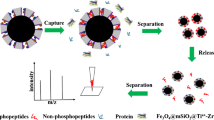
Abstract
A selectively modified porous metal/carbon nanocomposite was fabricated to enhance the enrichment of low-abundance phosphopeptides from biological samples. The carbon matrix derived from the metal-organic framework provides a suitable pore size to allow the diffusion of peptides, while the deliberately modified metal nanoparticles within the pores enhance their interaction with the phosphopeptides. This nanocomposite shows extremely high enrichment selectivity for phosphopeptides in the MALDI-TOF MS detection, even when the molar ratio of α-casein digests versus bovine serum albumin digests was up to about 1:20,000. By combining such nanocomposite with nano-LC-MS/MS, 4556 unique phosphopeptides were identified with high selectivity (95.2%) from HeLa cell extracts. Furthermore, phosphopeptides from prostate tissue digests were also determined. A total of 277 and 1242 phosphopeptides were identified from normal and tumor tissues of a patient with prostate cancer, respectively. This indicates that phosphorylation and prostate cancer can be related to each other.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu X, Xing X, Dowlut D, Zeng Y, Liu J, Liu X (2019) Integrating phosphoproteomics into kinase-targeted cancer therapies in precision medicine. J Proteome 191:68–79
Yan Y, Deng C (2019) Recent advances in nanomaterials for sample pre-treatment in phosphoproteomics research. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 120:115655
Wang MM, Chen S, Yu YL, Wang JH (2019) Novel Ti4+-chelated polyoxometalate/polydopamine composite microspheres for highly selective isolation and enrichment of phosphoproteins. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:37471–37478
Matheron L, van den Toorn H, Heck AJ, Mohammed S (2014) Characterization of biases in phosphopeptide enrichment by Ti4+-immobilized metal affinity chromatography and TiO2 using a massive synthetic library and human cell digests. Anal Chem 86:8312–8320
Xu D, Gao M, Deng C, Zhang X (2016) Ultrasensitive enrichment of phosphopeptides with Ti4+ immobilized SiO2 graphene-like multilayer nanosheets. Analyst 141:3421–3427
Zhang H, Li X, Ma S, Ou J, Wei Y, Ye M (2019) One-step preparation of phosphate-rich carbonaceous spheres via a hydrothermal approach for phosphopeptide analysis. Green Chem 21:2052–2060
Hong Y, Zhan Q, Zheng Y, Pu C, Zhao H, Lan M (2019) Hydrophilic phytic acid-functionalized magnetic dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres with immobilized Ti4+: a dual-purpose affinity material for highly efficient enrichment of glycopeptides/phosphopeptides. Talanta 197:77–85
Ding F, Zhao Y, Liu H, Zhang W (2020) Core-shell magnetic microporous covalent organic framework with functionalized Ti(IV) for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Analyst 145:4341–4351. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0an00038h
Su J, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2017) Adenosine phosphate functionalized magnetic mesoporous graphene oxide nanocomposite for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:2188–2196
Hong Y, Pu C, Zhao H, Sheng Q, Zhan Q, Lan M (2017) Yolk-shell magnetic mesoporous TiO2 microspheres with flowerlike NiO nanosheets for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Nanoscale 9:16764–16772
Hong Y, Zhan Q, Pu C, Sheng Q, Zhao H, Lan M (2018) Highly efficient enrichment of phosphopeptides from HeLa cells using hollow magnetic macro/mesoporous TiO2 nanoparticles. Talanta 187:223–230
Wang J, Wang Z, Sun N, Deng C (2019) Immobilization of titanium dioxide/ions on magnetic microspheres for enhanced recognition and extraction of mono- and multi-phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 186:236
Gao C, Bai J, He Y, Zheng Q, Ma W, Lei Z, Zhang M, Wu J, Fu F, Lin Z (2019) Postsynthetic functionalization of Zr4+-immobilized core-shell structured magnetic covalent organic frameworks for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:13735–13741
Liu Q, Sun N, Gao M, Deng CH (2018) Magnetic binary metal-organic framework as a novel affinity probe for highly selective capture of endogenous phosphopeptides. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:4382–4389
Zhou J, Liang Y, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2017) Dual-functionalized magnetic metal-organic framework for highly specific enrichment of phosphopeptides. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:11413–11421
Xie Y, Deng C (2016) Highly efficient enrichment of phosphopeptides by a magnetic lanthanide metal-organic framework. Talanta 159:1–6
Cao L, Zhao Y, Chu Z, Zhang X, Zhang W (2020) Core-shell magnetic bimetallic MOF material for synergistic enrichment of phosphopeptides. Talanta 206:120165
