Abstract
New green-emissive carbon dots (G-CDs) are described here and shown to be viable fluorescent nanoprobes for the detection of changes in cellular pH values. By using m-phenylenediamine as the carbon source, G-CDs with an absolute quantum yield of 36% were solvothermally synthesized in the presence of strong H2SO4. The G-CDs have an average size of 2.3 nm and display strong fluorescence with excitation/emission peaks at 450/510 nm. The fluorescence intensity depends on the pH value in the range from 6.0 to 10.0, affording the capability for sensitive detection of intracellular pH variation. The nanosensor with excellent photostability exhibited good fluorescence reversibility in different pH solutions, and showed excellent stability against the influence of other biological species. The nanoprobe was successfully used in confocal fluorescence microscopy to determine pH values in SMMC-7721 cells.

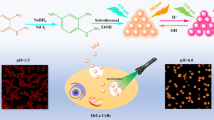
Schematic presentation of green-emissive carbon dots (G-CDs) synthesized using m-phenylenediamine and sufuric acid through a solvothermal method for real-time fluorometric monitoring of intracellular pH values. Mechanism can be ascribed to PET process from the electron lone pair in amino group to the CDs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kennedy RT, Huang L, Aspinwall CA (1996) Extracellular pH is required for rapid release of insulin from Zn−insulin precipitates in β-cell secretory vesicles during exocytosis. J Am Chem Soc 118:1795–1796
Janecki AJ, Montrose MH, Zimniak P, Zweibaum A, Tse CM, Khurana S, Donowitz M (1998) Subcellular redistribution is involved in acute regulation of the brush border Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3 in human colon adenocarcinoma cell line caco-2: protein kinase C-mediated inhibition of the exchanger. J Biol Chem 273:8790–8798
Zhang X, Lin Y, Gillies RJ (2010) Tumor pH and its measurement. J Nucl Med 51:1167–1170
Schindler M, Grabski S, Hoff E, Simon SM (1996) Defective pH regulation of acidic compartments in human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) is normalized in adriamycin-resistant cells (MCF-7adr). Biochemistry 35:2811–2817
Izumi H, Torigoe T, Ishiguchi H, Uramoto H, Yoshida Y, Tanabe M, Ise T, Murakami T, Yoshida T, Nomoto M, Kohno K (2003) Cellular pH regulators: potentially promising molecular targets for cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Treat Rev 29:541–549
Hou JT, Ren WX, Li K, Seo J, Sharma A, Yu XQ, Kim JS (2017) Fluorescent bioimaging of pH: from design to applications. Chem Soc Rev 46:2076–2090
Horak E, Kassal P, Hranjec M, Steinberg IM (2018) Benzimidazole functionalised Schiff bases: novel pH sensitive fluorescence turn-on chromoionophores for ion-selective optodes. Sensor Actuat B: Chem 258:415–423
Bao L, Ding L, Hui J, Ju H (2016) A light-up imaging protocol for neutral pH-enhanced fluorescence detection of lysosomal neuraminidase activity in living cells. Chem Commun 52:12897–12900
Tantama M, Hung YP, Yellen G (2011) Imaging intracellular pH in live cells with a genetically encoded red fluorescent protein sensor. J Am Chem Soc 133:10034–10037
Esposito A, Gralle M, Dani MAC, Lange D, Wouters FS (2008) pHlameleons: a family of FRET-based protein sensors for quantitative pH imaging. Biochemistry 47:13115–13126
Mutuyimana FP, Liu J, Na M, Nsanzamahoro S, Rao Z, Chen HL, Chen XG (2018) Synthesis of orange-red emissive carbon dots for fluorometric enzymatic determination of glucose. Microchim Acta 185:518
Mutuyimana FP, Liu J, Nsanzamahoro S, Na M, Chen HL, Chen XG (2019) Yellow-emissive carbon dots as a fluorescent probe for chromium (VI). Microchim Acta 186:163
Sun YQ, Wang XJ, Wang C, Tong DY, Wu Q, Jiang KL, Jiang YN, Wang CX, Yang MH (2018) Red emitting and highly stable carbon dots with dual response to pH values and ferric ions. Microchim Acta 185:83
Shangguan JF, He DG, He XX, Wang KM, Xu FZ, Liu JQ, Tang JL, Yang X, Huang J (2016) Label-free carbon-dots-based ratiometric fluorescence pH nanoprobes for intracellular pH sensing. Anal Chem 88:7837–7843
Wang RX, Wang XF, Sun YM (2017) One-step synthesis of self-doped carbon dots with highly photoluminescence as multifunctional biosensors for detection of iron ions and pH. Sensor Actuat B: Chem 241:73–79
Hou P, Yang T, Liu H, Li YF, Huang CZ (2017) An active structure preservation method for developing functional graphitic carbon dots as an effective antibacterial agent and a sensitive pH and Al3+ nanosensor. Nanoscale 9:17334–17341
