Abstract
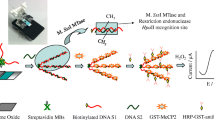
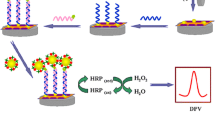
We describe a turn-on electrochemical biosensor for the detection of methyltransferases (MTases) causing DNA adenine methylation. This biosensor is based on insertion, methylation-resistant cleavage, signal enrichment caused by gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), and a signal probe-dragging strategy. A double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) containing identical MTase and methylation-resistant endonuclease (Mbo I) sites was immobilized on the surface of a gold electrode via Au-S covalent binding. The surface was subsequently treated with MTase and Mbo I and then washed. Results revealed that the surface of the electrode contains methylated dsDNA and 12-base nucleotides residual. Depending on biotin-streptavidin interactions that enabled signal probes and nucleotide residue hybridization and AuNP enrichment, a large number of signal probes labeled with ferrocene (Fc) are captured by the electrode. Under optimal conditions, the differential pulse voltammetry signals of Fc tags (at a working voltage of 0.24 V vs. Ag/AgCl) are linearly related to the log of the MTase activity in the 0.1 to 40 U·mL−1 range. The dynamic range extends from 0.05 to 50 U·mL−1, and the limit of detection is 0.024 U·mL−1 (at an S/N ratio of 3). The assay is well reproducible and highly selective. In our perception, this strategy provides a promising approach for simple, sensitive and selective detection of Dam MTase and may be extended to the determination of other MTase by exchanging the corresponding DNA.

Proximity-based electrochemical biosensor for highly sensitive detection of DNA adenine methylation methyltransferase (Dam MTase) activity using methylation-resistant cleavage coupled with gold nanoparticle based cooperative signal amplification.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heithoff DM, Sinsheimer RL, Low DA, Mahan MJ (1999) An essential role for DNA adenine methylation in bacterial virulence. Science 284(5416):967–970
Robertson KD (2005) DNA methylation and human disease. Nat Rev Genet 6(8):597–610
Matzke MA, Mosher RA (2014) RNA-directed DNA methylation: an epigenetic pathway of increasing complexity. Nat Rev Genet 15(6):394–408
Hansen RS, Wijmenga C, Luo P, Stanek AM, Canfield TK, Weemaes CM, Gartler SM (1999) The DNMT3B DNA methyltransferase gene is mutated in the ICF immunodeficiency syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96(25):14412–14417
Richardson B, Scheinbart L, Strahler J, Gross L, Hanash S, Johnson M (1990) Evidence for impaired T cell DNA methylation in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 33(11):1665–1673
Das PM, Singal R (2004) DNA methylation and cancer. J Clin Oncol 22(22):4632–4642
Jurkowska RZ, Ceccaldi A, Zhang Y, Arimondo PB, Jeltsch A (2011) DNA methyltransferase assays. In: Epigenetics protocols. Springer, pp 157–177
Herman JG, Graff JR, Myöhänen S, Nelkin BD, Baylin SB (1996) Methylation-specific PCR: a novel PCR assay for methylation status of CpG islands. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93(18):9821–9826
Zhang Y, Rohde C, Tierling S, Stamerjohanns H, Reinhardt R, Walter J, Jeltsch A (2009) DNA methylation analysis by bisulfite conversion, cloning, and sequencing of individual clones. In: DNA Methylation. Springer, pp 177–187
Johnston JW, Harding K, Bremner DH, Souch G, Green J, Lynch PT, Grout B, Benson EE (2005) HPLC analysis of plant DNA methylation: a study of critical methodological factors. Plant Physiol Biochem 43(9):844–853
Zhao C, Qu K, Song Y, Ren J, Qu X (2011) A universal, label-free, and sensitive optical enzyme-sensing system for nuclease and methyltransferase activity based on light scattering of carbon nanotubes. Adv Funct Mater 21(3):583–590
Zhao Y, Chen F, Wu Y, Dong Y, Fan C (2013) Highly sensitive fluorescence assay of DNA methyltransferase activity via methylation-sensitive cleavage coupled with nicking enzyme-assisted signalamplification. Biosens Bioelectron 42:56–61
Li W, Liu Z, Lin H, Nie Z, Chen J, Xu X, Yao S (2010) Label-free colorimetric assay for methyltransferase activity based on a novel methylation-responsive DNAzyme strategy. Anal Chem 82(5):1935–1941
Li W, Wu P, Zhang H, Cai C (2012) Signal amplification of graphene oxide combining with restriction endonuclease for site-specific determination of DNA methylation and assay of methyltransferase activity. Anal Chem 84(17):7583–7590
