Abstract
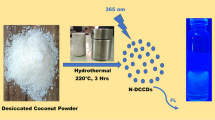
The authors describe blue-green emitting nitrogen doped carbon dots (NCDs) synthesized through a microwave assisted polyol method and by using lactose as the carbon source, ammonium chloride as nitrogen source and PEG 200 as the reaction medium. The surfaces of the NCDs is rich in carboxy groups and can be functionalized with aminophenylboronic acid (APBA) to obtain APBA-modified carbon dots which are shown to a viable fluorescent probe for dopamine (DA). Operated best at excitation wavelength of 370 nm, the fluorescence of the probe increases with increasing concentration of DA. The detection limit is as low as 89 pM. The probe has good selectivity for DA over other interfering neurotransmitters, saccharides, amino acids and antioxidants. It was successfully employed for the detection of DA in (spiked) human serum samples and gave good recoveries.

Aminophenylboronic acid (APBA) functionalized fluorescent nitrogen doped carbon dots (NCD-APBA) were synthesized for fluorescent turn on detection of dopamine (DA). This dopamine assay exhibited high sensitivity and selectivity with a detection limit as low as 89 pM.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolfbeis OS (2015) An overview of nanoparticles commonly used in fluorescent bio imaging. ChemSoc Rev 44:4743–4768. doi:10.1039/c4cs00392f
Li H, Kang Z, Liu Y, Lee S-T (2012) Carbon nanodots: synthesis, properties and applications. J Mater Chem 22:24230. doi:10.1039/c2jm34690g
Lim SY, Shen W, Gao Z (2015) Carbon quantum dots and their applications. ChemSoc Rev 44:362–381. doi:10.1039/C4CS00269E
Xu X, Ray R, Gu Y, Ploehn HJ, Gearheart L, Raker K, Scrivens WA (2004) Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J Am Chem Soc 126:12736–12737. doi:10.1021/ja040082h
Liu J-M, Lin L, Wang X-X, Lin S-Q, Cai W-L, Zhang L-H, Zheng Z-Y (2012) Highly selective and sensitive detection of Cu2+ with lysine enhancing bovine serum albumin modified-carbon dots fluorescent probe. Analyst 137:2637. doi:10.1039/c2an35130g
Qu K, Wang J, Ren J, Qu X (2013) Carbon dots prepared by hydrothermal treatment of dopamine as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for the label-free detection of iron(III) ions and dopamine. Chem Eur J 19:7243–7249. doi:10.1002/chem.201300042
Zheng M, Xie Z, Qu D, Li D, Du P, Jing X, Sun Z (2013) On–off–on fluorescent carbon dot nanosensor for recognition of chromium (VI) and ascorbic acid based on the inner filter effect. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:13242–13247. doi:10.1021/am4042355
Sun Y-P, Zhou B, Lin Y, Wang W, Fernando KAS, Pathak P, Meziani MJ, Harruff BA, Wang X, Wang H, Luo PG, Yang H, Kose ME, Chen B, Veca LM, Xie S-Y (2013) Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J Am Chem Soc 128:7756–7757. doi:10.1021/ja062677d
Yang Y, Kong W, Li H, Liu J, Yang M, Huang H, Liu Y, Wang Z, Wang ST-K, Zhong J, Wang C, Liu Z, Lee S-T, Kang Z (2015) Fluorescent N-doped carbon dots as in vitro and in vivo nanothermometer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:27324–27330. doi:10.1021/acsami.5b08782
Chandra S, Laha D, Pramanik A, Ray Chowdhuri A, Karmakar P, Sahu SK (2016) Synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen and phosphorus doped carbon dots for the detection of Fe 3+ ions in cancer cells: synthesis of highly fluorescent N and P doped carbon dots. Luminescence 31:81–87. doi:10.1002/bio.2927
Dong Y, Pang H, Yang HB, Guo C, Shao J, Chi Y, Li CM, Yu T (2013) Carbon-based dots co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur for high quantum yield and excitation-independent emission. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:7800–7804. doi:10.1002/anie.201301114
Xu Y, Ji X-H, Yin X-B, He X-W, Zhang Y-K (2014) Carbon quantum dot stabilized gadolinium nanoprobe prepared via a one-pot hydrothermal approach for magnetic resonance and fluorescence dual-modality bio imaging. Anal Chem 86:12122–12129. doi:10.1021/ac503002c
Wang Y, Hu A (2014) Carbon quantum dots: synthesis, properties and applications. J Mater Chem C 2:6921. doi:10.1039/C4TC00988F
Rasheed PA, Lee J-S (2017) Recent advances in optical detection of dopamine using nanomaterials. Microchim Acta. doi:10.1007/s00604-017-2183-6
Dua T (2004) World Federation of Neurology, World Health Organization, World Health Organization (Eds.) Atlas: country resources for neurological disorders 2004: results of a collaborative study of the World Health Organization and the world Federation of Neurology. Programme for neurological diseases and neuroscience, Department of Mental Health and Substance Abuse, World Health Organization, Geneva
