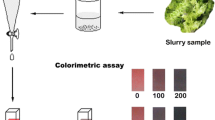
Abstract
A method was developed for the detection of the insecticide acetamiprid based on the strong interaction of the cyano group of acetamiprid with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). The interaction results in the aggregation of gold nanoparticles and is accompanied by a color change from red to purple. The concentration of acetamiprid can be determined qualitatively and quantitatively by visually monitoring the color change or by using a spectrometer. Transmittance electron microscopy and UV-vis spectroscopy have been used to characterize the process. The experimental parameters were optimized with regard to the size of the AuNPs, pH, and incubation time. Under optimal experimental conditions, linear relationships between the logarithm of the concentration of acetamiprid and the absorbance were found over the range of 0.66 to 6.6 μM for AuNPs with diameters of 22.0 ± 1.0 nm and of 6.6–66 μM for AuNPs with diameters of 15.0 ± 1.0 nm. This method was successfully applied to detect acetamiprid in vegetables.

A method was developed for the detection of acetamiprid based on the strong interaction of the cyano group of acetamiprid with gold nanoparticles. This method is rapid, sensitive and low-cost. It can be used for pesticide residues detection.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yao XH, Min H, Lu ZH, Yuan HP (2006) Influence of acetamiprid on soil enzymatic activities and respiration. Eur J Soil Biol 42:120–126
http://www.forbes.com/2009/10/16/bayer-bees-drugs-business-media-bayer.html
Zhou QX, Ding YJ, Xiao JP (2006) Sensitive determination of thiamethoxam, imidacloprid and acetamiprid in environmental water samples with solid-phase extraction packed with multiwalled carbon nanotubes prior to high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem 385:1520–1525
Obana H, Okihashi M, Akutsu K, Kitagawa Y, Hori S (2002) Determination of acetamiprid, imidacloprid, and nitenpyram residues in vegetables and fruits by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detection. J Agr Food Chem 50:4464–4467
Zhang BH, Pan XP, Venne L, Dunnum S, McMurry ST, Cobb GP, Anderson TA (2008) Development of a method for the determination of 9 currently used cotton pesticides by gas chromatography with electron capture detection. Talanta 75:1055–1060
Mateu-Sanchez M, Moreno M, Arrebola FJ, Vidal JLM (2003) Analysis of acetamiprid in vegetables using gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Sci 19:701–704
Radisic M, Grujic S, Vasiljevic T, Lausevic M (2009) Determination of selected pesticides in fruit juices by matrix solid-phase dispersion and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 113:712–719
Muccio AD, Fidente P, Barbini DA, Dommarco R, Seccia S, Morrica P (2006) Application of solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry to the determination of neonicotinoid pesticide residues in fruit and vegetables. J Chromatogr A 1108:1–6
Obana H, Okihashi M, Akutsu K, Kitagawa Y, Hori S (2003) Determination of neonicotinoid pesticide residues in vegetables and fruits with solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. J Agr Food Chem 51:2501–2505
Wanatabe S, Ito S, Kamata Y, Omoda N, Yamazaki T, Munakata H, Kaneko T, Yuasa Y (2001) Development of competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) based on monoclonal antibodies for chloronicotinoid insecticides imidacloprid and acetamiprid. Anal Chim Acta 427:211–219
Wang W, Wu WY, Wang W, Zhu JJ (2010) Tree-shaped paper strip for semiquantitative colorimetric detection of protein with self-calibration. J Chromatogr A 1217:3896–3899
Mascini M, Guilbault GG, Monk IR, Hill C, Carlo MD, Compagnone D (2008) Screening of rationally designed oligopeptides for Listeria monocytogenes detection by means of a high density colorimetric microarray. Microchim Acta 163:227–235
Wang Y, Wang J, Yang F, Yang XR (2010) Spectrophotometric detection of lead(II) ion using unimolecular peroxidase-like deoxyribozyme. Microchim Acta 171:195–201
