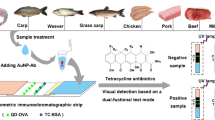
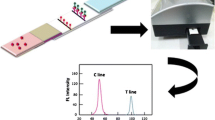
Abstract
The authors describe two kinds of immunochromatographic assays. The first is based on the use of dyed polymer microspheres (MICA), the another on the use of quantum dots (QICA). Both enable visual detection of enrofloxacin (ENR) in animal tissue and milk. Both the MICA and the QICA have visual limits of detection of 1 μg·L−1 when working in buffer, of 5 μg·kg−1 in case of animal tissue, and of 10 μg·L−1 in case of milk. Other quinolones do not interfere. The MICA and QICA described here are convenient and fairly rapid in that the detection process (including sample pretreatment and assay) takes 20 min only which is far less than the commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test kit which requires 120 min. The MICA and QICA are more sensitive than the immunochromatographic assay using colloidal gold labels and the same polyclonal antibody. The results of analysis of spiked samples via MICA and QICA are in good agreement with those obtained by the commercial ELISA test kit.

A visual dyed polymer microsphere-based immunochromatographic assay (MICA) and a visual quantum-dot-based immunochromatographic assay (QICA) are described for the rapid, specific, qualitative, semi-quantitative, and on-site detection of enrofloxacin residues in animal origin foods.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martinez M, McDermott P, Walker R (2006) Pharmacology of the fluoroquinolones: a perspective for the use in domestic animals. Vet J 172:10–28
Petrović J, Baltić M, Ćupić V, Stefanović S, Stojanović D (2006) Residues of enrofloxacin and its main metabolite ciprofloxacin in broiler chickens. Acta Vet (Beograd) 56:497–506
San Martin B, Cornejo J, Lapierre L, Iragüen D, Pérez F, Hidalgo H, Andre F (2009) Withdrawal time of four pharmaceutical formulations of enrofloxacin in poultry according to different maximum residues limits. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 33:246–251
Shim JH, Shen JY, Kim MR, Lee CJ, Kim IS (2003) Determination of the fluoroquinolone enrofloxacin in edible chicken muscle by supercritical fluid extraction and liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J Agric Food Chem 51:7528–7532
Ferrari SPG, Bonassa KPD, Coelho MB, Ferreira CR, da Costa HF, Jara JLP, Miguel MCV, Reyes FGR, Eberlin MN, Nogueira GP, Simas RC (2015) High precision and selectivity for quantitation of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in five chicken tissues using solid phase extraction and ESI LC-MS/MS for application in monitoring residues. Anal Methods 7:3291–3297
Xu XY, Liu LH, Jia ZM, Shu Y (2015) Determination of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in foods of animal origin by capillary electrophoresis with field amplified sample stacking-sweeping technique. Food Chem 176:219–225
Choma IM, Choma A, Komaniecka I, Pilorz K, Staszczuk K (2004) Semiquantitative estimation of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin by thin-layer chromatography-direct bioautography. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 27:2071–2085
Cao LM, Lin H, Mirsky VM (2007) Surface plasmon resonance biosensor for enrofloxacin based on deoxyribonucleic acid. Anal Chim Acta 589:1–5
Xu Y, Du YP, Li QQ, Wang X, Pan YC, Zhang H, Wu T, Hu HL (2014) Ultrasensitive detection of enrofloxacin in chicken muscles by surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy using amino-modified glycidyl methacrylate-ethylene dimethacrylate (GMA-EDMA) powdered porous material. Food Anal Methods 7:1219–1228
Manaspong C, Wongphanit P, Palaga T, Puthong S, Sooksai S, Komolpis K (2013) Production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody against enrofloxacin. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:69–75
Wang ZH, Zhang HY, Ni HJ, Zhang SX, Shen JZ (2014) Development of a highly sensitive and specific immunoassay for enrofloxacin based on heterologous coating haptens. Anal Chim Acta 820:152–158
Kim NG, Kim MA, Park YI, Jung TS, Son SW, So BJ, Kang HG (2015) Magnetic nanoparticle based purification and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using monoclonal antibody against enrofloxacin. J Vet Sci 16:431–437
Yu F, Yu SC, Yu LL, Li YQ, Wu YJ, Zhang HQ, Qu LB, Harrington PDB (2014) Determination of residual enrofloxacin in food samples by a sensitive method of chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay. Food Chem 149:71–75
Chen JX, Xu F, Jiang HY, Hou YL, Rao QX, Guo PJ, Ding SY (2009) A novel quantum dot-based fluoroimmunoassay method for detection of enrofloxacin residue in chicken muscle tissue. Food Chem 113:1197–1201
