Abstract
Purpose
A preoperative immunonutrition pharmaceutics diet (IMPACT) significantly reduced the incidence of postoperative infectious complications, but the optimal regimen still remains unclear. We evaluated the optimal dose of a preoperative IMPACT for patients with esophageal carcinoma and the incidence of postoperative complications based on the dose of IMPACT.
Methods
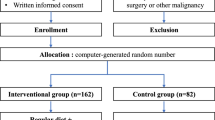
This study design was a prospective nonrandomized study. Twenty patients with thoracic esophageal carcinoma who underwent a right transthoracic subtotal esophagectomy were divided into two groups. These patients were administered immunonutrition of 500 ml/day (IMP500) or 1000 ml/day (IMP1000) for 7 days before the operation.
Results
The incidence of postoperative mortality and morbidity was not different between the IMP500 group and the IMP1000 group. No difference was observed in the perioperative changes in inflammatory, immunological and nutritional variables between the two groups. There were no adverse effects in the IMP500 group, but four patients (40%) had diarrhea and four patients (40%) had appetite loss in the IMP1000 group. In the IMP1000 group, only four patients (40%) could take 1000 ml, but others reduced the quantity of IMPACT because of diarrhea and discomfort.
Conclusion
This study suggests that 500 ml of IMPACT is recommended as an optimal dose for patients with esophageal cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muller JM, Erasmi H, Stelzner M, Zieren U, Pichlmaier H. Surgical therapy of oesophageal carcinoma. Br J Surg 1990;77:845–857.
Fujita H, Kakegawa T, Yamana H, Shima I, Toh Y, Tomita Y, et al. Mortality and morbidity rates, postoperative course, quality of life, and prognosis after extended radical lymphadenectomy for esophageal cancer. Comparison of three-field lymphadenectomy with two-field lymphadenectomy. Ann Surg 1995;222:654–662.
Avendano CE, Flume PA, Silvestri GA, King LB, Reed CE. Pulmonary complications after esophagectomy. Ann Thorac Surg 2002;73:922–926.
Fang W, Kato H, Tachimori Y, Igaki H, Sato H, Daiko H. Analysis of pulmonary complications after tree-field lymph node dissection for esophageal cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 2003;76:903–908.
Whooley BP, Law S, Murthy SC, Alexandrou A, Wong J. Analysis of reduced death and complication rates after esophageal resection. Ann Surg 2001;233:338–344.
Law S, Wong KH, Kwok KF, Chu KM, Wong J. Predictive factors for postoperative pulmonary complications and mortality after esophagectomy for cancer. Ann Surg 2004;240:791–800.
Nakamura M, Iwahashi M, Nakamori M, Ishida K, Naka T, Iida T, et al. An analysis of the factors contributing to a reduction in the incidence of pulmonary complications following an esophagectomy for esophageal cancer. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2008;393:127–133.
Shichinohe T, Hirano S, Kondo S. Video-assisted esophagectomy for esophageal cancer. Surg Today 2008;38:206–213.
Braga M, Gianotti L, Gentilini O, Parisi V, Salis C, Di Carlo V. Early postoperative enteral nutrition improves gut oxygenation and reduces costs compared with total parenteral nutrition. Crit Care Med 2001;29:242–248.
Bozzetti F, Braga M, Gianotti L, Gavazzi C, Mariani L. Postoperative enteral versus parenteral nutrition in malnourished patients with gastrointestinal cancer: a randomized multicenter trial. Lancet 2001;358:1487–1492.
Kudsk KA, Croce MA, Fabian TC, Minard G, Tolley EA, Poret HA, et al. Enteral versus parenteral feeding: effect on septic morbidity after blunt and penetrating trauma. Ann Surg 1992;215:503–511.
Kemen M, Senkal M, Homann HH, Mumme A, Dauphin AK, Baier J, et al. Early postoperative enteral nutrition with arginine, omega-3 fatty acids and ribonucleic acid-supplemented diet versus placebo in cancer patients: an immunologic evaluation of Impact. Crit Care Med 1995;23:652–659.
Senkal M, Kemen M, Homann HH, Eickhoff U, Baier J, Zumtobel V. Modulation of postoperative immune response by enteral nutrition with a diet enriched with arginine, RNA, and omega-3 fatty acids in patients with upper gastrointestinal cancer. Eur J Surg 1995;161:115–122.
Hall JC, Heel K, McCauley R. Glutamine. Br J Surg 1996;83:305–312.
Braga M, Vignali A, Gianotti L, Cestari A, Profili M, Di Carlo V. Immune and nutritional effects of early enteral nutrition after major abdominal operations. Eur J Surg 1996;162:105–112.
Daly JM, Lieberman MD, Goldfine J, Shou J, Weintraub F, Rosato EF, et al. Enteral nutrition with supplemental arginine, RNA, and omega-3 fatty acids in patients after operation: immunologic, metabolic and clinical outcome. Surgery 1992;112:56–67.
Van der Hulst RRW, Van Kreel BK, Von Meyenfeld MF, Brummer RJ. Glutamine and the prevention of gut integrity. Lancet 1993;341:1363–1365.
Braga M, Gianotti L, Radaelli G, Vignali A, Mari G, Gentilini O, et al. Perioperative immunonutrition in patients undergoing cancer surgery: results of a randomized double-blind phase 3 trial. Arch Surg 1999;134:428–433.
Senkal M, Zumtobel V, Bauer KH, Marpe B, Wolfram G, Frei A, et al. Outcome and cost-effectiveness of perioperative enteral immunonutrition in patients undergoing elective upper gastrointestinal tract surgery: a prospective randomized study. Arch Surg 1999;134:1309–1316.
Braga M, Gianotti L, Vignali A, Carlo VD. Preoperative oral arginine and n-3 fatty acid supplementation improves the immunometabolic host response and outcome after colorectal resection for cancer. Surgery 2002;132:805–814.
Xu J, Zhong Y, Jing D, Wu Z. Preoperative enteral immunonutrition improves postoperative outcome in patients with gastrointestinal cancer. World J Surg 2006;30:1284–1289.
Heys SD, Walker LG, Smith I, Eremin O. Enteral nutritional supplementation with key nutrients in patients with critical illness and cancer. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Ann Surg 1999;229:467–477.
Sato N, Koeda K, Ikeda K, Kimura Y, Aoki K, Iwaya T, et al. Randomized study of the benefits of preoperative corticosteroid administration on the postoperative morbidity and cytokine response in patients undergoing surgery for esophageal cancer. Ann Surg 2002;236:184–190.
Atkinson S, Sieffert E, Bihari D. A prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial of enteral immunonutrition in the critically ill. Guy’s Hospital Intensive Care Group. Crit Care Med 1998;26:1164–1172.
Gianotti L, Braga M, Gentilini O, Balzano G, Zerbi A, Di Carlo V. Artificial nutrition after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Pancreas 2000;21:344–351.
Takeuchi H, Ikeuchi S, Kawaguchi Y, Kitagawa Y, Isobe Y, Kubochi K, et al. Clinical significance of perioperative immunonutrition for patients with esophageal cancer. World J Surg 2007;31:2160–2167.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamura, M., Iwahashi, M., Takifuji, K. et al. Optimal dose of preoperative enteral immunonutrition for patients with esophageal cancer. Surg Today 39, 855–860 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-009-3967-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-009-3967-z