Liu SQ, Yuan L, Yue XL, Zhang ZZ, Tang ZY (2008) Recent advances in nanosensors for organophosphate pesticide detection. Adv Powder Technol 19:419–441
Liu JW, Lu Y (2006) Fast colorimetric sensing of adenosine and cocaine based on a general sensor design involving aptamers and aanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:90–94
Wu WY, Bian ZP, Wang W, Zhu JJ (2010) PDMS gold nanoparticle composite film-based silver enhanced colorimetric detection of cardiac troponin. Sensor Actuat B 147:298–303
Zhang YM, Lin Q, Wei TB, Wang DD, Yao H, Wang YL (2009) Simple colorimetric sensors with high selectivity for acetate and chloride in aqueous solution. Sensor Actuat B 137:447–455
Zhang SH, Wang J, Han L, Li CG, Wang W, Yuan Z (2010) Colorimetric detection of bis-phosphorylated peptides using zinc (II) dipicolylamine-appended gold nanoparticles. Sensor Actuat B 147:687–690
Rosi NL, Mirkin CA (2005) Nanostructures in biodiagnostics. Chem Rev 105:1547–1562
Ai KL, Liu YL, Lu LH (2009) Hydrogen-bonding recognition-induced color change of gold nanoparticles for visual detection of melamine in raw milk and infant formula. J Am Chem Soc 131:9496–9497
Han CP, Zeng LL, Li HB, Xie GY (2009) Colorimetric detection of pollutant aromatic amines isomers with p-sulfonatocalix[6]arene-modified gold nanoparticles. Sensor Actuat B 137:704–709
Zhao W, Brook MA, Li YF (2008) Design of gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric biosensing assays. ChemBioChem 9:2363–2371
Zhao W, Chiuman W, Lam JCF, McManus SA, Chen W, Cui YG, Pelton R, Brook MA, Li YF (2008) DNA aptamer folding on gold nanoparticles: from colloid chemistry to biosensors. J Am Chem Soc 130:3610–3618
Zhao W, Chiuman W, Brook MA, Li YF (2007) Simple and rapid colorimetric biosensors based on DNA aptamer and noncrosslinking gold nanoparticle aggregation. ChemBioChem 8:727–731
Zhang YF, Li BX, Chen XL (2010) Simple and sensitive detection of dopamine in the presence of high concentration of ascorbic acid using gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probes. Microchim Acta 168:107–113
Doron A, Katz E, Willner I (1995) Organization of Au colloids as monolayer films onto ITO glass surfaces: application of the metal colloid films as base interfaces to construct redox-active monolayers. Langmuir 11:1313–1317
Li H, Rothberg LJ (2004) Label-free colorimetric detection of specific sequences in genomic DNA amplified by the polymerase chain reaction. J Am Chem Soc 126:10958–10961
Kuhn S, Baisch B, Jung U, Johannsen T, Kubitschke J, Herges R, Magnussen O (2010) Self-assembly of triazatriangulenium-based functional adlayers on Au(111) surfaces. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:4481–4487
Napper DH (1983) Polymeric stabilization of colloidal dispersions. Academic, New York
Jiang ZL, Feng ZW, Li TS, Li F, Zhong FX, Xie JY, Yi XH (2001) Resonance scattering spectroscopy of gold nanoparticle. Sci China Ser B 44:175–181
Papanastasiou G, Ziogas I (1989) Acid-base equilibria in ternary water/methanol/dioxane solvent systems: determination of pK values of citric acid at 25 °C. Anal Chim Acta 222:189–200
Kim T, Lee C-H, Joo S-W, Lee K (2008) Kinetics of gold nanoparticle aggregation: experiments and modeling. J Colloid Interf Sci 318:238–243
Kim T, Lee K, Gong M, Joo S-W (2005) Control of gold nanoparticle aggregates by manipulation of interparticle interaction. Langmuir 21:9524–9528
Templeton AC, Hostetler MJ, Kraft CT, Murray RW (1998) Reactivity of monolayer-protected gold cluster molecules: steric effects. J Am Chem Soc 120:1906–1911
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 20675071, 20705030, 20875081), 863 Program Foundation (2009AA03Z331), the Foundation of Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Environmental Material and Engineering (K08021) and the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (20090461161).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Q., Du, S., Jin, Gd. et al. Determination of acetamiprid by a colorimetric method based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 173, 323–329 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0562-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-011-0562-y