Abstract
A ratiometric electrochemical aptamer-based assay is described for the ultrasensitive and highly specific determination of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It is based on ATP aptamer-mediated triple-helix molecular switch (THMS). The method uses (a) a hairpin DNA (MB-DNA-SH) labeled with the redox probe Methylene Blue (MB) at the 3′ end, and a thiol group at the 5′ end, and (b) a single strand ATP aptamer modified with two ferrocenes at each end (Fc-DNA-Fc). The labeled probe of type MB-DNA-SH was self-assembled onto the surface of a gold electrode via gold-thiol binding. On exposure to Fc-DNA-Fc, it will hybridize with MB-DNA-SH to form a stable THMS structure on electrode surface. In the presence of ATP, it hybridizes with the loop portion of Fc-DNA-Fc, and this results in the unwinding of the THMS structure. Such variation caused the changes of the differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) peak currents of both MB (at around −0.25 V) and Fc (at around 0.39 V; both vs. Ag/AgCl). A significant enhancement is found for the ratio of the two DPV peaks. Under the optimum experimental conditions, this assay has a response that covers the 0.05 to 100 pM ATP concentration range, and the detection limit is 5.2 fM (for S/N = 3). The method is highly selective for ATP over its analogs.

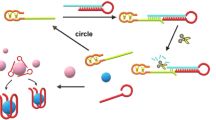
Schematic presentation of a novel ratiometric electrochemical aptasensor for ATP via triple-helix molecular switch (THMS) strategy. MB-DNA-SH was self-assembled on GE surface through gold-thiol binding. Fc-DNA-Fc hybridized with MB-DNA-SH to form THMS structure. ATP specifically bond with its aptamer sequence of Fc-DNA-Fc to unwind the THMS structure. The ratio of DPV peak currents of MB and Fc was applied to monitor the concentration of ATP in real samples over its analogs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jia J, Feng J, Chen HG, Luo HQ, Li NB (2016) A simple electrochemical method for the detection of ATP using target-induced conformational change of dual-hairpin DNA structure. Sensors Actuators B 222:1090–1095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.08.045
Wang P, Chen ZY, Chen Q, Qu LL, Miao XM, Feng QM (2018) Construction of a paper-based electrochemical biosensing platform for rapid and accurate detection of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Sensors Actuators B 256:931–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.10.024
Lu L, Si JC, Gao ZF, Zhang Y, Lei JL, Luo HQ, Li NB (2015) Highly selective and sensitive electrochemical biosensor for ATP based on the dual strategy integrating the cofactor-dependent enzymatic ligation reaction with self-cleaving DNAzyme-amplified electrochemical detection. Biosens Bioelectron 63:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.07.007
Ning Y, Wei K, Cheng LJ, Hu J, Xiang Q (2017) Fluorometric aptamer based determination of adenosine triphosphate based on deoxyribonuclease I-aided target recycling and signal amplification using graphene oxide as a quencher. Microchim Acta 184:1847–1854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2194-3
Qu F, Sun C, Lv XX, You JM (2018) A terbium-based metal-organic framework@gold nanoparticle system as a fluorometric probe for aptamer based determination of adenosine triphosphate. Microchim Acta 185:359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2888-1
Liu XJ, Lin BX, Yu Y, Cao YJ, Guo ML (2018) A multifunctional probe based on the use of labeled aptamer and magnetic nanoparticles for fluorometric determination of adenosine 5′-triphosphate. Microchim Acta 185:243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2774-x
Zhou CY, Yu Z, Yu WL, Liu HW, Zhang H, Guo CL (2019) Split aptamer-based detection of adenosine triphosphate using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and two kinds of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186:251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3356-2
Liu YT, Lei JP, Huang Y, Ju HX (2014) “Off-on” electrochemiluminescence system for sensitive detection of ATP via target-induced structure switching. Anal Chem 86:8735–8741. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac501913c
Huang YF, Chang HT (2007) Analysis of adenosine triphosphate and glutathione through gold nanoparticles assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 79:4852–4859. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac070023x
Wang GX, Xu QJ, Liu L, Su XL, Lin JH, Xu GY, Luo XL (2017) Mixed self-assembly of polyethylene glycol and aptamer on polydopamine surface for highly sensitive and low-fouling detection of adenosine triphosphate in complex media. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:31153–31160. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b09529
Wang DM, Xiao XQ, Xu S, Liu Y, Li YX (2018) Electrochemical aptamer-based nanosensor fabricated on single au nanowire electrodes for adenosine triphosphate assay. Biosens Bioelectron 99:431–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.08.020
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1990) In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346:818–822. https://doi.org/10.1038/346818a0
Zhang XY, Song CX, Yang K, Hong WW, Lu Y, Yu P, Mao LQ (2018) Photoinduced regeneration of an aptamer-based electrochemical sensor for sensitively detecting adenosine triphosphate. Anal Chem 90:4968–4971. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b05442
Bao T, Shu HW, Wen W, Zhang XH, Wang SF (2015) A sensitive electrochemical aptasensor for ATP detection based on exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification strategy. Anal Chim Acta 862:64–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.12.049
Kashefi-Kheyrabadi L, Mehrgardi MA (2013) Aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for detection of adenosine triphosphate using a nanoporous gold platform. Bioelectrochemistry 94:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2013.05.005
