Abstract
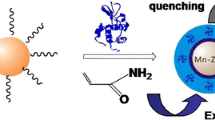
Epitope imprinted polymer nanoparticles (EI-NPs) were prepared by one-pot polymerization of N-isopropylacrylamide in the presence of CdTe quantum dots and an epitope (consisting of amino acids 598 to 609) of human serum albumin (HSA). The resulting EI-NPs exhibit specific recognition ability and enable direct fluorescence quantification of HSA based on a fluorescence turn-on mode. The polymer was characterized by FT-IR, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy and dynamic light scattering. The linear calibration graph was obtained in the range of 0.25–5 μmol · mL−1 with the detection limit of 44.3 nmol · mL−1. The EI-NPs were successfully applied to the direct fluorometric quantification of HSA in samples of human serum. Overall, this approach provides a promising tool to design functional fluorescent materials with protein recognition capability and specific applications in proteomics.

Epitope imprinted polymer nanoparticles containing fluorescent quantum dots were prepared for recognition and direct fluorescence quantification of human serum albumin.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wulff G (2013) Fourty years of molecular imprinting in synthetic polymers: origin, features and perspectives. Microchim Acta 180(15–16):1359–1370. doi:10.1007/s00604-013-0992-9
Dickert FL, Hayden O (1999) Imprinting with sensor development - On the way to synthetic antibodies. Fresenius J Anal Chem 364(6):506–511. doi:10.1007/s002160051376
Bossi A, Piletsky SA, Piletska EV, Righetti PG, Turner APF (2001) Surface-grafted molecularly imprinted polymers for protein recognition. Anal Chem 73(21):5281–5286. doi:10.1021/ac0006526
Ye L, Mosbach K (2001) Polymers recognizing biomolecules based on a combination of molecular imprinting and proximity scintillation: a new sensor concept. J Am Chem Soc 123(12):2901–2902. doi:10.1021/ja005896m
Dai H, Xiao D, He H, Li H, Yuan D, Zhang C (2014) Synthesis and analytical applications of molecularly imprinted polymers on the surface of carbon nanotubes: a review. Microchim Acta. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1376-5
Suedee R, Intakong W, Lieberzeit PA, Wanichapichart P, Chooto P, Dickert FL (2007) Trichloroacetic acid-imprinted polypyrrole film and its property in piezoelectric quartz crystal microbalance and electrochemical sensors to application for determination of haloacetic acids disinfection by-product in drinking water. J Appl Polym Sci 106(6):3861–3871. doi:10.1002/app-26934
Hoshino Y, Koide H, Urakami T, Kanazawa H, Kodama T, Oku N, Shea KJ (2010) Recognition, neutralization, and clearance of target peptides in the bloodstream of living mice by molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles: a plastic antibody. J Am Chem Soc 132(19):6644. doi:10.1021/ja102148f
Hayden O, Haderspock C, Krassnig S, Chen XH, Dickert FL (2006) Surface imprinting strategies for the detection of trypsin. Analyst 131(9):1044–1050. doi:10.1039/b608354b
Pan J, Xue X, Wang J, Xie H, Wu Z (2009) Recognition property and preparation of Staphylococcus aureus protein A-imprinted polyacrylamide polymers by inverse-phase suspension and bulk polymerization. Polymer 50(11):2365–2372. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2009.04.004
Ge Y, Turner APF (2008) Too large to fit? Recent developments in macromolecular imprinting. Trends Biotechnol 26(4):218–224. doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2008.01.001
Zhao YY, Ma YX, Li H, Wang LY (2012) Composite QDs@MIP nanospheres for specific recognition and direct fluorescent quantification of pesticides in aqueous media. Anal Chem 84(1):386–395. doi:10.1021/ac202735v
Ren X, Liu H, Chen L (2014) Fluorescent detection of chlorpyrifos using Mn(II)-doped ZnS quantum dots coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer. Microchim Acta. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1317-3
Bruchez M, Moronne M, Gin P, Weiss S, Alivisatos AP (1998) Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 281(5385):2013–2016. doi:10.1126/science.281.5385.2013
Tu RY, Liu BH, Wang ZY, Gao DM, Wang F, Fang QL, Zhang ZP (2008) Amine-capped ZnS-Mn2+ nanocrystals for fluorescence detection of trace TNT explosive. Anal Chem 80(9):3458–3465. doi:10.1021/ac800060f
Lin HY, Ho MS, Lee MH (2009) Instant formation of molecularly imprinted poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol)/quantum dot composite nanoparticles and their use in one-pot urinalysis. Biosens Bioelectron 25(3):579–586. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2009.03.039
Tan L, Rang CC, Xu SY, Tang YW (2013) Selective room temperature phosphorescence sensing of target protein using Mn-doped ZnS QDs-embedded molecularly imprinted polymer. Biosens Bioelectron 48:216–223. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2013.04.024
Tan L, Huang C, Peng RF, Tang YW, Li WM (2014) Development of hybrid organic–inorganic surface imprinted Mn-doped ZnS QDs and their application as a sensing material for target proteins. Biosens Bioelectron 61:506–511. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2014.06.004
Zhang W, He XW, Chen Y, Li WY, Zhang YK (2011) Composite of CdTe quantum dots and molecularly imprinted polymer as a sensing material for cytochrome c. Biosens Bioelectron 26(5):2553–2558. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2010.11.004
Zhang W, He XW, Chen Y, Li WY, Zhang YK (2012) Molecularly imprinted polymer anchored on the surface of denatured bovine serum albumin modified CdTe quantum dots as fluorescent artificial receptor for recognition of target protein. Biosens Bioelectron 31(1):84–89. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2011.09.042
