Abstract
A surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor for the pesticide carbendazim is described that has enhanced performance due to the use of a Au/Fe3O4 nanocomposite as an amplifying label on the surface the carboxymethyldextran-coated gold layer of the sensor. The surface was further modified with monoclonal antibody to obtain a sensor for real-time detection of carbendazim. Binding of carbendazim results in a change in refractive index. SPR detection in the absence of Au/Fe3O4 nanocomposite and by UPLC-MS analysis demonstrated the improved performance to be due to the use of the Au/Fe3O4 nanocomposite. Response is linear in the 0.05 to 150 ng·mL−1 carbendazim concentration range, and the limit of detection is 0.44 ng·mL−1. This is more than 1 order of magnitude lower than that of the conventional SPR assay. The recoveries from spiked medlar are between 102.4 and 115.0%. The selectivity was tested by using the pesticides benzimidazole, 2-mercaptobenzimidazole, 2-benzimidazole propionic acid, and 2-(2-aminoethyl) benzimidazole as potential interferents. Conceivably, this Au/Fe3O4 nanocomposite-based method has a large potential for the detection of other small analytes at trace concentrations.

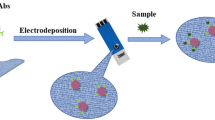
Schematic presentation of the SPR sensor for the detection of the fungicide carbendazim (methyl 2-benzimidazole carbamate; MBC) based on the use of a gold/Fe3O4 nanocomposites.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh S, Singh N, Kumar V, Datta S, Wani AB, Singh D, Singh K, Singh J (2016) Toxicity, monitoring and biodegradation of the fungicide carbendazim. Environ Chem Lett 14:317–329
Cui R, Xu D, Xie X, Yi Y, Quan Y, Zhou M, Gong J, Han Z, Zhang G (2017) Phosphorus-doped helical carbon nanofibers as enhanced sensing platform for electrochemical detection of carbendazim. Food Chem 221:457–463
Xu X, Chen J, Li B, Tang L (2018) Carbendazim residues in vegetables in China between 2014 and 2016 and a chronic carbendazim exposure risk assessment. Food Control 91:20–25
Zhou J, Xiong K, Yang Y, Ye X, Liu J, Li F (2015) Deleterious effects of benomyl and carbendazim on human placental trophoblast cells. Reprod Toxicol 51:64–71
Mohapatra S, S L (2016) Residue level and dissipation of carbendazim in/on pomegranate fruits and soil. Environ Monit Assess 188:406
Chayata H, Lassalle Y, Nicol E, Manolikakes S, Souissi Y, Bourcier S, Gosmini C, Bouchonnet S (2016) Characterization of the ultraviolet-visible photoproducts of thiophanate-methyl using high performance liquid chromatography coupled with high resolution tandem mass spectrometry-detection in grapes and tomatoes. J Chromatogr A 1441:75–82
China's Ministry of Agriculture (MOV). Reply to the carbendazim matter. Available at: http://www.chinapesticide.gov.cn/zwdt4xw/5786.jhtml. Accessed 15 Jul 2017
Gilbert-Lopez B, Garcia-Reyes JF, Ortega-Barrales P, Molina-Diaz A, Fernandez-Alba AR (2007) Analyses of pesticide residues in fruit-based baby food by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom : RCM 21:2059–2071
Yang Y, Huo D, Wu H, Wang X, Yang J, Bian M, Ma Y, Hou C (2018) N, P-doped carbon quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing platform for carbendazim detection based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Sensors Actuators B Chem 274:296–303
Li S, Wu X, Zhang Q, Li P (2016) Synergetic dual recognition and separation of the fungicide carbendazim by using magnetic nanoparticles carrying a molecularly imprinted polymer and immobilized β-cyclodextrin. Microchim Acta 183:1433–1439
Eissa S, Zourob M (2017) Selection and characterization of DNA aptamers for electrochemical biosensing of Carbendazim. Anal Chem 89:3138–3145
Zhang P, Chen YP, Wang W, Shen Y, Guo JS (2016) Surface plasmon resonance for water pollutant detection and water process analysis. TrAC-Trends Anal Chem 85:153–165
Daems D, Lu J, Delport F, Marien N, Orbie L, Aernouts B, Adriaens I, Huybrechts T, Saeys W, Spasic D, Lammertyn J (2017) Competitive inhibition assay for the detection of progesterone in dairy milk using a fiber optic SPR biosensor. Anal Chim Acta 950:1–6
Masson JF (2017) Surface Plasmon resonance clinical biosensors for medical diagnostics. ACS Sensors 2:16–30