Bagheri E, Abnous K, Alibolandi M, Ramezani M, Taghdisi SM (2018) Triple-helix molecular switch-based aptasensors and DNA sensors. Biosens Bioelectron 111:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.03.070, 1
Zheng J, Li JS, Jiang Y, Jin JY, Wang KM, Yang RH, Tan WH (2011) Design of aptamer-based sensing platform using triple-helix molecular switch. Anal Chem 83:6586–6592. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac201314y
Wang XZ, Jiang AW, Hou T, Li F (2014) A sensitive and versatile “signal-on” electrochemical aptasensor based on a triple-helix molecular switch. Analyst 139:6272–6278. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4an01320d
Wang XZ, Jiang AW, Hou T, Li F (2015) A versatile label-free and signal-on electrochemical biosensing platform based on triplex-forming oligonucleotide probe. Anal Chim Acta 890:91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.06.059
Abnous K, Danesh NM, Ramezani M, Alibolandi M, Hassanabad KY (2017) A triple-helix molecular switch-based electrochemical aptasensor for interferon-gamma using a gold electrode and methylene blue as a redox probe. Microchim Acta 184:4151–4157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2457-z
Liu XY, Deng KQ, Wang H, Li CX, Zhang SW, Huang HW (2019) Aptamer based ratiometric electrochemical sensing of 17β-estradiol using an electrode modified with gold nanoparticles, thionine, and multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 186:347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3465-y
Li YR, Chang YY, Ma J, Wu ZY, Yuan R, Chai YQ (2019) Programming a target-initiated bifunctional DNAzyme nanodevice for sensitive ratiometric electrochemical biosensing. Anal Chem 91:6127–6133. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00690
Xiong EH, Li ZZ, Zhang XH, Zhou JW, Yan XX, Liu YQ, Chen JH (2017) Triple-helix molecular switch electrochemical ratiometric biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of nucleic acids. Anal Chem 89:8830–8835. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01251
Huang S, Feng MM, Li JW, Liu Y, Xiao Q (2018) Voltammetric determination of attomolar levels of a sequence derived from the genom of hepatitis B virus by using molecular beacon mediated circular strand displacement and rolling circle amplification. Microchim Acta 185:206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2744-3
Huang S, Lu SY, Huang CS, Sheng JR, Zhang LX, Su W, Xiao Q (2016) An electrochemical biosensor based on single-stranded DNA modified gold electrode for acrylamide determination. Sensors Actuators B 224:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.10.008
Das R, Goel AK, Sharma MK, Upadhyay S (2015) Electrochemical DNA sensor for anthrax toxin activator gene atxA-detection of PCR amplicons. Biosens Bioelectron 74:939–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.07.066
Cheng W, Zhang W, Yan YR, Shen B, Zhu D, Lei PH, Ding SJ (2014) A novel electrochemical biosensor for ultrasensitive and specific detection of DNA based on molecular beacon mediated circular strand displacement and rolling circle amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 62:274–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.06.056
Wang L, Fang L, Liu SF (2015) Responsive hairpin DNA aptamer switch to program the strand displacement reaction for the enhanced electrochemical assay of ATP. Analyst 140:5877–5880. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5an00725a
Hu TX, Wen W, Zhang XH, Wang SF (2016) Nicking endonuclease-assisted recycling of target–aptamer complex for sensitive electrochemical detection of adenosine triphosphate. Analyst 141:1506–1511. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5an02484f
Chen LF, Chen ZN (2015) A multifunctional label-free electrochemical impedance biosensor for Hg2+, adenosine triphosphate and thrombin. Talanta 132:664–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.10.039
Wu L, Zhang XH, Liu W, Xiong EH, Chen JH (2013) Sensitive electrochemical aptasensor by coupling “signal-on” and “signal-off” strategies. Anal Chem 85:8397–8402. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac401810t
Mao YF, Liu JQ, He DG, He XX, Wang KM, Shi H, Wen L (2015) Aptamer/target binding-induced triple helix forming for signal-on electrochemical biosensing. Talanta 143:381–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.05.009
Hou T, Li W, Zhang LF, Li F (2015) A versatile and highly sensitive homogeneous electrochemical strategy based on the split aptamer binding-induced DNA three-way junction and exonuclease III-assisted target recycling. Analyst 140:5748–5753. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5an01176k
Li X, Yang JM, Xie JQ, Jiang BY, Yuan R, Xiang Y (2018) Cascaded signal amplification via target-triggered formation of aptazyme for sensitive electrochemical detection of ATP. Biosens Bioelectron 102:296–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.11.005
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21864006, 21563006, 21763005), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2017GXNSFDA198034, 2016GXNSFBA380118, 2017GXNSFFA198005), Guangxi Scientific and Technological Development Projects (AD17195081), the China Scholarship Council Project (201708455047, liujinfa[2017]5086), the Thousands of Young Teachers Training Program of Guangxi Province (guijiaoren[2018]18), the High-Level-Innovation Team (guijiaoren[2017]38) and Outstanding Scholar Project of Guangxi Higher Education Institutes, and BAGUI Scholar Program of Guangxi Province of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 577 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Q., Feng, J., Feng, M. et al. A ratiometric electrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive determination of adenosine triphosphate via a triple-helix molecular switch. Microchim Acta 186, 478 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3630-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3630-3