Alzheimer’s Association: Alzheimer’s Disease and Dimentia, Chicago, USA (2016) Alzheimer's disease facts and figures http://www.alz.org/facts/. Accessed 22 June 2016
World Health Organization (2006) Neurological disorders: public health challenges. World Health Organization, Geneva
Carrera V, Sabater E, Vilanova E, Sogorb MA (2007) A simple and rapid HPLC-MS method for the simultaneous determination of epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine: application to the secretion of bovine chromaffin cell cultures. J Chromatogr B 847:88–94. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.09.0327
Chen Z, Zhang C, Zhou T, Ma H (2015) Gold nanoparticle based colorimetric probe for dopamine detection based on the interaction between dopamine and melamine. Microchim Acta 182:1003–1008. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1417-0
Yusoff N, Pandikumar A, Ramaraj R, Lim HN, Huang NM (2015) Gold nanoparticle based optical and electrochemical sensing of dopamine. Microchim Acta 182:2091–2114
Xu Y, Hun X, Liu F, Wen X, Luo X (2015) Aptamer biosensor for dopamine based on a gold electrode modified with carbon nanoparticles and thionine labeled gold nanoparticles as probe. Microchim Acta 182:1797–1802. doi:10.1007/s00604-015-1509-5
Wang B, Chen Y, Wu Y, Weng B, Liu Y, Li CM (2016) Synthesis of nitrogen- and iron-containing carbon dots, and their application to colorimetric and fluorometric determination of dopamine. Microchim Acta 183:2491–2500. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1885-5
Secor KE, Glass TE (2004) Selective amine recognition: development of a chemosensor for dopamine and norepinephrine. Org Lett 6:3727–3730. doi:10.1021/ol048625f
Freeman R, Bahshi L, Finder T, Gill R, Willner I (2009) Competitive analysis of saccharides or dopamine by boronic acid-functionalized CdSe–ZnS quantum dots. Chem Commun 764. doi:10.1039/b820112a
Tao Y, Lin Y, Ren J, Qu X (2013) A dual fluorometric and colorimetric sensor for dopamine based on BSA-stabilized au nanoclusters. BiosensBioelectron 42:41–46. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2012.10.014
Hall DG (2005) Boronic acids –preparation, applications in organic synthesis and medicine. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Na W, Liu H, Wang M, Su X (2017) A boronic acid based glucose assay based on the suppressionof the inner filter effect of gold nanoparticles on the orange fluorescence of graphene oxide quantum dots. Microchim Acta 184:1463–1470. doi:10.1007/s00604-017-2090-x
Liu X, Hu X, Xie Z, Chen P, Sun X, Yan J, Zhou S (2016) In situ bifunctionalized carbon dots with boronic acid and amino groups for ultrasensitive dopamine detection. Anal Methods 8:3236–3241. doi:10.1039/C6AY00142D
Coskun A, Akkaya EU (2004) Three-point recognition and selective fluorescence sensing of l -DOPA. Org Lett 6:3107–3109. doi:10.1021/ol0488744
Germain ME, Knapp MJ (2009) Optical explosives detection: from color changes to fluorescence turn-on. Chem Soc Rev 38:2543. doi:10.1039/b809631g
Liu Y, Xiao N, Gong N, Wang H, Shi X, Gu W, Ye L (2014) One-step microwave-assisted polyol synthesis of green luminescent carbon dots as optical nanoprobes. Carbon 68:258–264. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2013.10.086
Shen P, Xia Y (2014) Synthesis-modification integration: one-step fabrication of boronic acid functionalized carbon dots for fluorescent blood sugar sensing. Anal Chem 86:5323–5329. doi:10.1021/ac5001338
Fischer MJE (2010) Amine coupling through EDC/NHS: a practical approach. In: Mol NJ, Fischer MJE (eds) Surface Plasmon Resonance. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 55–73
Zhang L, Wang D, Huang H, Liu L, Zhou Y, Xia X, Deng K, Liu X (2016) Preparation of gold−carbon dots and ratiometric fluorescence cellular imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:6646–6655
Shen J, Zhu Y, Yang X, Li C (2012) Graphene quantum dots: emergent nanolights for bio imaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem Commun 48:3686–3699
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Department of Science and Technology, Government of India for DST-INSPIRE Fellowship (IF 150393). The authors also express gratitude to Department of Chemistry, University of Kerala, Thiruvananthapuram, India for providing the instrumental facilities and support as well as STIC, Cochin, India for facilitating the HR-TEM analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2953 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anjali Devi, J.S., Anulekshmi, A.H., Salini, S. et al. Boronic acid functionalized nitrogen doped carbon dots for fluorescent turn-on detection of dopamine. Microchim Acta 184, 4081–4090 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2433-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2433-7