Abstract
A hydrophilic material consisting of a magnetite core coated with mercaptosuccinic acid modified mesoporous titania (denoted as Fe3O4@mTiO2-MSA) has been fabricated. It is shown to be a viable sorbent for capturing glycopeptides and phosphopeptides. The sorbent combines the features of metal oxide-based affinity chromatography and of hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) with the advantages of using mesoporous titania. The use of magnetic microspheres provides magnetic response and simplifies separation. Following elution with 10% ammonia, the peptides were submitted to LC-MS/MS analysis. The method enabled 327 phosphopeptides and 65 glycopeptides to be identified in three isolated replicates of merely 5 μL samples of human saliva. Among them, the phosphorylation sites and glycosylation sites were detected in 20 peptide segments.

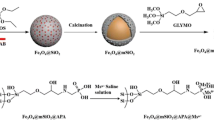
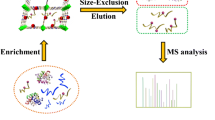
Schematic presentation of preparation of novel hydrophilic magnetic mesoporous titania nanomaterials (Fe3O4@mTiO2-MSA). This specific sorbent exhibits highly selective and efficient simultaneous adsorption ability for both glycopeptides and phosphopeptides from biosamples by mass spectrometric analysis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mann M, Jensen ON (2003) Proteomic analysis of post-translational modifications. Nat Biotechnol 21(3):255–261
Drickamer K, Taylor ME (1998) Evolving views of protein glycosylation. Trends Biochem Sci 23(9):321–324
Kontou M, Weidemann W, Bork K, Horstkorte R (2009) Beyond glycosylation: sialic acid precursors act as signaling molecules and are involved in cellular control of differentiation of PC12 cells. Biol Chem 390(7):575–579
Bajaj SO (2015) A de novo approach towards glycosylation using iterative Pd-/B-dual catalysis: applications in natural products synthesis, digitoxin analogues, oligomannose motifs and their SAR studies. J Appl Phys 76(10):5760–5763
Dominik E, Lena H, Khoa PT, Christopher B, Qiu W, Wright PC, Sonja-Verena A, Bettina S (2016) Protein phosphorylation and its role in archaeal signal transduction. FEMS Microbiol Rev 40(5):625–647
Haystead TAJ, Sim ATR, Carling D, Honnor RC, Tsukitani Y, Cohen P, Hardie DG (1989) Effects of the tumour promoter okadaic acid on intracellular protein phosphorylation and metabolism. Nature 337(6202):78–81
Mi K, Johnson GV (2006) The role of tau phosphorylation in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 3(5):449–463
Muntané G, Dalfó E, Martinez A, Ferrer I (2008) Phosphorylation of tau and alpha-synuclein in synaptic-enriched fractions of the frontal cortex in Alzheimer's disease, and in Parkinson's disease and related alpha-synucleinopathies. Neuroscience 152(4):913–923
Guerry P (1997) Nonlipopolysaccharide surface antigens of campylobacter species. J Infect Dis 176(2):122–124
Lefebvre T, Ferreira S, Dupont-Wallois L, Bussière T, Dupire M-J, Delacourte A, Michalski J-C, Caillet-Boudin M-L (2003) Evidence of a balance between phosphorylation and O-GlcNAc glycosylation of tau proteins—a role in nuclear localization. BBA-Gen Subjects 1619(2):167–176
Robertson LA, Moya KL, Breen KC (2004) The potential role of tau protein O-glycosylation in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 6(5):489–495
Del Grosso F, De Mariano M, Passoni L, Luksch R, Tonini GP, Longo L (2011) Inhibition of N-linked glycosylation impairs ALK phosphorylation and disrupts pro-survival signaling in neuroblastoma cell lines. BMC Cancer 11:525
Liu F, Zaidi T, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Merkle RK, Gong C-X (2002) Role of glycosylation in hyperphosphorylation of tau in Alzheimer's disease. FEBS Lett 512:101–106
Zhang H, Guo T, Li X, Datta A, Park JE, Yang J, Lim SK, Tam JP, Sze SK (2010) Simultaneous characterization of glyco- and phosphoproteomes of mouse brain membrane proteome with electrostatic repulsion hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Mol Cell Proteomics 9(4):635–647
Zou X, Jie J, Yang B (2017) Single-step enrichment of N-Glycopeptides and Phosphopeptides with novel multifunctional Ti4+-immobilized dendritic Polyglycerol coated chitosan Nanomaterials. Anal Chem 89(14):7520–7526
Wang X-D, Liu Y-J, Li F-J, Li Z-L (2017) Poplar catkin: a natural biomaterial for highly specific and efficient enrichment of sialoglycopeptides. Chin Chem Lett 28(5):1018–1026
Wu Z, Xu N, Li W, Lin J-M (2019) A membrane separation technique for optimizing sample preparation of MALDI-TOF MS detection. Chin Chem Lett 30(1):95–98
