Abstract
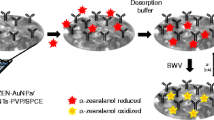
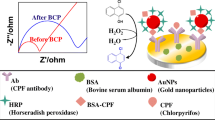
The family of zearalenones (ZENs) represents a major group of mycotoxins with estrogenic activity. They are produced by Fusarium fungi and cause adverse effects on human health and animal production. The authors describe here a label-free amperometric immunosensor for the direct determination of ZENs. A glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was first modified with polyethyleneimine-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Next, gold and platinum nanoparticles (AuPt-NPs) were electro-deposited. This process strongly increased the surface area for capturing a large amount of antibodies and enhanced the electrochemical performance. In a final step, monoclonal antibody against zearalenone was orientedly immobilized on the electrode, this followed by surface blocking with BSA. The resulting biosensor was applied to the voltammetry determination of ZENs, best at a working voltage of 0.18 V (vs SCE). Under optimized conditions, the method displays a wide linear range that extends from 0.005 to 50 ng mL−1, with a limit of detection of 1.5 pg mL−1 (at an S/N ratio of 3). The assay is highly reproducible and selective, and therefore provides a sensitive and convenient tool for determination of such mycotoxins.

An amperometric immunosensor for the direct determination of ZENs has been developed by immobilizing anti-ZEN monoclonal antibody on multi-walled carbon nanotubest hat were deposited, along with gold and platinum nanoparticles, on a glassy carbon electrode modified with Staphylococcus protein A.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shier WT, Shier AC, Xie W, Mirocha CJ (2001) Structure-activity relationships for human estrogenic activity in zearalenone mycotoxins. Toxicon 39:1435–1438
Kakeya H, Takahashi-Ando N, Kimura M, Onose R, Yamaguchi I, Osada H (2002) Biotransformation of the mycotoxin, zearalenone, to a non-estrogenic compound by a fungal strain of Clonostachys sp. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66:2723–2726
Juan C, Ritieni A, Mañes J (2012) Determination of trichothecenes and zearalenones in grain cereal, flour and bread by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 134:2389–2397
Busk Ø, Ndossi D, Frizzell C, Verhaegen S, Uhlig S, Eriksen G, Connolly L, Ropstad E, Sørlie M (2012) Changes in the proteome of the H295R steroidogenesis model associated with exposure to the mycotoxin zearalenone and its metabolites, α- and β-zearalenol. In: Rodrigues P, Eckersall D, de Almeida A (eds) Farm animal proteomics. Wageningen, Netherlands, pp. 55–58
Aldana JR, Silva LJ, Pena A, Mañes J, Lino CM (2014) Occurrence and risk assessment of zearalenone in flours from Portuguese and Dutch markets. Food Control 45:51–55
Qian M, Zhang H, Wu L, Jin N, Wang J, Jiang K (2015) Simultaneous determination of zearalenone and its derivatives in edible vegetable oil by gel permeation chromatography and gas chromatography–triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Food Chem 166:23–28
Hsieh HY, Shyu CL, Liao CW, Lee RJ, Lee MR, Vickroy TW, Chou CC (2012) Liquid chromatography incorporating ultraviolet and electrochemical analyses for dual detection of zeranol and zearalenone metabolites in mouldy grains. J Sci Food Agric 92:1230–1237
Huang H, Tan Y, Shi J, Liang G, Zhu JJ (2010) DNA aptasensor for the detection of ATP based on quantum dots electrochemiluminescence. Nanoscale 2:606–612
Monerris MJ, Arévalo FJ, Fernández H, Zon MA, Molina PG (2015) Development of a very sensitive electrochemical immunosensor for the determination of 17β-estradiol in bovine serum samples. Sens Actuator B Chem 208:525–531
Tang D, Su B, Tang J, Ren J, Chen G (2010) Nanoparticle-based sandwich electrochemical immunoassay for carbohydrate antigen 125 with signal enhancement using enzyme-coated nanometer-sized enzyme-doped silica beads. Anal Chem 82:1527–1534
Loyprasert S, Thavarungkul P, Asawatreratanakul P, Wongkittisuksa B, Limsakul C, Kanatharana P (2008) Label-free capacitive immunosensor for microcystin-LR using self-assembled thiourea monolayer incorporated with Ag nanoparticles on gold electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 24:78–86
Thavarungkul P, Dawan S, Kanatharana P, Asawatreratanakul P (2007) Detecting penicillin G in milk with impedimetric label-free immunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 23:688–694
Dai S, Wu S, Duan N, Wang Z (2016) A luminescence resonance energy transfer based aptasensor for the mycotoxin ochratoxin a using upconversion nanoparticles and gold nanorods. Microchim Acta 183:1909–1916
Moreno V, Zougagh M, Ríos Á (2016) Hybrid nanoparticles based on magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotube-nanoC18SiO2 composites for solid phase extraction of mycotoxins prior to their determination by LC-MS. Microchim Acta 183:871–880
Viswanathan S, Rani C, Anand AV, Ho JA (2009) Disposable electrochemical immunosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen using ferrocene liposomes and MWCNT screen-printed electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 24:1984–1989
Kavosi B, Salimi A, Hallaj R, Amani K (2014) A highly sensitive prostate-specific antigen immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles/PAMAM dendrimer loaded on MWCNTS/chitosan/ionic liquid nanocomposite. Biosens Bioelectron 52:20–28