Liu S, Chen H, Lu X, Deng C, Zhang X, Yang P (2010) Facile synthesis of copper(II) immobilized on magnetic mesoporous silica microspheres for selective enrichment of peptides for mass spectrometry analysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(41):7557–7561
Qian K, Gu W, Yuan P, Liu F, Wang Y, Monteiro M, Yu C (2012) Enrichment and detection of peptides from biological systems using designed periodic mesoporous organosilica microspheres. Small 8(2):231–236
Lu Y, Wang Y, Li H, Lin Y, Jiang Z, Xie Z, Kuang Q, Zheng L (2015) MOF-derived porous Co/C nanocomposites with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:13604–13611
Song X, Chen Y, Rong M, Xie Z, Zhao T, Wang Y, Chen X, Wolfbeis OS (2016) A phytic acid induced super-amphiphilic multifunctional 3D graphene-based foam. Angew Chem Int Ed 55:3936–3941
Zhou C, Chen Z, Yang H, Hou K, Zeng X, Zheng Y, Cheng J (2017) Nature-inspired strategy toward superhydrophobic fabrics for versatile oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:9184–9194
Li Z, He G, Zhang B, Cao Y, Wu H, Jiang Z, Tiantian Z (2014) Enhanced proton conductivity of Nafion hybrid membrane under different humidities by incorporating metal-organic frameworks with high phytic acid loading. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:9799–9807
Shi L, Li Y, Cai X, Zhao H, Lan M (2017) ZIF-67 derived cobalt-based nanomaterials for electrocatalysis and nonenzymatic detection of glucose: difference between the calcination atmosphere of nitrogen and air. J Electroanal Chem 799:512–518
Wang S, Chen M, Xie Y, Fan Y, Wang D, Jiang JJ, Li Y, Grutzmacher H, Su CY (2016) Nanoparticle cookies derived from metal-organic frameworks: controlled synthesis and application in anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Small 12:2365–2375
Hong Y, Yao Y, Zhao H, Sheng Q, Ye M, Yu C, Lan M (2018) Dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles with abundant Ti4+ for phosphopeptide enrichment from cancer cells with 96% specificity. Anal Chem 90:7617–7625
Zhang K, Hu D, Deng S, Han M, Wang X, Liu H, Liu Y, Xie M (2019) Phytic acid functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles loaded with Ti(IV) ions for phosphopeptide enrichment in mass spectrometric analysis. Microchim Acta 186:68
Hong Y, Zhao H, Pu C, Zhan Q, Sheng Q, Lan M (2018) Hydrophilic phytic acid-coated magnetic graphene for titanium(IV) immobilization as a novel hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-immobilized metal affinity chromatography platform for glyco- and phosphopeptide enrichment with controllable selectivity. Anal Chem 90:11008–11015
Xu L, Zhu W, Sun R, Ding Y (2015) A Ti4+-immobilized phosphate polymer-patterned silicon substrate for on-plate selective enrichment and self-desalting of phosphopeptides. Analyst 140:3216–3224
Huang YL, Wang J, Jiang YH, Yang PY, Wang GW, Liu F (2019) Development of amphiphile 4-armed PEO-based Ti4+ complex for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Talanta 204:670–676
Trejo R, Dokland T, Jurat Fuentes J, Harte F (2011) Cryo-transmission electron tomography of native casein micelles from bovine milk. J Dairy Sci 94:5770–5775
Sun N, Zhang X, Deng C (2015) Designed synthesis of MOF-derived magnetic nanoporous carbon materials for selective enrichment of glycans for glycomics analysis. Nanoscale 7:6487–6491
Zhu B, Zhou Q, Zhen D, Wang Y, Cai Q, Chen P (2019) Preparation of TiO2/bi/Fe/Zr nanocomposite for the highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Talanta 194:870–875
Luo B, Yang M, Jiang P, Lan F, Wu Y (2018) Multi-affinity sites of magnetic guanidyl-functionalized metal-organic framework nanospheres for efficient enrichment of global phosphopeptides. Nanoscale 10:8391–8396
Furic L, Rong L, Larsson O, Koumakpayi IH, Yoshida K, Brueschke A, Petroulakis E, Robichaud N, Pollak M, Gaboury LA, Pandolfi PP, Saad F, Sonenberg N (2010) eIF4E phosphorylation promotes tumorigenesis and is associated with prostate cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:14134–14139
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Research Center of Analysis and Test of East China University of Science and Technology for the help of mass spectrometry analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (19ZR1412000), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (STCSM, No. 20520712500), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 50321102017022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, C., Zhao, H., Gu, Q. et al. Targeted immobilization of titanium (IV) on magnetic mesoporous nanomaterials derived from metal-organic frameworks for high-efficiency phosphopeptide enrichment in biological samples. Microchim Acta 187, 568 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04556-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04556-5