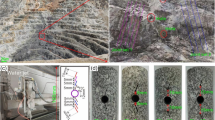
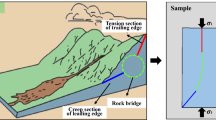
Abstract
Rock structural deterioration induced by coupled freeze–thaw and stress disturbance are a great concern for jointed rock mass during rock constructions in cold regions. Previous studies focused on fracture evolution of intact rock or flawed rock under freeze–thaw–static loads, but the coupling effect of freeze–thaw and cyclic loads on the pre-flawed hollow-cylinder rock is not well understood. This work investigated the influence of freeze–thaw on rock microstructure change and fatigue mechanical behaviors. Testing results show that rock strength, volumetric strain, and lifetime decrease with increasing F–T number. The stiffness degradation caused by cyclic loads is also impacted by the previous freeze–thaw damage. Additionally, the AE ring count and energy count decrease with the increase of F–T treatment. Large fracture signals are captured for rock that has smaller F–T cycles and at the stress-increasing moment. The AE b-value increases with F–T cycles, and it decreases rapidly near rock failure. Spectral analysis indicates that large-scaled cracking is prone to form for a sample having high F–T cycles. Moreover, 2D CT images reveal the differential crack network pattern at rock bridge segments and how it is affected by the previous freeze–thaw damage. The crack coalescence and hole collapse patterns and the associated structural deterioration of the rock bridge segment are obviously influenced by the F–T treatment.
Highlights
-
Fracture behaviors of pre-flawed hollow-cylinder granite under freeze-thaw-fatigue loads were analyzed.
-
Cyclic freeze-thaw weathering influences rock microstructure and geomechanical properties.
-
Acoustic emission parameters and spectral analysis reveals the impact of F-T on rock progressive failure.
-
The crack coalescence and hole collapse patterns are obviously influenced by the F-T treatment.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The experimental data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
ASTM (2007) Standard test method for compressive strength and elastic moduli of intact rock core specimens under varying states of stress and temperatures. Annual book of ASTM standards
Alsayed MI (2002) Utilising the Hoek triaxial cell for multiaxial testing of hollow rock cylinders. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 39(3):355–366
Bagde MN, Petroš V (2005) Fatigue properties of intact sandstone samples subjected to dynamic uniaxial cyclical loading. Int J Rock Mech Min 42:237–250
Cerfontaine B, Collin F (2018) Cyclic and fatigue behaviour of rock materials: review, interpretation and research perspectives. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(2):391–414
Dresen G, Kwiatek G, Goebel T, Ben-Zion Y (2020) Seismic and aseismic preparatory processes before large stick–slip failure. Pure Appl Geophys 177(12):5741–5760
Forte G, Verrucci L, Di Giulio A, De Falco M, Tommasi P, Lanzo G, Santo A (2021) Analysis of major rock slides that occurred during the 2016–2017 Central Italy seismic sequence. Eng Geol 290:106194
Ghobadi MH, Babazadeh R (2015) Experimental studies on the effects of cyclic freezing–thawing, salt crystallization, and thermal shock on the physical and mechanical characteristics of selected sandstones. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48:1001–1016
Huang SB, Liu QS, Cheng AP, Liu YZ, Liu GF (2018) A fully coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical model including the determination of coupling parameters for freezing rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 103:205–214
Karpyn ZT, Alajmi A, Radaelli F, Halleck PM, Grader AS (2009) X-ray CT and hydraulic evidence for a relationship between fracture conductivity and adjacent matrix porosity. Eng Geol 103(3–4):139–145
Kong LW, Zeng ZX, Bai W, Wang M (2018) Engineering geological properties of weathered swelling mudstones and their effects on the landslides occurrence in the Yanji section of the Jilin-Hunchun high-speed railway. Bull Eng Geol Env 77(4):1491–1503
Lee DH, Juang CH, Chen JW, Lin HM, Shieh WH (1999) Stress paths and mechanical behavior of a sandstone in hollow cylinder tests. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 36(7):857–870
Li G, Cheng X, Hu L, Tang C (2021a) The material-structure duality of rock mass: Insight from numerical modeling. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 144:104821
Li Y, Zhai Y, Meng F, Zhang Y (2021b) Study on the influence of freeze-thaw weathering on the mechanical properties of Huashan granite strength. Rock Mech Rock Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02497-w
Lu YN, Li XP, Chan A (2019) Damage constitutive model of single flaw sandstone under freeze–thaw and load. Cold Reg Sci Technol 159:20–28