Hlavata L, Striesova I, Ignat T, Blaskovisova J, Ruttkay-Nedecky B, Kopel P, Adam V, Kizek R, Labuda J (2015) An electrochemical DNA-based biosensor to study the effects of CdTe quantum dots on UV-induced damage of DNA. Microchim Acta 182(9-10):1715–1722
Jing X, Cao X, Wang L, Lan T, Li Y, Xie G (2014) DNA-AuNPs based signal amplification for highly sensitive detection of DNA methylation, methyltransferase activity and inhibitor screening. Biosens and Bioelectron 58:40–47
Wang C, Zhang L, Guo Z, Xu J, Wang H, Zhai K, Zhuo X (2010) A novel hydrazine electrochemical sensor based on the high specific surface area graphene. Microchim Acta 169(1–2):1–6
Liu T, Chen X, Hong C-Y, Xu X-P, Yang H-H (2014) Label-free and ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence detection of microRNA based on long-range self-assembled DNA nanostructures. Microchim Acta 181(7–8):731–736
Fang X, Jiang W, Han X, Zhang Y (2013) Molecular beacon based biosensor for the sequence-specific detection of DNA using DNA-capped gold nanoparticles-streptavidin conjugates for signal amplification. Microchim Acta 180(13–14):1271–1277
Drummond TG, Hill MG, Barton JK (2003) Electrochemical DNA sensors. Nat Biotechnol 21(10):1192–1199
Josephs EA, Ye T (2013) Nanoscale spatial distribution of thiolated DNA on model nucleic acid sensor surfaces. ACS Nano 7(4):3653–3660
Hu J, Yu Y, Brooks JC, Godwin LA, Somasundaram S, Torabinejad F, Kim J, Shannon C, Easley CJ (2014) A reusable electrochemical proximity assay for highly selective, real-time protein quantitation in biological matrices. J Am Chem Soc 136(23):8467–8474
Qiu L, Qiu L, Wu Z-S, Shen G, Yu R-Q (2013) Cooperative amplification-based electrochemical sensor for the zeptomole detection of nucleic acids. Anal Chem 85(17):8225–8231
Haiss W, Thanh NT, Aveyard J, Fernig DG (2007) Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV-vis spectra. Anal Chem 79(11):4215–4221
Jin R, Wu G, Li Z, Mirkin CA, Schatz GC (2003) What controls the melting properties of DNA-linked gold nanoparticle assemblies? J Am Chem Soc 125(6):1643–1654
Li J, Chu X, Liu Y, Jiang J-H, He Z, Zhang Z, Shen G, Yu R-Q (2005) A colorimetric method for point mutation detection using high-fidelity DNA ligase. Nucleic Acids Res 33(19):e168
Liu J, Lu Y (2006) Preparation of aptamer-linked gold nanoparticle purple aggregates for colorimetric sensing of analytes. Nat Protoc 1(1):246–252
Nam J-M, Thaxton CS, Mirkin CA (2003) Nanoparticle-based bio-bar codes for the ultrasensitive detection of proteins. Science 301(5641):1884–1886
Müller WD, Nascimento ML, Zeddies M, Córsico M, Gassa LM, Mele MAFL (2007) Magnesium and its alloys as degradable biomaterials: corrosion studies using potentiodynamic and EIS electrochemical techniques. Maters Res 10(1):5–10
Zuker M (2003) Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3406–3415
Ouyang X, Liu J, Li J, Yang R (2011) A carbon nanoparticle-based low-background biosensing platform for sensitive and label-free fluorescent assay of DNA methylation. Chem Commun 48(1):88–90
Yang Z, Wang F, Wang M, Yin H, Ai S (2014) A novel signal-on strategy for M. SssI methyltransfease activity analysis and inhibitor screening based on Photoelectrochemical immunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 66:109–114
Wu Z, Z-K W, H T, Tang L-J, Jiang J-H (2013) Activity-based DNA-gold nanoparticle probe as colorimetric biosensor for DNA methyltransferase/glycosylase assay. Anal Chem 85(9):4376–4383
Xu Z, Yin H, Tian Z, Zhou Y, Ai S (2014) Electrochemical immunoassays for the detection the activity of DNA methyltransferase by using the rolling circle amplification technique. Microchim Acta 181(3–4):471–477
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Research Foundation of China (81171415) and the science & technology bureau of Yibin (2014SF015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 11835 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Sheng, S., Cao, X. et al. Proximity-based electrochemical biosensor for highly sensitive determination of methyltransferase activity using gold nanoparticle-based cooperative signal amplification. Microchim Acta 182, 2329–2336 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1564-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1564-y