Abstract
A multiple amplified electrochemiluminescence immunosensor is described for the determination of the illicit β-adrenergic agonist brombuterol. Firstly, cystein-coated silver nanowires (SCNW) were modified with polyamidoamine dendrimers (PAMAM) and then immobilized on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE). Then, Ag@Au core/shell nanoparticles (NPs) were deposited on the surface of the modified GCE via gold-nitrogen bonds. The use of Cys-coated silver nanowires accelerates the electron transfer process and also prevents the aggregation of the Ag@Au NPs. The nanocomposites on the GCE have a large surface and outstanding electrical conductivity. It can carry a large amount of coating antigen to amplify the ECL signal. Moreover, PAMAM-Au-CdSe quantum dot bioprobes were prepared, and the unique dendrimer-encapsulated gold nanoparticles with numerous functional amino groups were employed to load abundant activated CdSe quantum dots for further enhancement of the ECL signal. On the basis of signal amplification of the SCNW-PAMAM-Ag@Au-based immunosensor and the PAMAM-Au-CdSe quantum dot bioprobes. The assay has a wide linear range that extends over the 0.001–1000 ng·mL−1 brombuterol concentration range and a lower detection limit of 37 fg·mL−1. The method is well reproducible, stable and specific. It was applied to the determination of brombuterol in spiked samples of pork and feed where it gave satisfactory recoveries.

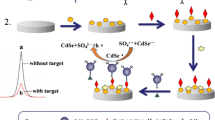
Schematic of a multiple signal amplification electrochemiluminescent immunoassay for ultrasensitive detection of the β-adrenergic agonist brombuterol. It is based on PAMAM-Au-CdSe QDs as bioprobes and SCNWs-PAMAM-Ag@Au as substrates.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
He PL, Shen L, Liu RY, Luo ZP, Li Z (2011) Direct detection of β-agonists by use of gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assays. Anal Chem 83:6988–6955
Newman DJ (2016) Natural product-derived drugs based on β-adrenergic agents and nucleosides. J Braz Chem Soc 27:1320–1333
Goyal RN, Oyama M, Singh SP (2007) Fast determination of salbutamol, abused by athletes for doping, in pharmaceuticals and human biological fluids by square wave voltammetry. J Electroanal Chem 611:140–148
Strydom PE, Frylinck L, Montgomery JL, Smith MF (2009) The comparison of three β-agonists for growth performance, carcass characteristics and meat quality of feedlot cattle. Meat Sci 81:557–564
Johnson BJ, Smith SB, Chung KY (2014) Historical overview of the effect of β-adrenergic agonists on beef cattle production. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 27:757–766
Zhang GP, Wang XN, Yang JF, Yang YY, Xing GX, Li QM, Zhao D, Chai SJ, Guo JQ (2006) Development of an immunochromatographic lateral flow test strip for detection of β-adrenergic agonist Clenbuterol residues. J Immunol Methods 312:27–33
Kuiper HA, Noordam MY, van Dooren-Flipsen MMH, Schilt R, Roos AH (1998) Illegal use of β-adrenergic agonists: European Community. J Anim Sci 76:195–207
Harkins JD, Woods WE, Lehner AF, Fisher M, Tobin T (2001) Clenbuterol in the horse: urinary concentrations determined by ELISA and GC/MS after clinical doses. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 24:7–14
Wang L, Li YQ, Zhou YK, Yang Y (2010) Determination of four β2-agonists in meat, liver and kidney by GC-MS with dual internal standards. Chromatographia 71:737–739
Juan C, Igualada C, Moragues F, León N, Manes J (2010) Development and validation of a liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the analysis of β-agonists in animal feed and drinking water. J Chromatogr A 1217:6061–6068
Du HJ, Chu YX, Yang H, Zhao K, Li JG, She P, Zhang X, Deng AP (2016) Sensitive and specific detection of a new β-agonist brombuterol in tissue and feed samples by a competitive polyclonal antibody based ELISA. Anal Methods 8:3578
Zhao YY, Jiang DN, Wu K, Yang H, Du HJ, Zhao K, Li JG, Deng AP (2016) Development of a sensitive monoclonal antibody-based ELISA for the determination of a β-adrenergic agonist brombuterol in swine meat, liver and feed samples. Anal Methods 8:6941–6948
Wang WY, Zhang YL, Wang JY, Shi X, Ye JN (2010) Determination of β-agonists in pig feed, pig urine and pig liver using capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical detection. Meat Sci 85:302–305
Cai C, Cheng HY, Wang YC, Yang MY, Yang YM (2013) Simultaneous determination of four β-agonist residues in pig feed and urine by capillary electrophoresis with field amplified sample injection and electrochemiluminescent detection. Anal Methods 5:4978–4983
Wu BN, Miao CC, Yu LL, Wang ZY, Huang CS, Jia NQ (2014) Sensitive electrochemiluminescence sensor based on ordered mesoporous carbon composite film for dopamine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 195:22–27
Miao WJ (2008) Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence and its Biorelated applications. Chem Rev 108:2506–2553
Gao WH, Chen YS, Xi J, Zhang A, Chen YW, Lu FS, Chen ZG (2012) A novel electrochemiluminescence sensor based on Ru(bpy)32+ immobilized by graphene on glassy carbon electrode surface via in situ wet-chemical reaction. Sensors Actuators B Chem 171-172:1159–1165
Zhuo Y, Chai YQ, Yuan R, Mao L, Yuan YL, Han J (2011) Glucose oxidase and ferrocene labels immobilized at Au/TiO2 nanocomposites with high load amount and activity for sensitive immunoelectrochemical measurement of ProGRP biomarker. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3838–3844