Yang YQ, He XW, Wang YZ, Li WY, Zhang YK (2014) Epitope imprinted polymer coating CdTe quantum dots for specific recognition and direct fluorescent quantification of the target protein bovine serum albumin. Biosens Bioelectron 54:266–272. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2013.11.004
Aramwit P, Kasettratat N (2004) Evaluation of serum albumin utilization in inpatient at a private hospital in Bangkok. Yakugaku Zasshi-J Pharm Soc Jpn 124(9):631–634. doi:10.1248/yakushi.124.631
Drummond GB, Ludlam CA (1999) Is albumin harmful? Br J Haematol 106(2):266–269. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.1999.01587.x
Fielding BA, Price DA, Houlton CA (1983) Enzyme immunoassay for urinary albumin. Clin Chem 29(2):355–357
Muratsugu M, Ohta F, Miya Y, Hosokawa T, Kurosawa S, Kamo N, Ikeda H (1993) Quartz crystal microbalance for the detection of microgram quantities of human serum albumin: relationship between the frequency change and the mass of protein adsorbed. Anal Chem 65(20):2933–2937. doi:10.1021/ac00068a036
Ci YX, Chen L (1988) Fluorimetric determination of human serum albumin with eriochrome cyanine R. Analyst 113(4):679–681. doi:10.1039/an9881300679
Madrakian T, Bagheri H, Afkhami A (2014) Determination of human albumin in serum and urine samples by constant-energy synchronous fluorescence method. Luminescence: J Biol Chem Luminescence. doi:10.1002/bio.2788
Wang YY, Cheng P, Chan DW (2003) A simple affinity spin tube filter method for removing high-abundant common proteins or enriching low-abundant biomarkers for serum proteomic analysis. Proteomics 3(3):243–248. doi:10.1002/pmic.200390036
Ahmed N, Barker G, Oliva K, Garfin D, Talmadge K, Georgiou H, Quinn M, Rice G (2003) An approach to remove albumin for the proteomic analysis of low abundance biomarkers in human serum. Proteomics 3(10):1980–1987. doi:10.1002/pmic.200300465
Li DY, Wang YZ, Zhao XL, He XW, Li WY, Zhang YK (2014) Facile synthesis of ionic liquid functionalized silica-capped CdTe quantum dots for selective recognition and detection of hemoproteins. J Mat Chem B 2(34):5659–5665. doi:10.1039/c4tb00865k
Nishino H, Huang CS, Shea KJ (2006) Selective protein capture by epitope imprinting. Angew Chem-Int Edit 45(15):2392–2396. doi:10.1002/anie.200503760
Bossi AM, Sharma PS, Montana L, Zoccatelli G, Laub O, Levi R (2012) Fingerprint-imprinted polymer: rational selection of peptide epitope templates for the determination of proteins by molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal Chem 84(9):4036–4041. doi:10.1021/ac203422r
Takahashi N, Takahashi Y, Blumberg BS, Putnam FW (1987) Amino acid substitutions in genetic variants of human serum albumin and in sequences inferred from molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84(13):4413–4417. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.13.4413
Meloun B, Moravek L, Kostka V (1975) Complete amino acid sequence of human serum albumin. FEBS Lett 58(1):134–137. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(75)80242-0
Temple A, Yen TY, Gronert S (2006) Identification of specific protein carbonylation sites in model oxidations of human serum albumin. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 17(8):1172–1180. doi:10.1016/j.jasms.2006.04.030
He XM, Carter DC (1992) Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature 358(6383):209–215. doi:10.1038/358209a0
Sugio S, Kashima A, Mochizuki S, Noda M, Kobayashi K (1999) Crystal structure of human serum albumin at 2.5 angstrom resolution. Protein Eng 12(6):439–446. doi:10.1093/protein/12.6.439
Bhattacharya AA, Curry S, Franks NP (2000) Binding of the general anesthetics propofol and halothane to human serum albumin - High resolution crystal structures. J Biol Chem 275(49):38731–38738. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005460200
Wang Y, Zheng JW, Zhang ZJ, Yuan CW, Fu DG (2009) CdTe nanocrystals as luminescent probes for detecting ATP, folic acid and L-cysteine in aqueous solution. Colloid Surf A-Physicochem Eng Asp 342(1–3):102–106. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2009.04.020
Chao MR, Hu CW, Chen JL (2014) Fluorescent turn-on detection of cysteine using a molecularly imprinted polyacrylate linked to allylthiol-capped CdTe quantum dots. Microchim Acta 181(9–10):1085–1091. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1209-6
Li DY, Qin YP, Li HY, He XW, Li WY, Zhang YK (2015) A “turn-on” fluorescent receptor for detecting tyrosine phosphopeptide using the surface imprinting procedure and the epitope approach. Biosens Bioelectron 66:224–230. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2014.11.023
Inoue Y, Kuwahara A, Ohmori K, Sunayama H, Ooya T, Takeuchi T (2013) Fluorescent molecularly imprinted polymer thin films for specific protein detection prepared with dansyl ethylenediamine-conjugated O-acryloyl L-hydroxyproline. Biosens Bioelectron 48:113–119. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2013.03.005
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (Nos. 2011CB707703 and 2012CB910601) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21275078 and 21475069).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1.14 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YZ., Li, DY., He, XW. et al. Epitope imprinted polymer nanoparticles containing fluorescent quantum dots for specific recognition of human serum albumin. Microchim Acta 182, 1465–1472 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1464-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1464-1