Abstract
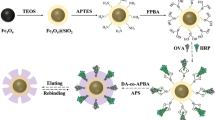
Highly specific novel glycopeptide-based fluorescent molecularly imprinting polymers (g-FMIPs) were constructed to recognize and determine the target glycoprotein in complex biological samples. The glycopeptide of ovalbumin (OVA), with the unique structural characteristics of glycan and peptide, and potential application in improving the specificity recognition of g-FMIPs, was selected as the template molecule. The nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) were introduced for fluorescence response. The obtained g-FMIPs possessed rapid binding kinetics and high adsorption capacity. Notably, the g-FMIPs exhibited remarkable selectivity and sensitivity with a high imprinting factor of 6.57, good linearity of 0.625 − 5.00 μM, and limit of detection of 0.208 μM. After treatment with g-FMIPs, the concentration of OVA in eluted solution was 1.07 μM. The obtained recoveries at 1.43 μM, 2.86 μM, and 4.29 μM spiked concentrations were 97.2%, 93.5%, and 101%, respectively, and the relative standard deviations were 2.6%, 4.2%, and 1.1%, respectively. In summary, the proposed strategy will expand the MIPs construction method and its application prospects in precision recognition and sensitive detection of trace glycoproteins from complex biosamples.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xing RR, Wang SS, Bie ZJ, He H, Liu Z (2017) Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers specific to glycoproteins, glycans and monosaccharides via boronate affinity controllable-oriented surface imprinting. Nat Protoc 12:964–987. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2017.015
Li DJ, Tu TY, Wu XY (2018) Efficient preparation of template immobilization-based boronate affinity surface-imprinted silica nanoparticles using poly(4-aminobenzyl alcohol) as an imprinting coating for glycoprotein recognition. Anal Methods 10:4419–4429. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ay00632f
Lai YX, Zhang CX, Deng Y, Yang GJ, Li S, Tang CL, He NY (2019) A novel α-fetoprotein-MIP immunosensor based on AuNPs/PTh modified glass carbon electrode. Chin Chem Lett 30:160–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2018.07.011
Song YJ, Li WJ, Ma CY, Sun Y, Qiao JW, Li HL, Hong CL (2020) First use of inorganic copper silicate-transduced enzyme-free electrochemical immunosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen detection. Sens Actuators B Chem 319:128311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128311
Ludwig JA, Weinstein JN (2005) Biomarkers in cancer staging, prognosis and treatment selection. Nat Rev Cancer 5:845–856. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1739
Ma YY, Li XL, Li W, Liu Z (2018) Glycan-imprinted magnetic nanoparticle-based SELEX for efficient screening of glycoprotein-binding aptamers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:40918–40926. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b14441
Zhou LL, Wang YJ, Xing RR, Chen J, Liu J, Li W, Liu Z (2019) Orthogonal dual molecularly imprinted polymer-based plasmonic immunosandwich assay: a double characteristic recognition strategy for specific detection of glycoproteins. Biosens Bioelectron 145:111729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111729
Carneiro MCCG, Sousa-Castillo A, Correa-Duarte MA, Sales MGF (2019) Dual biorecognition by combining molecularly imprinted polymer and antibody in SERS detection: application to carcinoembryonic antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 146:111761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111761
Li SW, Yang KG, Liu JX, Jiang B, Zhang LH, Zhang YK (2015) Surface-imprinted nanoparticles prepared with a His-tag-anchored epitope as the template. Anal Chem 87:4617–4620. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac5047246
Zhao MH, Huang S, Xie HY, Wang JY, Zhao XL, Li MY, Zhao MP (2020) Construction of specific and reversible nanoreceptors for proteins via sequential surface-imprinting strategy. Anal Chem 92:10540–10547. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01366
Tawfik SM, Elmasry MR, Sharipov M, Azizov S, Lee CH, Lee YI (2020) Dual emission nonionic molecular imprinting conjugated polythiophenes-based paper devices and their nanofibers for point-of-care biomarkers detection. Biosens Bioelectron 160:112211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112211
Sun C, Pan L, Zhang L, Huang J, Yao D, Wang CZ, Zhang Y, Jiang N, Chen L, Yuan CS (2019) A biomimetic fluorescent nanosensor based on imprinted polymers modified with carbon dots for sensitive detection of alpha-fetoprotein in clinical samples. Analyst 144:6760–6772. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9an01065c
Wei JR, Ni YL, Zhang W, Zhang ZQ, Zhang J (2017) Detection of glycoprotein through fluorescent boronic acid-based molecularly imprinted polymer. Anal Chim Acta 960:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.12.046
Dong YR, Li W, Gu ZK, Xing R, Ma YY, Zhang Q, Liu Z (2019) Inhibition of HER2-positive breast cancer growth by blocking the HER2 signaling pathway with HER2-glycan-imprinted nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 58:10621–10625. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201904860
Xie XY, Hu Q, Ke RF, Zhen XY, Bu YS, Wang SC (2019) Facile preparation of photonic and magnetic dual responsive protein imprinted nanomaterial for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Chem Eng J 371:130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.019
Yang Q, Li JH, Wang XY, Peng HL, Xiong H, Chen LX (2018) Strategies of molecular imprinting-based fluorescence sensors for chemical and biological analysis. Biosens Bioelectron 112:54–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.04.028
Lu HZ, Xu SF (2020) Ultrasensitive turn on molecularly imprinted fluorescence sensor for glycoprotein detection based on nanoparticles signal amplification. Sens Actuators B Chem 306:127566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127566
