Abstract
The authors are presenting a novel strategy for global phosphoproteome recognition in practical samples. It integrates metal oxide affinity chromatography (MOAC) and immobilization metal ion affinity chromatography (IMAC). This resulted in a kind of titanium dioxide/ion-based multifunctional probe (dubbed T2M). The T2M combines the features of MOAC and IMAC including their recognition preferences towards mono- and multi-phosphorylated peptides. Hence, they exhibit an outstanding recognition capability towards global phosphoproteome, high sensitivity (the limit of detection of which is merely 10 fmol) and excellent specificity in MALDI-TOF MS detection. Their performance is further demonstrated by the identification of the phosphoproteome in non-fat milk and human saliva. By combining T2M with nano LC-MS/MS, remarkable results are obtained in the tryptic digestion of healthy eye lens and cataract lens phosphoproteomes. A total of 658 and 162 phosphopeptides, respectively, were identified. This indicates that phosphorylation and the appearance of cataract can be related to each other.

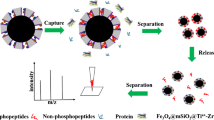
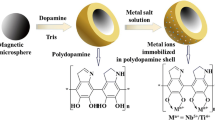
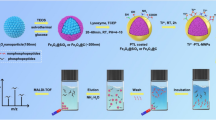
Schematic presentation of the preparation of titanium dioxide/ion-based multifunctional magnetic nanomaterials (T2M). The T2M based enrichment protocol exhibits outstanding recognition capability towards global phosphoproteome. This protocol shows great prospect for clarifying mechanism of phosphorylation-related diseases via further information acquisition.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P, Mann M (2006) Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell 127(3):635–648
Wiseman RL, Kelly JW (2011) Phosphatase inhibition delays translational recovery. Science 332(6025):44–45
Redpath NT, Price NT, Severinov KV, Proud CG (1993) Regulation of elongation factor-2 by multisite phosphorylation. Eur J Biochem 213(2):689–699
Scott DB, Blanpied TA, Ehlers MD (2003) Coordinated PKA and PKC phosphorylation suppresses RXR-mediated ER retention and regulates the surface delivery of NMDA receptors. Neuropharmacology 45(6):755–767
Vicente-Manzanares M, Horwitz AR (2010) Myosin light chain mono- and di-phosphorylation differentially regulate adhesion and polarity in migrating cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 402(3):537–542
Deng X, Gao F, Flagg T, May WS (2004) Mono- and multisite phosphorylation enhances Bcl2's antiapoptotic function and inhibition of cell cycle entry functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:153–158
Narasimha AM, Kaulich M, Shapiro GS, Choi YJ, Sicinski P, Dowdy SF (2014) Cyclin D activates the Rb tumor suppressor by mono-phosphorylation. Elife 3
Park K-S, Mohapatra DP, Misonou H, Trimmer JS (2006) Graded regulation of the Kv2.1 Potassium Channel by variable phosphorylation. Science 313:976–979
Lee CW, Ferreon JC, Ferreon AC, Arai M, Wright PE (2010) Graded enhancement of p53 binding to CREB-binding protein (CBP) by multisite phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(45):19290–19295
Long X-Y, Zhang Z-J, Li J-Y, Sheng D, Lian H-Z (2017) Controllable preparation of CuFeMnO4 Nanospheres as a novel multifunctional affinity probe for efficient adsorption and selective enrichment of low-abundance peptides and Phosphopeptides. Anal Chem 89(19):10446–10453
Tan S, Wang J, Han Q, Liang Q, Ding M (2018) A porous graphene sorbent coated with titanium(IV)-functionalized polydopamine for selective lab-in-syringe extraction of phosphoproteins and phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 185(7):316
Zhang L, Gan Y, Sun H, Yu B, Jin X, Zhang R, Zhang W, Zhang L (2017) Magnetic mesoporous carbon composites incorporating hydrophilic metallic nanoparticles for enrichment of phosphopeptides prior to their determination by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Microchim Acta 184(2):547–555
Chen C-T, Chen Y-C (2005) Fe3O4/TiO2 Core/Shell nanoparticles as affinity probes for the analysis of Phosphopeptides using TiO2 surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 77(18):5912–5919
Kailasa SK, Wu H-F (2014) Recent developments in nanoparticle-based MALDI mass spectrometric analysis of phosphoproteomes. Microchim Acta 181(9):853–864
Yue X, Schunter A, Hummon AB (2015) Comparing multistep immobilized metal affinity chromatography and multistep TiO2 methods for Phosphopeptide enrichment. Anal Chem 87(17):8837–8844