Masoumi H, Saydam S, Hagan PC (2015) A modification to radial strain calculation in rock testing. Geotech Test J 38(6):813–822
Mateos RM, García-Moreno I, Azañón JM (2012) Freeze–thaw cycles and rainfall as triggering factors of mass movements in a warm Mediterranean region: the case of the Tramuntana Range (Majorca, Spain). Landslides 9(3):417–432
Miao S, Pan PZ, Li S, Chen J, Konicek P (2021) Quantitative fracture analysis of hard rock containing double infilling flaws with a novel DIC-based method. Eng Fract Mech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2021.107846
Mogi K (1981) Earthquake prediction program in Japan. In: Simpson DW, Richards PG (eds) Earthquake prediction: an international review, vol 4. AGU, Washington, DC, pp 635–666
Muñoz-Ibáñez A, Delgado-Martín J, Herbón-Penabad M, Alvarellos-Iglesias J (2021) Acoustic emission monitoring of mode I fracture toughness tests on sandstone rocks. J Pet Sci Eng 205:108906
Nicholson DT, Nicholson FH (2000) Physical deterioration of sedimentary rocks subjected to experimental freeze–thaw weathering. Earth Surf Proc Land 25(12):1295–1307
Niu Y, Zhou XP, Zhou LS (2020) Fracture damage prediction in fissured red sandstone under uniaxial compression: acoustic emission b-value analysis. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 43(1):175–190
Ohnaka M, Mogi K (1982) Frequency characteristics of acoustic emission in rocks under uniaxial compression and its relation to the fracturing process to failure. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 87(B5):3873–3884
Scholz CH (1968) Microfracturing and the inelastic deformation of rock in compression. J Geophys Res 73:1417–1432
Wang Y, Zhang B, Li B, Li CH (2021a) A strain-based fatigue damage model for naturally fractured marble subjected to freeze-thaw and uniaxial cyclic loads. Int J Damage Mech 30(10):1594–1616
Wang Y, Feng WK, Hu RL, Li CH (2021b) Fracture evolution and energy characteristics during marble failure under triaxial fatigue cyclic and confining pressure unloading (FC-CPU) conditions. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54(2):799–818
Wang Y, Han JQ, Song ZY, Zhu C (2021c) Macro–meso failure behavior of pre-flawed hollow-cylinder granite under multi-level cyclic loads: insights from acoustic emission and post-test CT scanning. Eng Fract Mech 258:108074
Wang Y, Zhu C, Song ZY, Gong S (2022a) Macro–meso failure characteristics of circular cavity-contained granite under unconventional cyclic loads: a lab-scale testing. Measurement 188:110608
Wang Y, Yang HN, Han JQ, Zhu C (2022b) Effect of rock bridge length on fracture and damage modelling in granite containing hole and fissures under cyclic uniaxial increasing-amplitude decreasing-frequency (CUIADF) loads. Int J Fatigue. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.106741
Wang Y, Cao Z, Song Z, Zhu C, Han J (2022c) On fracture and damage evolution modelling of fissure-hole containing granite induced by multistage constant-amplitude variable-frequency cyclic loads. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct. https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.13663
Xu J, Liu Y, Ni Y (2019) Hierarchically weighted rough-set genetic algorithm of rock slope stability analysis in the freeze–thaw mountains. Environ Earth Sci 78(6):1–14
Yang SQ (2018) Fracturing mechanism of compressed hollow-cylinder sandstone evaluated by X-ray micro-CT scanning. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(7):2033–2053
Yang J, Mu ZL, Yang SQ (2020) Experimental study of acoustic emission multi-parameter information characterizing rock crack development. Eng Fract Mech 232:107045
Zhou JW, Cui P, Hao MH (2016) Comprehensive analyses of the initiation and entrainment processes of the 2000 Yigong catastrophic landslide in Tibet. China Landslides 13(1):39–54
Zhou XP, Niu Y, Zhang JZ, Shen XC, Zheng Y, Berto F (2019) Experimental study on effects of freeze-thaw fatigue damage on the cracking behaviors of sandstone containing two unparallel fissures. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 42(6):1322–1340
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52174069), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (8202033), Key Laboratory of Geological Environment Intelligent Monitoring and Disaster Prevention and Control of Henan Province, North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (ZDZX2020001), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (FRF–TP-20-004A2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Song, Z., Mao, T. et al. Macro–Meso Fracture and Instability Behaviors of Hollow-Cylinder Granite Containing Fissures Subjected to Freeze–Thaw–Fatigue Loads. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55, 4051–4071 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-02860-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-02860-5