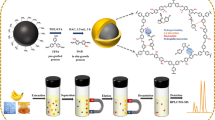
Abstract
Magnetic covalent organic framework nanocomposite denoted as Fe3O4@TAPB-Tp with core-shell structure was fabricated via a simple template-mediated precipitation polymerization method at mild conditions. The polyimine network shell was created through the polymerization of 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)-benzene (TAPB) and 1,3,5-triformyl-phloroglucinol (Tp) in tetrahydrofuran (THF) by the Schiff-base reaction. Featuring with large specific surface area (163.19 m2 g−1), good solution dispersibility, and high stability, the obtained Fe3O4@TAPB-Tp exhibited high adsorption capacities and fast adsorption for zearalenone and its derivatives (ZEAs). The adsorption isotherms showed multilayer adsorption dominated at low concentration and monolayer adsorption at high concentration between the interface of ZEAs and Fe3O4@TAPB-Tp. With the Fe3O4@TAPB-Tp as sorbent, a magnetic solid-phase extraction-ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) method was established for simultaneous adsorption and detection of five ZEAs in complex samples. The proposed method displayed favorable linearity, low limits of detection (0.003 ~ 0.018 μg kg−1), and good repeatability (2.37~10.4%). The developed method has been applied for real sample analysis, with recoveries of 81.27~90.26%. These results showed that Fe3O4@TAPB-Tp has a good application potential for the adsorption of ZEAs in food samples.
Graphical abstract

Magnetic covalent organic framework nanocomposite (Fe3O4@TAPB-Tp) were quickly fabricated at mild conditions and used as effective adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction of zearalenone and its derivatives (ZEAs) from food samples prior to ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) analysis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang Y, Li G, Wu D, Liu J, Li X, Luo P, Hu N, Wang H, Wu Y (2020) Recent advances on toxicity and determination methods of mycotoxins in foodstuffs. Trends Food Sci Technol 96:233–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.12.021
S-j L, Sheng W, Wen W, Gu Y, Wang J-p, Wang S (2018) Three kinds of lateral flow immunochromatographic assays based on the use of nanoparticle labels for fluorometric determination of zearalenone. Microchim Acta 185(4):238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2778-6
Llorent-Martínez EJ, Fernández-Poyatos MP, Ruiz-Medina A (2019) Automated fluorimetric sensor for the determination of zearalenone mycotoxin in maize and cereals feedstuff. Talanta 191:89–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.08.049
Huang Z, He J, Li H, Zhang M, Wang H, Zhang Y, Li Y, You L, Zhang S (2020) Synthesis and application of magnetic-surfaced pseudo molecularly imprinted polymers for zearalenone pretreatment in cereal samples. Food Chem 308:125696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125696
Sun X, Tang Q, Du X, Xi C, Tang B, Wang G, Zhao H (2017) Simultaneous determination of ractopamine, chloramphenicol, and zeranols in animal-originated foods by LC-MS/MS analysis with immunoaffinity clean-up column. Food Anal Methods 10(10):3239–3246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-0858-6
Jiang K, Huang Q, Fan K, Wu L, Nie D, Guo W, Wu Y, Han Z (2018) Reduced graphene oxide and gold nanoparticle composite-based solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of 9 mycotoxins in milk. Food Chem 264:218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.05.041
Rogowska A, Pomastowski P, Sagandykova G, Buszewski B (2019) Zearalenone and its metabolites: effect on human health, metabolism and neutralisation methods. Toxicon 162:46–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2019.03.004
Luo L, Ma S, Li L, Liu X, Zhang J, Li X, Liu D, You T (2019) Monitoring zearalenone in corn flour utilizing novel self-enhanced electrochemiluminescence aptasensor based on NGQDs-NH2-Ru@SiO2 luminophore. Food Chem 292:98–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.04.050
Hang Y, Liu D, Peng J, Cui Y, Shi Y, He H (2020) Magnetic hyperbranched molecularly imprinted polymers for selective enrichment and determination of zearalenone in wheat proceeded by HPLC-DAD analysis. Talanta 209:120555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120555
Li Y, Zhang H, Chen Y, Huang L, Lin Z, Cai Z (2019) Core–shell structured magnetic covalent organic framework nanocomposites for triclosan and triclocarban adsorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(25):22492–22500. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b06953
Han Z, Jiang K, Fan Z, Diana Di Mavungu J, Dong M, Guo W, Fan K, Campbell K, Zhao Z, Wu Y (2017) Multi-walled carbon nanotubes-based magnetic solid-phase extraction for the determination of zearalenone and its derivatives in maize by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Control 79:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.03.044