Chen Y, Xu J, Su J, Xiang Y, Yuan R, Chai YQ (2012) In situ Hybridizatio chain reaction amplification for universal and highly sensitive Electrochemiluminescent detection of DNA. Anal Chem 84:7750–7755
Rivera VR, Gamez FJ, Keener WK, White JA, Poli MA (2006) Rapid detection of clostridium botulinum toxins A, B, E, and F in clinical samples, selected food matrices, and buffer using paramagnetic bead-based electrochemiluminescence detection. Anal Biochem 353:248–256
Jie GF, Zhang JJ, Wang DC, Cheng C, Chen HY, Zhu JJ (2008) Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor based on CdSe nanocomposites. Anal Chem 80:4033–4039
Zhang J, Cai FD, Deng AP, Li JG (2014) CdSe quantum dots based Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor with simple structure for ultrasensitive detection of salbutamol. Electroanalysis 26:873–881
Li QL, Bao N, Ding SN (2014) Electrochemiluminescence sensor for phosphate ions based on europium(III)-modulated CdSe quantum dots. Electroanalysis 26:2710–2715
Huang K, Xu KL, Zhu W, Yang L, Hou XD, Zheng CB (2016) Hydride generation for headspace solid-phase extraction with CdTe quantum dots immobilized on paper for sensitive visual detection of selenium. Anal Chem 88:789–795
Hou J, Zhang HC, Yang Q, Li MZ, Song YL, Jiang L (2014) Bio-inspired photonic-crystal microchip for fluorescent Ultratrace detection. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:5791–5795
Li MZ, He F, Liao Q, Liu J, Xu L, Jiang L, Song YL, Wang S, Zhu DB (2008) Ultrasensitive DNA detection using photonic crystals. Angew Chem Int Ed 47:7258–7262
Bahadir EB, Sezgintürk MK (2016) Poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM): an emerging material for electrochemical bio(sensing) applications. Talanta 148:427–438
Liu LZ, Jiang ST, Wang L, Zhang Z, Xie GM (2015) Direct detection of microRNA-126 at a femtomolar level using a glassy carbon electrode modified with chitosan, graphene sheets, and a poly(amidoamine) dendrimer composite with gold and silver nanoclusters. Microchim Acta 182:77–84
Niu YZ, He JL, Li YL, Zhao YL, Xia CY, Yuan GL, Zhang L, Zhang YC, Yu C (2016) Determination of α2,3-sialylated glycans in human serum using a glassy carbon electrode modified with carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes, a polyamidoamine dendrimer, and a glycan-recognizing lectin from Maackia amurensis. Microchim Acta 183:2337–2344
Xia H, Li LL, Yin ZY, Hou XD, Zhu JJ (2015) Biobar-coded gold nanoparticles and DNAzyme-based dual signal amplification strategy for ultrasensitive detection of protein by Electrochemiluminescence. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:696–703
Yusoff N, Pandikumar A, Ramaraj R, Lim HN, Huang NM (2015) Gold nanoparticle based optical and electrochemical sensing of dopamine. Microchim Acta 182:2091–2114
Yang XJ, Wang YH, Liu YW, Jiang X (2013) A sensitive hydrogen peroxide and glucose biosensor based on gold/silver core–shell nanorods. Electrochim Acta 108:39–44
Liu HP, Liu TZ, Zhang L, Han L, Gao CB, Yin YD (2015) Etching-free epitaxial growth of gold on silver nanostructures for high chemical stability and Plasmonic activity. Adv Funct Mater 25:5435–5443
Chen WJ, Zheng LY, Wang ML, Chi YW, Chen GN (2013) Preparation of protein-like silver-cysteine hybrid nanowires and application in ultrasensitive immunoassay of cancer biomarker. Anal Chem 85:9655–9663
Chen K, Lu ZK, Qin YQ, Jie GF (2015) A novel PAMAM-au nanostructure-amplified CdSe quantum dots electrochemiluminescence for ultrasensitive immunoassay. J Electroanal Chem 754:160–164
Tang QH, Cai FD, Deng AP, Li JG (2015) Ultrasensitive competitive electrochemiluminescence immunoassay for the β-adrenergic agonist phenylethanolamine A using quantum dots and enzymatic amplification. Microchim Acta 182:139–147
Dong TT, Hu LY, Zhao K, Deng AP, Li JG (2016) Multiple signal amplified electrochemiluminescent immunoassay for brombuterol detection using gold nanoparticles and polyamidoamine dendrimers-silver nanoribbon. Anal Chim Acta 945:85–94
Sangiorgi E, Curatolo M (1997) Application of a sequential analytical procedure for the detection of the β-agonist brombuterol in bovine urine samples. J Chromatogr B 693:468–478
Zhu Q, Cai FD, Zhang J, Zhao K, Deng AP, Li JG (2016) Highly sensitive electrochemiluminescent immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles-functionalized zinc oxide nanorod and poly (amidoamine)-graphene for detecting brombuterol. Biosens Bioelectron 86:899–906
Acknowledgments
We really appreciate the support from the Science Fund from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21075087, No. 21175097), the Project of Scientific and Technologic Infrastructure of Suzhou (SZS201207), and the Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (No. YX10900212).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 538 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, L., Dong, T., Zhao, K. et al. Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescent brombuterol immunoassay by applying a multiple signal amplification strategy based on a PAMAM-gold nanoparticle conjugate as the bioprobe and Ag@Au core shell nanoparticles as a substrate. Microchim Acta 184, 3415–3423 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2359-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2359-0