Arabi M, Ostovan A, Li JH, Wang XY, Zhang ZY, Choo J, Chen LX (2021) Molecular imprinting: green perspectives and strategies. Adv Mater 33:2100543. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202100543
Arabi M, Ostovan A, Bagheri AR, Guo XT, Wang LY, Li JH, Wang XY, Li BW, Chen LX (2020) Strategies of molecular imprinting-based solid-phase extraction prior to chromatographic analysis. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 128:115923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115923
Gholami H, Ghaedi M, Ostovan A, Arabi M, Bagheri AR (2019) Preparation of hollow porous molecularly imprinted and aluminum(III) doped silica nanospheres for extraction of the drugs valsartan and losartan prior to their quantitation by HPLC. Microchim Acta 186:702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3794-x
Arabi M, Ostovan A, Zhang ZY, Wang YQ, Mei RC, Fu LW, Wang XY, Ma JP, Chen LX (2021) Label-free SERS detection of Raman-inactive protein biomarkers by Raman reporter indicator: toward ultrasensitivity and universality. Biosens Bioelectron 174:112825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112825
Qin YT, Peng H, He XW, Li WY, Zhang YK (2019) Highly effective drug delivery and cell imaging using fluorescent double-imprinted nanoparticles by targeting recognition of the epitope of membrane protein. Anal Chem 91:12696–12703. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b02123
Bie ZJ, Chen Y, Ye J, Wang SS, Liu Z (2015) Boronate-affinity glycan-oriented surface imprinting: a new strategy to mimic lectins for the recognition of an intact glycoprotein and its characteristic fragments. Angew Chem Int Ed 54:10211–10215. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201503066
Li WY, Ma YY, Guo ZC, Xing RR, Liu Z (2020) Efficient screening of glycan-specific aptamers using a glycosylated peptide as a scaffold. Anal Chem 93:956–963. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03675
Bie ZJ, Xing RR, He XP, Ma YY, Chen Y, Liu Z (2018) Precision imprinting of glycopeptides for facile preparation of glycan-specific artificial antibodies. Anal Chem 90:9845–9852. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01903
He PY, Zhu HJ, Ma Y, Li N, Niu XH, Wei MB, Pan JM (2019) Rational design and fabrication of surface molecularly imprinted polymers based on multi-boronic acid sites for selective capture glycoproteins. Chem Eng J 367:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.140
Chen GS, Kou XX, Huang SM, Huang SY, Zhang R, Liu C, Shen J, Zhu F, Ouyang GF (2018) Allochroic-graphene oxide linked 3D oriented surface imprinting strategy for glycoproteins assays. Adv Funct Mater 28:1804129. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201804129
Qu D, Zheng M, Zhang LG, Zhao HF, Xie ZG, Jing XB, Haddad RE, Fan HY, Sun ZC (2015) Formation mechanism and optimization of highly luminescent N-doped graphene quantum dots. Sci Rep 5:7998. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07998
Wang YC, Luo J, Liu XY (2020) Fluorescent molecularly imprinted nanoparticles with boronate affinity for selective glycoprotein detection. J Mater Chem B 8:6469–6480. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9tb02648g
Li S, Qin Y, Zhong G, Cai C, Chen X, Chen C (2018) Highly efficient separation of glycoprotein by dual-functional magnetic metal−organic framework with hydrophilicity and boronic acid affinity. ACS Appl Mater Inter 10:27612–27620. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b07671
Zhu SJ, Meng QN, Wang L, Zhang JH, Song YB, Jin H, Zhang K, Sun HC, Wang HY, Yang B (2013) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:3953–3957. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201300519
Luo LH, Zhang F, Chen CY, Cai CQ (2019) Visual simultaneous detection of hepatitis A and B viruses based on a multifunctional molecularly imprinted fluorescence sensor. Anal Chem 91:15748–15756. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04001
Yang Q, Li CY, Li JH, Wang XY, Arabi M, Peng HL, Xiong H, Chen LX (2020) Rational construction of a triple emission molecular imprinting sensor for accurate naked-eye detection of folic acid. Nanoscale 12:6529–6536. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nr00765j
Yan M, Wu Y, Zhang K, Lin R, Jia S, Lu J, Xing W (2021) Multifunctional-imprinted nanocomposite membranes with thermo-responsive biocompatibility for selective/controllable recognition and separation application. J Colloid Interf Sci 582:991–1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.08.108
Sun XY, Ma RT, Chen J, Shi YP (2018) Synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted nanoparticles with multiple recognition sites for the simultaneous and selective capture of two glycoproteins. J Mater Chem B 6:688–696. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tb03001k
Xie J, Zhong G, Cai C, Chen C, Chen X (2017) Rapid and efficient separation of glycoprotein using pH double-responsive imprinted magnetic microsphere. Talanta 169:98–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.03.065
Wang P, Zhu H, Liu J, Ma Y, Yao J, Dai X, Pan J (2019) Double affinity integrated MIPs nanoparticles for specific separation of glycoproteins: a combination of synergistic multiple bindings and imprinting effect. Chem Eng J 358:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.09.168
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Jiamei Liu and Dr Ying Hao at the Instrument Analysis Center of Xi’an Jiaotong University for their assistance with XPS and FT-IR analysis.
Funding
We gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82073807) and the Opening Fund of National & Local Joint Engineering Research Center of High-throughput Drug Screening Technology (No. K20201005) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Yang, Y., Zhu, A. et al. Improved detection and recognition of glycoproteins using fluorescent polymers with a molecular imprint based on glycopeptides. Microchim Acta 188, 439 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05099-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05099-z