Liu M, Tran TM, Abbas Elhaj AA, Bøen Torsetnes S, Jensen ON, Sellergren B, Irgum K (2017) Molecularly imprinted porous monolithic materials from melamine–formaldehyde for selective trapping of Phosphopeptides. Anal Chem 89(17):9491–9501
Yan Y, Zheng Z, Deng C, Li Y, Zhang X, Yang P (2013) Hydrophilic Polydopamine-coated Graphene for metal ion immobilization as a novel immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography platform for Phosphoproteome analysis. Anal Chem 85(18):8483–8487
Jiang J, Sun X, She X, Li J, Li Y, Deng C, Duan G (2018) Magnetic microspheres modified with Ti(IV) and Nb(V) for enrichment of phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 185(6):309
Tan S, Wang J, Han Q, Liang Q, Ding M (2018) A porous graphene sorbent coated with titanium(IV)-functionalized polydopamine for selective lab-in-syringe extraction of phosphoproteins and phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 185(7):316
Liu H, Yang T, Dai J, Zhu J, Li X, Wen R, Yang X (2015) Hydrophilic modification of titania nanomaterials as a biofunctional adsorbent for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Analyst 140(19):6652–6659
Leitner A, Sakeye M, Zimmerli CE, Smatt J-H (2017) Insights into chemoselectivity principles in metal oxide affinity chromatography using tailored nanocast metal oxide microspheres and mass spectrometry-based phosphoproteomics. Analyst 142(11):1993–2003
Hong Y, Pu C, Zhao H, Sheng Q, Zhan Q, Lan M (2017) Yolk-shell magnetic mesoporous TiO2 microspheres with flowerlike NiO nanosheets for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Nanoscale 9(43):16764–16772
Li Y, Xu X, Qi D, Deng C, Yang P, Zhang X (2008) Novel Fe3O4@TiO2 core-shell microspheres for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides in phosphoproteome analysis. J Proteome Res 7(6):2526–2538
Ma WF, Zhang Y, Li LL, You LJ, Zhang P, Zhang YT, Li JM, Yu M, Guo J, Lu HJ (2012) Tailor-made magnetic Fe3O4@mTiO2 microspheres with a tunable Mesoporous Anatase Shell for highly selective and effective enrichment of Phosphopeptides. ACS Nano 6(4):3179–3188
Yao J, Wang J, Sun N, Deng C (2017) One-step functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles with 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid for a highly efficient analysis of N-glycopeptides. Nanoscale 9(41):16024–16029
Wang Y, Hai X, E S CM, Yang T, Wang J (2018) Boronic acid functionalized g-C3N4 nanosheets for ultrasensitive and selective sensing of glycoprotein in the physiological environment. In: Nanoscale
Jin S, Liu L, Zhou P (2018) Amorphous titania modified with boric acid for selective capture of glycoproteins. Microchim Acta 185(6):308
Ma W, Xu L, Li Z, Sun Y, Bai Y, Liu H (2016) Post-synthetic modification of an amino-functionalized metal-organic framework for highly efficient enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides. Nanoscale 8(21):10908–10912
Jiang B, Wu Q, Deng N, Chen Y, Zhang L, Liang Z, Zhang Y (2016) Hydrophilic GO/Fe O /au/PEG nanocomposites for highly selective enrichment of glycopeptides. Nanoscale 8(9):4894–4897
Sun N, Wang J, Yao J, Deng C (2017) Hydrophilic Mesoporous silica materials for highly specific enrichment of N-linked Glycopeptide. Anal Chem 89(3):1764–1771
Zhang Y, Zhuang Y, Shen H, Chen X, Wang J (2017) A super hydrophilic silsesquioxane-based composite for highly selective adsorption of glycoproteins. Microchim Acta 184(4):1037–1044
Callan JF, Mulrooney RC (2009) Luminescent detection of cu(II) ions in aqueous solution using CdSe and CdSe-ZnS quantum dots functionalised with mercaptosuccinic acid. Phys Status Solidi 6(4):920–923
Xu Y, Bailey UM, Punyadeera C, Schulz BL (2014) Identification of salivary N-glycoproteins and measurement of glycosylation site occupancy by boronate glycoprotein enrichment and liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 28(5):471–482
Yao J, Sun N, Wang J, Xie Y, Deng C, Zhang X (2017) Rapid synthesis of titanium(IV)-immobilized magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for endogenous phosphopeptides enrichment. Proteomics 17(8):1600320
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0507501) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21425518).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2114 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, N., Wang, J., Yao, J. et al. Magnetite nanoparticles coated with mercaptosuccinic acid-modified mesoporous titania as a hydrophilic sorbent for glycopeptides and phosphopeptides prior to their quantitation by LC-MS/MS. Microchim Acta 186, 159 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3274-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3274-3