Zhou B, Zhang K, Zhang J, Wang K, Zhao LL, Jin J, Huang B (2013) A novel and sensitive method for the detection of enrofloxacin in food using time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay. Toxicol Mech Methods 23:323–328
Wutz K, Niessner R, Seidel M (2011) Simultaneous determination of four different antibiotic residues in honey by chemiluminescence multianalyte chip immunoassays. Microchim Acta 173:1–9
Ha MS, Chung MS, Bae DH (2016) Simple detection of residual enrofloxacin in meat products using microparticles and biochips. Food Addit Contam, Part A 33:817–823
Xu YH, Liu ML, Kong N, Liu JQ (2016) Lab-on-paper micro- and nano-analytical devices: fabrication, modification, detection and emerging applications. Microchim Acta 183:1521–1542
Hu LM, Luo K, Xia J, Xu GM, Wu CH, Han JJ, Zhang GG, Liu M, Lai WH (2017) Advantages of time-resolved fluorescent nanobeads compared with fluorescent submicrospheres, quantum dots, and colloidal gold as label in lateral flow assays for detection of ractopamine. Biosens Bioelectron 91:95–103
Kim YK, Kim HJ (2009) Immuno-strip biosensor system to detect enrofloxacin residues. J Ind Eng Chem 15:229–232
Zhao YL, Zhang GP, Liu QT, Teng M, Yang JF, Wang JH (2008) Development of a lateral flow colloidal gold immunoassay strip for the rapid detection of enrofloxacin residues. J Agric Food Chem 56:12138–12142
Chen XL, Xu HY, Lai WH, Chen Y, Yang XH, Xiong YH (2012) A sensitive chromatographic strip test for the rapid detection of enrofloxacin in chicken muscle. Food Addit Contam, Part A 29:383–391
Wu YC, Guo S, Dong Q, Song YZ (2016) Development of an immunochromatographic test strip for rapid simultaneous detection of enrofloxacin and ofloxacin in tissue of chicken muscle and pork. Food Anal Methods 9:2807–2813
Sheng W, Li YZ, Xu X, Yuan M, Wang S (2011) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic assay for several (fluoro)quinolones in milk. Microchim Acta 173:307–316
Mei ZL, Deng Y, Chu HQ, Xue F, Zhong YH, Wu JJ, Yang H, Wang ZC, Zheng L, Chen W (2013) Immunochromatographic lateral flow strip for on-site detection of bisphenol A. Microchim Acta 180:279–285
Taranova NA, Byzova NA, Zaiko VV, Starovoitova TA, Vengerov YY, Zherdev AV, Dzantiev BB (2013) Integration of lateral flow and microarray technologies for multiplex immunoassay: application to the determination of drugs of abuse. Microchim Acta 180:1165–1172
Wang LM, Cai J, Wang YL, Fang QK, Wang SY, Cheng Q, Du D, Lin YH, Liu FQ (2014) A bare-eye-based lateral flow immunoassay based on the use of gold nanoparticles for simultaneous detection of three pesticides. Microchim Acta 181:1565–1572
Zhong YH, Chen YJ, Yao L, Zhao DP, Zheng L, Liu GD, Ye YW, Chen W (2016) Gold nanoparticles based lateral flow immunoassay with largely amplified sensitivity for rapid melamine screening. Microchim Acta 183:1989–1994
Yang YH, Ozsoz M, Liu GD (2017) Gold nanocage-based lateral flow immunoassay for immunoglobulin G. Microchim Acta 184:2023–2029
Fu XQ, Chu YX, Zhao K, Li JG, Deng AP (2017) Ultrasensitive detection of the β-adrenergic agonist brombuterol by a SERS-based lateral flow immunochromatographic assay using flower-like gold-silver core-shell nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184:1711–1719
Zhang KY, Wu JC, Li YN, Wu YR, Huang TF, Tang DP (2014) Hollow nanogold microsphere-signalized lateral flow immunodipstick for the sensitive determination of the neurotoxin brevetoxin B. Microchim Acta 181:1447–1454
Wiriyachaiporn N, Sirikett H, Maneeprakorn W, Dharakul T (2017) Carbon nanotag based visual detection of influenza A virus by a lateral flow immunoassay. Microchim Acta 184:1827–1835
Bamrungsap S, Apiwat C, Chantima W, Dharakul T, Wiriyachaiporn N (2014) Rapid and sensitive lateral flow immunoassay for influenza antigen using fluorescently-doped silica nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 181:223–230
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Project No. 2016YFD0401204), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 31201353), and Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Commission (Project No. 13JCQNJC15300 and 16PTSYJC00130).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 701 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, W., Li, S., Liu, Y. et al. Visual and rapid lateral flow immunochromatographic assay for enrofloxacin using dyed polymer microspheres and quantum dots. Microchim Acta 184, 4313–4321 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2474-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2474-y