Genslein C, Hausler P, Kirchner EM, Bierl R, Baeumner AJ, Hirsch T (2016) Graphene-enhanced plasmonic nanohole arrays for environmental sensing in aqueous samples. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 7:1564–1573
Xia YQ, Su RX, Huang RL, Ding L, Wang LB, Qi W, He ZM (2017) Design of elution strategy for simultaneous detection of chloramphenicol and gentamicin in complex samples using surface plasmon resonance. Biosens Bioelectron 92:266–272
Liu X, Li L, Liu YQ, Shi XB, Li WJ, Yang Y, Mao LG (2014) Ultrasensitive detection of deltamethrin by immune magnetic nanoparticles separation coupled with surface plasmon resonance sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 59:328–334
Wu Q, Li S, Sun Y, Wang J (2017) Hollow gold nanoparticle-enhanced SPR based sandwich immunoassay for human cardiac troponin I. Microchim Acta 184:2395–2402
Rastegarzadeh S, Hashemi F (2014) A surface plasmon resonance sensing method for determining captopril based on in situ formation of silver nanoparticles using ascorbic acid. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 122:536–541
Wu Q, Sun Y, Zhang D, Li S, Zhang Y, Ma P, Yu Y, Wang X, Song D (2017) Ultrasensitive magnetic field-assisted surface plasmon resonance immunoassay for human cardiac troponin I. Biosens Bioelectron 96:288–293
Luckarift HR, Balasubramanian S, Paliwal S, Johnson GR, Simonian AL (2007) Enzyme-encapsulated silica monolayers for rapid functionalization of a gold surface. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 58:28–33
Lin K, Yonghua L, Chen J, Zheng R, Wang P, Ming H (2008) Surface plasmon resonancehydrogen sensor based on metallic grating with high sensitivity. Opt Express 16:18599–18604
Zeng S, Baillargeat D, Ho H-P, Yong K-T (2014) Nanomaterials enhanced surface plasmon resonance for biological and chemical sensing applications. Chem Soc Rev 43:3426–3452
Yuan H, Ji W, Chu S, Qian S, Wang F, Masson JF, Han X, Peng W (2018) Fiber-optic surface plasmon resonance glucose sensor enhanced with phenylboronic acid modified au nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 117:637–643
Hang L, Zhou F, Men D, Li H, Li X, Zhang H, Liu G, Cai W, Li C, Li Y (2017) Functionalized periodic au@MOFs nanoparticle arrays as biosensors for dual-channel detection through the complementary effect of SPR and diffraction peaks. Nano Res 10:2257–2270
Lyon JL, Fleming DA, Stone MB, Schiffer P, Williams ME (2004) Synthesis of Fe oxide CoreAu Shell nanoparticles by iterative hydroxylamine. Nano Lett 4:719–723
Zhao XL, Cai YQ, Wang T, Shi YL, Jiang GB (2008) Preparation of alkanethiolate-functionalized core-shell Fe3O4@au nanoparticles and its interaction with several typical target molecules. Anal Chem 80:9091–9096
Wang J, Sun Y, Wang L, Zhu X, Zhang H, Song D (2010) Surface plasmon resonance biosensor based on Fe3O4/Au nanocomposites. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 81:600–606
Homola J (1997) On the sensitivity of surface plasmon resonance sensors with spectral interrogation. Sensors Actuators B Chem 41:207–211
Zhang H, Sun Y, Wang J, Zhang J, Zhang H, Zhou H, Song D (2012) Preparation and application of novel nanocomposites of magnetic-au nanorod in SPR biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 34:137–143
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81703699, 81573595, and 81603398), CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (No. 2016-I2M-1-012 and 2017-I2M-1-013), the Graduate Student Innovation Fund of Peking Union Medical College (No. 2017-1007-14), and National Science and Technology Major Project for ‘Significant New Drugs Development’ (2018ZX09721004-010). The authors acknowledge Beijing Inter-bio Tech CO., LTD for providing the surface plasmon resonance device.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 393 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Dou, X., Zhao, X. et al. A gold/Fe3O4 nanocomposite for use in a surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for carbendazim. Microchim Acta 186, 313 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3402-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3402-0