Pallarés N, Font G, Mañes J, Ferrer E (2017) Multimycotoxin LC–MS/MS analysis in tea beverages after dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME). J Agric Food Chem 65(47):10282–10289. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03507
Zhao Z, Yang X, Zhao X, Bai B, Yao C, Liu N, Wang J, Zhou C (2017) Vortex-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the analysis of major Aspergillus and Penicillium mycotoxins in rice wine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Control 73:862–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.09.035
Rico-Yuste A, Walravens J, Urraca JL, Abou-Hany RAG, Descalzo AB, Orellana G, Rychlik M, De Saeger S, Moreno-Bondi MC (2018) Analysis of alternariol and alternariol monomethyl ether in foodstuffs by molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 243:357–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.09.125
W-k L, Y-p S (2019) Recent advances and applications of carbon nanotubes based composites in magnetic solid-phase extraction. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 118:652–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.06.039
Socas-Rodríguez B, Hernández-Borges J, Herrera-Herrera AV, Rodríguez-Delgado MÁ (2018) Multiresidue analysis of oestrogenic compounds in cow, goat, sheep and human milk using core-shell polydopamine coated magnetic nanoparticles as extraction sorbent in micro-dispersive solid-phase extraction followed by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 410(7):2031–2042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-0882-4
Sun M, Feng J, Han S, Ji X, Li C, Feng J, Sun H, Fan J (2021) Poly(ionic liquid)-hybridized silica aerogel for solid-phase microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons prior to gas chromatography-flame ionization detection. Microchim Acta 188(3):96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04730-3
Wang M, Gao M, Zhang K, Wang L, Wang W, Fu Q, Xia Z, Gao D (2019) Magnetic covalent organic frameworks with core-shell structure as sorbents for solid phase extraction of fluoroquinolones, and their quantitation by HPLC. Microchim Acta 186(12):827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3757-2
Guo W, Wang W, Yang Y, Zhang S, Yang B, Ma W, He Y, Lin Z, Cai Z (2021) Facile fabrication of magnetic covalent organic frameworks and their application in selective enrichment of polychlorinated naphthalenes from fine particulate matter. Microchim Acta 188(3):91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04750-z
Zhang H, Song H, Tian X, Wang Y, Hao Y, Wang W, Gao R, Yang W, Ke Y, Tang Y (2021) Magnetic imprinted nanoparticles with synergistic tailoring of covalent and non-covalent interactions for purification and detection of procyanidin B2. Microchim Acta 188(1):17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04693-x
Deng Z-H, Wang X, Wang X-L, Gao C-L, Dong L, Wang M-L, Zhao R-S (2019) A core-shell structured magnetic covalent organic framework (type Fe3O4@COF) as a sorbent for solid-phase extraction of endocrine-disrupting phenols prior to their quantitation by HPLC. Microchim Acta 186(2):108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3198-3
Qiu X-L, Li Q-L, Zhou Y, Jin X-Y, Qi A-D, Yang Y-W (2015) Sugar and pH dual-responsive snap-top nanocarriers based on mesoporous silica-coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for cargo delivery. Chem Commun 51(20):4237–4240. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CC10413G
Li N, Du J, Wu D, Liu J, Li N, Sun Z, Li G, Wu Y (2018) Recent advances in facile synthesis and applications of covalent organic framework materials as superior sorbents in sample pretreatment. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 108:154–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.08.025
Lu Y-Y, Wang X-L, Wang L-L, Zhang W, Wei J, Lin J-M, Zhao R-S (2021) Room-temperature synthesis of amino-functionalized magnetic covalent organic frameworks for efficient extraction of perfluoroalkyl acids in environmental water samples. J Hazard Mater 407:124782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124782
Li G, Ye J, Fang Q, Liu F (2019) Amide-based covalent organic frameworks materials for efficient and recyclable removal of heavy metal lead (II). Chem Eng J 370:822–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.260
Jiang Y, Liu C, Huang A (2019) EDTA-functionalized covalent organic framework for the removal of heavy-metal ions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(35):32186–32191. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b11850