Banks CE, Compton RG (2006) New electrodes for old: from carbon nanotubes to edge plane pyrolytic graphite. Analyst 131:15–21
Popov VN (2004) Carbon nanotubes: properties and application. Mater Sci Eng R 43:61–102
Chen Y, Cao H, Shi W, Liu H, Huang Y (2013) Fe–Co bimetallic alloy nanoparticles as a highly active peroxidase mimetic and its application in biosensing. Chem Commun 49:5013–5015
Chen KJ, Lee CF, Rick J, Wang SH, Liu CC, Hwang BJ (2012) Fabrication and application of amperometric glucose biosensor based on a novel PtPd bimetallic nanoparticle decorated multi-walled carbon nanotube catalyst. Biosens Bioelectron 33:75–81
Safavi A, Farjami F (2011) Electrodeposition of gold–platinum alloy nanoparticles on ionic liquid–chitosan composite film and its application in fabricating an amperometric cholesterol biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2547–2552
Feng R, Zhang Y, Li H, Wu D, Xin X, Zhang S, Yu H, Wei Q, Du B (2013) Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for zeranol detection based on signal amplification strategy of nanoporous gold films and nano-montmorillonite as labels. Anal Chim Acta 758:72–79
Liu L, Chao Y, Cao W, Wang Y, Luo C, Pang X, Fan D, Wei Q (2014) A label-free amperometric immunosensor for detection of zearalenone based on trimetallic Au-core/AgPt-shell nanorattles and mesoporous carbon. Anal Chim Acta 847:29–36
Xue X, Wei D, Feng R, Wang H, Wei Q, Du B (2013) Label-free electrochemical immunosensors for the detection of zeranol using graphene sheets and nickel hexacyanoferrate nanocomposites. Anal Methods 5:4159–4164
Regiart M, Seia MA, Messina GA, Bertolino FA, Raba J (2015) Electrochemical immunosensing using a nanostructured functional platform for determination of α-zearalanol. Microchim Acta 182:531–538
Regiart M, Pereira SV, Spotorno VG, Bertolino FA, Raba J (2014) Food safety control of zeranol through voltammetric immunosensing on Au–Pt bimetallic nanoparticle surfaces. Analyst 139:4702–4709
Tang DQ, Zhang DJ, Tang DY, Ai H (2006) Amplification of the antigen–antibody interaction from quartz crystal microbalance immunosensors via back-filling immobilization of nanogold on biorecognition surface. J Immunol Methods 316:144–152
Oh BK, Kim YK, Park KW, Lee WH, Choi JW (2004) Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for the detection of salmonella typhimurium. Biosens Bioelectron 19:1497–1504
Oh BK, Chun BS, Park KW, Lee W, Lee WH, Choi JW (2004) Fabrication of protein G LB film for immunoglobulin G immobilization. Mat Sci Eng C Mater 24:65–69
Makaraviciute A, Ramanaviciene A (2013) Site-directed antibody immobilization techniques for immunosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 50:460–471
Trilling AK, Beekwilder J, Zuilhof H (2013) Antibody orientation on biosensor surfaces: a minireview. Analyst 138:1619–1627
Anderson GP, Jacoby MA, Ligler FS, King KD (1997) Effectiveness of protein a for antibody immobilization for a fiber optic biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 12:329–336
Liu Y, Yu J (2016) Oriented immobilization of proteins on solid supports for use in biosensors and biochips: a review. Microchim Acta 183:1–19
Lee W, Oh BK, Bae YM, Paek SH, Lee WH, Choi JW (2003) Fabrication of self-assembled protein a monolayer and its application as an immunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 19:185–192
Liu G, Han Z, Nie D, Yang J, Zhao Z, Zhang J, Li H, Liao Y, Song S, De Saeger S, Wu AB (2012) Rapid and sensitive quantitation of zearalenone in food and feed by lateral flow immunoassay. Food Control 27:200–205
Arribas AS, Bermejo E, Chicharro M, Zapardiel A, Luque GL, Ferreyra NF, Rivas GA (2007) Analytical applications of glassy carbon electrodes modified with multi-wall carbon nanotubes dispersed in polyethylenimine as detectors in flow systems. Anal Chim Acta 596:183–194
Upadhyay S, Rao GR, Sharma MK, Bhattacharya BK, Rao VK, Vijayaraghavan R (2009) Immobilization of acetylcholineesterase–choline oxidase on a gold–platinum bimetallic nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode for the sensitive detection of organophosphate pesticides, carbamates and nerve agents. Biosens Bioelectron 25:832–838
Tao M, Li X, Wu Z, Wang M, Hua M, Yang Y (2011) The preparation of label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on the Pt–Au alloy nanotube array for detection of human chorionic gonadotrophin. Clin Chim Acta 412:550–555
Sun X, Zhu Y, Wang X (2012) Amperometric immunosensor based on deposited gold nanocrystals/4, 4′-thiobisbenzenethiol for determination of carbofuran. Food Control 28:184–191
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the “973” program (2013CB127801), Shanghai Municipal Commission for Science and Technology (15230724400 and 14391901800), and the Public Science and Technology Research Funds of State Grains Bureau (201313005-01-2 and 201513006-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 598 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, N., Nie, D., Tan, Y. et al. An ultrasensitive amperometric immunosensor for zearalenones based on oriented antibody immobilization on a glassy carbon electrode modified with MWCNTs and AuPt nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184, 147–153 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1996-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1996-z