Abstract
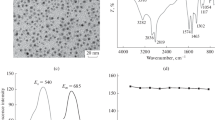
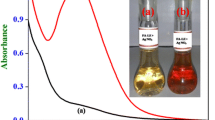
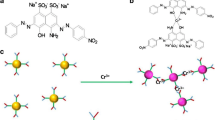
Selective determination of Ag(I) ion was accomplished based on the red-shift of the emission band of quantum dots (QDs). Under optimal conditions, a linear relationship does exist between the red-shift of the emission and the concentration of Ag(I) in the range from 1.0 × 10−7 to 1.5 × 10−5 mol L−1, with a detection limit of 5.0 × 10−8 mol L−1. The method has been successfully applied to the determination of Ag(I) ion in water samples. The possible reaction mechanism was investigated by ultraviolet–visible absorption, fluorescence, Raman spectroscopies and by high resolution transmission electron microscopy. The results suggest that the red-shift in emission be attributed to the stabilization of a charge-transfer state, but not due to the aggregation induced by AgI(I) ion.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rurack K, Kollmannsberger M, Resch-Genger U, Daub J (2000) A selective and sensitive fluoroionophore for HgII, AgI, and CuII with virtually decoupled fluorophore and receptor units. J Am Chem Soc 122:968
Yang RH, Chan WH, Lee AWM, Xia PF, Zhang HK, Li KA (2003) A ratiometric fluorescent sensor for AgI with high selectivity and sensitivity. J Am Chem Soc 125:2884
Bruchez M, Moronne M, Gin P, Weiss S, Alivisatos AP (1998) Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 281:2013
Mattoussi H, Manro JM, Goldman ER, Anderson GP, Sundar VC, Mikula FV, Bawendi MG (2000) Self-assembly of CcuhdSe–ZnS quantum dot bioconjugates using an engineered recombinant protein. J Am Chem Soc 122:12142
Chan WCW, Nie SM (1998) Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 281:2016
Han MY, Gao XH, Su JZ, Nie SM (2001) Quantum-dot-tagged microbeads for multiplexed optical coding of biomolecules. Nat Biotechnol 19:631
Chen YF, Rosenzweig Z (2002) Luminescent CdS quantum dots as selective ion probes. Anal Chem 74:5132
Gattás-Asfura KM, Leblanc RM (2003) Peptide-coated CdS quantum dots for the optical detection of copper(II) and silver(I). Chem Commun 21:2684
Liang JG, Ai XP, He ZK (2004) Functionalized CdSe quantum dots as selective silver ion chemodosimeter. Analyst 129:619
Banerjee S, Kar S, Santra S (2008) A simple strategy for quantum dot assisted selective detection of cadmium ions. Chem Commun 26:3037
Xia YS, Zhu CQ (2008) Use of surface-modified CdTe quantum dots as fluorescent probes in sensing mercury (II). Talanta 75:215
Xu C, Bakker E (2007) Multicolor quantum dot encoding for polymeric particle-based optical ion sensors. Anal Chem 79:3716
Wu HM, Liang JG, Han HY (2008) A novel method for the determination of Pb2+ based on the quenching of the fluorescence of CdTe quantum dots. Microchim Acta 161:81
Chen JL, Zhu CQ (2005) Functionalized cadmium sulfide quantum dots as fluorescence probe for silver ion determination. Anal Chim Acta 546:147
Shang ZB, Wang Y, Jin WJ (2009) Triethanolamine-capped CdSe quantum dots as fluorescent sensors for reciprocal recognition of mercury (II) and iodide in aqueous solution. Talanta 78:364
Lai SJ, Chang XJ, Fu C (2009) Cadmium sulfide quantum dots modified by chitosan as fluorescence probe for copper (II) ion determination. Microchim Acta 165:39
Zhang LJ, Xu CL, Li BX (2009) Simple and sensitive detection method for chromium(VI) in water using glutathione-capped CdTe quantum dots as fluorescent probes. Microchim Acta 166:61
Chen HQ, Liang AN, Wang L, Liu Y, Qian BB (2009) Ultrasensitive determination of Cu2+ by synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy with functional nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 164:453
Xia Y, Zhang T, Diao X, Zhu C (2007) Measurable emission color change: size-dependent reversible fluorescence quenching of CdTe quantum dots by molecular oxygen. Chem Lett 36:242
Yu WW, Qu L, Guo W, Peng X (2003) Experimental determination of the extinction coefficient of CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals. Chem Mater 15:2854
Schmelz O, Mews A, Basché T, Herrmann A, Müllen K (2001) Supramolecular complexes from CdSe nanocrystals and organic fluorophors. Langmuir 17:2861
Son DH, Hughes SM, Yin YD, Alivisatos AP (2004) Cation exchange reactions in ionic nanocrystals. Science 306:1009
Dong CQ, Qian HF, Fang NH, Ren JC (2006) Study of fluorescence quenching and dialysis process of CdTe quantum dots, using ensemble techniques and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B 110:11069
Leung LK, Komplin NJ, Ellis AB, Tabatabaie NJ (1991) Photoluminescence studies of silver-exchanged cadmium selenide crystals: modification of a chemical sensor for aniline derivatives by heterojunction formation. Phys Chem 95:5918
Tamar D, Nikolai G, Alexander E, Daniel M (2008) Studying the reactions of CdTe nanostructures and thin CdTe films with Ag+ and AuCl −4 . J Phys Chem C 112:8881
Xia YS, Cao C, Zhu CQ (2008) Two distinct photoluminescence responses of CdTe quantum dots to Ag (I). J Lumin 128:166
Isarov AV, Chrysochoos J (1997) Optical and photochemical properties of nonstoichiometric cadmium sulfide nanoparticles: surface modification with copper(II) ions. Langmuir 13:3142
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support for this research by National Natural Science Foundation of China (20675034), the Program for academic pacesetter of Wuhan (200851430484), Nature Science foundation key project from Hubei Province of China (2008CDA080), the Youth Chengguang Project of Science and Technology of Wuhan City of China (200850731359) and Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (No.2008CDB031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 100 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Liang, J., Sheng, Z. et al. A novel strategy for selective detection of Ag+ based on the red-shift of emission wavelength of quantum dots. Microchim Acta 167, 281–287 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-009-0244-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-009-0244-1