Li W, Liu Z, Fang B, Jin M, Tian Y (2020) Two-photon fluorescent Zn2+ probe for ratiometric imaging and biosensing of Zn2+ in living cells and larval zebrafish. Biosens Bioelectron 148:111666
Yoon S, Lee J, Lee M (2018) A ratiometric fluorescent probe for Zn2+ based on pyrene-appended naphthalimide-dipicolylamine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 258:50–55
Song Q, Ma Y, Wang X, Tang T, Song Y, Ma Y, Xu G, Wei F, Cen Y, Hu Q (2018) “On-off-on” fluorescent system for detection of Zn2+ in biological samples using quantum dots-carbon dots ratiometric nanosensor. J Colloid Interface Sci 516:522–528
Wang Y, Lao S, Ding W, Zhang Z, Liu S (2019) A novel ratiometric fluorescent probe for detection of iron ions and zinc ions based on dual-emission carbon dots. Sensors Actuators B Chem 284:186–192
Waheed A, Abdel-Azeim S, Ullah N, Oladepo S (2020) Design and synthesis of two new terbium and europium complex-based luminescent probes for the selective detection of zinc ions. Luminescence 35:1238–1247
Wu Z, Gao M, Wang T, Wan X, Zheng L, Huang C (2014) A general quantitative pH sensor developed with dicyandiamide N-doped high quantum yield graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 6:3868–3874
Yu L, Ren G, Tang M, Zhu B, Chai F, Li G, Xu D (2018) Effective determination of Zn2+, Mn2+, and Cu2+ simultaneously by using dual-emissive carbon dots as colorimetric fluorescent probe. Eur J Inorg Chem 29:3418–3426
Huang J, Zhong Z, Rong M, Zhou X, Chen X, Zhang M (2014) An easy approach of preparing strongly luminescent carbon dots and their polymer based composites for enhancing solar cell efficiency. Carbon 70:190–198
Pan L, Sun S, Zhang L, Jiang K, Lin H (2016) Near-infrared emissive carbon dots for two-photon fluorescence bioimaging. Nanoscale 8:17350–17356
Xu Q, Pu P, Zhao J, Dong C, Gao C, Chen Y, Chen J, Liu Y, Zhou H (2015) Preparation of highly photoluminescent sulfur-doped carbon dots for Fe (III) detection. J Mater Chem A 3:542–546
Sheng Z, Shao L, Chen J, Bao W, Wang F, Xia X (2011) Catalyst-free synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene via thermal annealing graphite oxide with melamine and its excellent electrocatalysis. ACS Nano 5:4350–4358
Li Y, Wang J, Li X, Geng D, Banis M, Tang Y, Wang D, Li R, Sham T, Sun X (2012) Discharge product morphology and increased charge performance of lithium-oxygen batteries with graphene nanosheet electrodes: the effect of sulphur doping. J Mater Chem 22:20170–20174
Nie R, Wang J, Wang L, Qin Y, Chen P, Hou Z (2012) Platinum supported on reduced graphene oxide as a catalyst for hydrogenation of nitroarenes. Carbon 50:586–596
Yang S, Sun J, Li X, Zhou W, Wang Z, He P, Ding G, Xie X, Kang Z, Jiang M (2014) Large-scale fabrication of heavy doped carbon quantum dots with tunable-photoluminescence and sensitive fluorescence detection. J Mater Chem A 2:8660–8667
Qu D, Zheng M, Du P, Zhou Y, Zhang L, Li D, Tan H, Zhao Z, Xie Z, Sun Z (2013) Highly luminescent S, N co-doped graphene quantum dots with broad visible absorption bands for visible light photocatalyst. Nanoscale 51:2272–12277
Liu H, Sun Y, Li Z, Yang J, Aryee A, Qu L, Du D, Lin Y (2019) Lysosome-targeted carbon dots for ratiometric imaging of formaldehyde in living cells. Nanoscale 11:8458–8463
Xu Z, Baek K, Kim H, Cui J, Qian X, Spring D, Yoon S (2010) Zn2+-triggered amide tautomerization produces a highly Zn2+-selective, cell-permeable, and ratiometric fluorescent sensor. J Am Chem Soc 132:601–610
Bharathi D, Krishna R, Siddlingeshwar B, Divakar D, Alkheraif A (2019) Understanding the interaction of carbon quantum dots with CuO and Cu2O by fluorescence quenching. J Hazard Mater 369:17–24
Luo P, Sahu S, Yang S, Sonkar S, Wang J, Wang H, LeCroy G, Cao L, Sun Y (2013) Carbon quantum dots for optical bioimaging. J Mater Chem B 1:2116–2127
Huang H, Cui Y, Liu M, Chen J, Wan Q, Wen Y, Deng F, Zhou N, Zhang X, Wei Y (2018) A one-step ultrasonic irradiation assisted strategy for the preparation of polymer-functionalized carbon quantum dots and their biological imaging. J Colloid Interface Sci 532:767–773
Zhao N, Wang Y, Hou S, Zhao L (2020) Functionalized carbon quantum dots as fluorescent nanoprobe for determination of tetracyclines and cell imaging. Microchim Acta 187:1–10
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No.21665001; 21874030), BAGUI Scholar Program and Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (No.2021GXNSFAA220113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Li, S., Liu, X. et al. Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon dot-based ratiometric fluorescent probe for Zn2+ sensing and imaging in living cells. Microchim Acta 189, 107 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05188-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05188-7