Park SY, Lee HU, Park ES, Lee SC, Lee JW, Jeong SW, Kim CH, Lee YC, Huh YS, Lee J (2014) Photoluminescent green carbon nanodots from food-waste-derived sources: large-scale synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:3365–3370
Liu DY, Qu F, Zhao XN, You JM (2015) Generalized one-pot strategy enabling different surface functionalizations of carbon nanodots to produce dual emissions in alcohol–water binary systems. J Phys Chem C 119:17979–17987
Dong YQ, Pang HC, Yang HB, Guo CX, Shao JW, Chi YW, Li CM, Yu T (2013) Carbon-based dots co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur for high quantum yield and excitation-independent emission. Angew Chem Int Edit 52:7800–7804
Ding H, Yu SB, Wei JS, Xiong HM (2016) Full-color light-emitting carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism. ACS Nano 10:484–491
Wang N, Zheng AQ, Liu X, Chen JJ, Yang T, Chen ML, Wang JH (2018) Deep eutectic solvent assisted preparation of nitrogen/chloride doped carbon dots for intracellular biological sensing and live cell imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:7901–7909
Wang Y, Lu LL, Peng H, Xu J, Wang FY, Qi RJ, Xu ZA, Zhang W (2016) Multi-doped carbon dots with ratiometric pH sensing properties for monitoring enzyme catalytic reactions. Chem Commun 52:9247–9250
Sun S, Zhang L, Jiang K, Wu A, Lin HW (2016) Towards high-efficient red emissive carbon dots: facile preparation, unique properties, and applications as multifunctional theranostic agents. Chem Mater 28:8659–8668
Zhou J, Zhou H, Tang JB, Deng S, Yan F, Li WJ, Qu MH (2017) Carbon dots doped with heteroatoms for fluorescent bioimaging: a review. Microchim Acta 184:343–368
Jiang K, Sun S, Zhang L, Lu Y, Wu AG, Cai CZ, Lin HW (2015) Red, green, and blue luminescence by carbon dots: full-color emission tuning and multicolor cellular imaging. Angew Chem Int Edit 54:5360–5363
Lindberg BJ, Hamrin K, Johansson G, Gelius U, Fahlman A, Nordling C, Siegbahn K (1970) Molecular spectroscopy by means of ESCA II. Sulfur compounds. Correlation of electron binding energy with structure. Phys Scr 1:286
Ge JC, Jia QY, Liu WM, Guo L, Liu QY, Lan MH, Zhang HY, Meng XM, Wang PF (2015) Red-emissive carbon dots for fluorescent, photoacoustic, and thermal theranostics in living mice. Adv Mater 27:4169–4177
Wang Q, Zhang SR, Zhong YG, Yang XF, Li Z, Li H (2017) Preparation of yellow-green-emissive carbon dots and their application in constructing a fluorescent turn-on nanoprobe for imaging of selenol in living cells. Anal Chem 89:1734–1741
Shi BF, Su YB, Zhang LL, Liu RJ, Huang MJ, Zhao SL (2016) Nitrogen-rich functional groups carbon nanoparticles based fluorescent pH sensor with broad-range responding for environmental and live cells applications. Biosens Bioelectron 82:233–239
Hutt JT, Aron ZD (2014) Synthesis and application of ratiometric and “turn-on” fluorescent pH sensors: an advanced organic undergraduate laboratory. J Chem Educ 91:1990–1994
Wang YY, Yang XF, Zhong YG, Gong XY, Li Z, Li H (2016) Development of a red fluorescent light-up probe for highly selective and sensitive detection of vicinal dithiol-containing proteins in living cells. Chem Sci 7:518–524
Zhang W, El-Reash YGA, Ding LJ, Lin ZZ, Lian Y, Song B, Yuan JL, Wang XD (2018) A lysosome-targeting nanosensor for simultaneous fluorometric imaging of intracellular pH values and temperature. Microchim Acta 185:533
Wang L, Chen Y (2018) Lanthanide doped carbon dots as a fluorescence chromaticity- based pH probe. Microchim Acta 185:489
Terrones YT, Leskow FC, Bordoni AV, Acebedo SL, Spagnuolo CC, Wolosiuk A (2017) A silica supported tricarbocyanine based pH nanosensor with a large stokes shift and a near infrared fluorescence response: performance in vitro and in live cells. J Mater Chem B 5:4031–4034
Näreoja T, Deguchi T, Christ S, Peltomaa R, Prabhakar N, Fazeli E, Perälä N, Rosenholm JM, Arppe R, Soukka T (2017) Ratiometric sensing and imaging of intracellular pH using polyethyleneimine-coated photon upconversion nanoprobes. Anal Chem 89:1501–1508
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21807068, 21373132, 21502109), the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (No. 2017JQ2017), and the Project of Shaanxi University of Technology (SLGKY14-08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3554 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Yang, H., Zhang, Q. et al. Strong acid-assisted preparation of green-emissive carbon dots for fluorometric imaging of pH variation in living cells. Microchim Acta 186, 468 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3569-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3569-4