Lin G, Gao C, Zheng Q, Lei Z, Geng H, Lin Z, Yang H, Cai Z (2017) Room-temperature synthesis of core–shell structured magnetic covalent organic frameworks for efficient enrichment of peptides and simultaneous exclusion of proteins. Chem Commun 53(26):3649–3652. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CC00482F
Sun Q, Gao C, Ma W, He Y, Wu J, Luo K, Ouyang D, Lin Z, Cai Z (2020) High-throughput screening of bisphenols using magnetic covalent organic frameworks as a SELDI-TOF-MS probe. Microchim Acta 187(7):370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04340-5
Lin X, Wang X, Wang J, Yuan Y, Di S, Wang Z, Xu H, Zhao H, Qi P, Ding W (2020) Facile synthesis of a core-shell structured magnetic covalent organic framework for enrichment of organophosphorus pesticides in fruits. Anal Chim Acta 1101:65–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.12.012
Li Y, Yang C-X, Yan X-P (2017) Controllable preparation of core–shell magnetic covalent-organic framework nanospheres for efficient adsorption and removal of bisphenols in aqueous solution. Chem Commun 53(16):2511–2514. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6CC10188G
Tan J, Namuangruk S, Kong W, Kungwan N, Guo J, Wang C (2016) Manipulation of amorphous-to-crystalline transformation: towards the construction of covalent organic framework hybrid microspheres with NIR photothermal conversion ability. Angew Chem Int Edit 55(45):13979–13984. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201606155
Li N, Wu D, Hu N, Fan G, Li X, Sun J, Chen X, Suo Y, Li G, Wu Y (2018) Effective enrichment and detection of trace polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in food samples based on magnetic covalent organic framework hybrid microspheres. J Agric Food Chem 66(13):3572–3580. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00869
Ma W-F, Zhang Y, Li L-L, You L-J, Zhang P, Zhang Y-T, Li J-M, Yu M, Guo J, Lu H-J, Wang C-C (2012) Tailor-made magnetic Fe3O4@mTiO2 microspheres with a tunable mesoporous anatase shell for highly selective and effective enrichment of phosphopeptides. ACS Nano 6(4):3179–3188. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn3009646
González-Sálamo J, Socas-Rodríguez B, Hernández-Borges J, Rodríguez-Delgado MÁ (2017) Core-shell poly(dopamine) magnetic nanoparticles for the extraction of estrogenic mycotoxins from milk and yogurt prior to LC–MS analysis. Food Chem 215:362–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.07.154
Li C-Y, Liu J-M, Wang Z-H, Lv S-W, Zhao N, Wang S (2020) Integration of Fe3O4@UiO-66-NH2@MON core-shell structured adsorbents for specific preconcentration and sensitive determination of aflatoxins against complex sample matrix. J Hazard Mater 384:121348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121348
Zhang W, Lan C, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Zhao W, Johnson C, Hu K, Xie F, Zhang S (2019) Facile preparation of dual-shell novel covalent–organic framework functionalized magnetic nanospheres used for the simultaneous determination of fourteen trace heterocyclic aromatic amines in nonsmokers and smokers of cigarettes with different tar yields based on UPLC-MS/MS. J Agric Food Chem 67(13):3733–3743. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b06372
Xu H, Tao S, Jiang D (2016) Proton conduction in crystalline and porous covalent organic frameworks. Nat Mater 15(7):722–726. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4611
Al-Ghouti MA, Da'ana DA (2020) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: a review. J Hazard Mater 393:122383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122383
Zhao Y, Yuan Y-C, Bai X-L, Liu Y-M, Wu G-F, Yang F-S, Liao X (2020) Multi-mycotoxins analysis in liquid milk by UHPLC-Q-exactive HRMS after magnetic solid-phase extraction based on PEGylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Food Chem 305:125429
Xu J, Chi J, Lin C, Lin X, Xie Z (1620) Towards high-efficient online specific discrimination of zearalenone by using gold nanoparticles@aptamer-based affinity monolithic column. J Chromatogr A 2020:461026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2020.461026
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC1603600) and the National “Ten thousand Plan” Scientific and Technological Innovation Leading Talent Project (Feng ZHANG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Informed consent
Informed consent is not applicable for this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1514 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, YF., Mu, GD., Wang, XJ. et al. Fast construction of core-shell structured magnetic covalent organic framework as sorbent for solid-phase extraction of zearalenone and its derivatives prior to their determination by UHPLC-MS/MS. Microchim Acta 188, 246 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04893-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04893-z