Bodenmiller B, Mueller LN, Mueller M, Domon B, Aebersold R (2007) Reproducible isolation of distinct, overlapping segments of the phosphoproteome. Nat Methods 4(3):231–237
Peng J, Zhang H, Li X, Liu S, Zhao X, Wu J, Kang X, Qin H, Pan Z, Ra W (2016) Dual-metal centered zirconium–organic framework: a metal-affinity probe for highly specific interaction with Phosphopeptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(51):35012–35020
Liu Q, Sun N, Gao M, Deng C-h (2018) Magnetic binary metal–organic framework as a novel affinity probe for highly selective capture of endogenous Phosphopeptides. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(3):4382–4389
Thingholm TE, Jensen ON, Robinson PJ, Larsen MR (2008) SIMAC (sequential elution from IMAC), a phosphoproteomics strategy for the rapid separation of monophosphorylated from multiply phosphorylated peptides. Mol Cell Proteomics 7(4):661–671
Long XY, Zhang ZJ, Li JY, Sheng D, Lian HZ (2017) A combination strategy using two novel cerium-based nanocomposite affinity probes for the selective enrichment of mono- and multi-phosphopeptides in mass spectrometric analysis. Chem Commun (Camb) 53(33):4620–4623
Wang S-T, Wang M-Y, Su X, Yuan B-F, Feng Y-Q (2012) Facile preparation of SiO2/TiO2 composite monolithic capillary column and its application in enrichment of Phosphopeptides. Anal Chem 84(18):7763–7770
Jiang J, Sun X, She X, Li J, Li Y, Deng C, Duan G (2018) Magnetic microspheres modified with Ti(IV) and Nb(V) for enrichment of phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 185(6):309
Wang J, Yao J, Sun N, Deng C (2017) Facile synthesis of thiol-polyethylene glycol functionalized magnetic titania nanomaterials for highly efficient enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides. J Chromatogr A 1512:1–8
Yang X, Xia Y (2016) Urea-modified metal-organic framework of type MIL-101(Cr) for the preconcentration of phosphorylated peptides. Microchim Acta 183(7):2235–2240
Shpitzer T, Hamzany Y, Bahar G, Feinmesser R, Savulescu D, Borovoi I, Gavish M, Nagler R (2009) Salivary analysis of oral cancer biomarkers. Brit J Cancer 101(7):1194
Su J, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2018) Adenosine phosphate functionalized magnetic mesoporous graphene oxide nanocomposite for highly selective enrichment of Phosphopeptides. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(2):2188–2196
Lin H, Deng C (2016) Development of immobilized Sn4+ affinity chromatography material for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Proteomics 16(21):2733–2741
Matsuyama M, Tanaka H, Inoko A, Goto H, Yonemura S, Kobori K, Hayashi Y, Kondo E, Itohara S, Izawa I, Inagaki M (2013) Defect of mitotic vimentin phosphorylation causes Microophthalmia and cataract via aneuploidy and senescence in Lens epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 288(50):35626–35635
Niceta M, Stellacci E, Gripp Karen W, Zampino G, Kousi M, Anselmi M, Traversa A, Ciolfi A, Stabley D, Bruselles A, Caputo V, Cecchetti S, Prudente S, Fiorenza Maria T, Boitani C, Philip N, Niyazov D, Leoni C, Nakane T, Keppler-Noreuil K, Braddock Stephen R, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Palleschi A, Campeau Philippe M, Lee Brendan HL, Pouponnot C, Stella L, Bocchinfuso G, Katsanis N, Sol-Church K, Tartaglia M (2015) Mutations impairing GSK3-mediated MAF phosphorylation cause cataract, deafness, intellectual disability, seizures, and a down syndrome-like facies. Am J Hum Genet 96(5):816–825
Aquilina JA, Benesch JLP, Ding LL, Yaron O, Horwitz J, Robinson CV (2004) Phosphorylation of alpha B-crystallin alters chaperone function through loss of dimeric substructure. J Biol Chem 279(27):28675–28680
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0507501) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21425518).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
All the experiments were performed in compliance with the relevant laws and institutional guidelines, conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Fudan University.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 4838 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Wang, Z., Sun, N. et al. Immobilization of titanium dioxide/ions on magnetic microspheres for enhanced recognition and extraction of mono- and multi-phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 186, 236 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3346-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3346-4