Abstract
Background
Pulmonary complications occur most frequently following a transthoracic esophagectomy for esophageal cancer and would get to be lethal occasionally. In this study, we sought to determine the effect of respiratory physiotherapy, corticosteroid administration, and the use of the video-assisted thoracoscopic (VATS) esophagectomy with a small thoracotomy incision, on the incidence of pulmonary complications following a transthoracic subtotal esophagectomy.
Materials and methods
Approximately 184 patients who had undergone a right transthoracic subtotal esophagectomy for squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus were studied. To reduce the incidence of pulmonary complications, we performed clinical trials using respiratory physiotherapy, corticosteroid administration, and the VATS-esophagectomy surgical technique.
Results
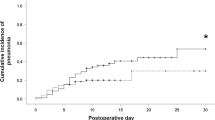
The independent risk factors for pulmonary complications in the multivariate logistic regression analysis were not administering corticosteroids, blood loss greater than 630 ml, and not providing respiratory physiotherapy. In addition, the use of a small surgical incision, less than 10 cm, for the thoracotomy had no effect on the prevention of pulmonary complications.
Conclusions
We concluded that patients with thoracic esophageal cancer could undergo a three-field dissection in comparative safety if the patients were provided with corticosteroid medication in the perioperative period, if the patients received sufficient respiratory physiotherapy, and if surgical blood loss was reduced.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARDS:
-
acute respiratory distress syndrome
- ICU:
-
Intensive Care Unit
- OR:
-
odds ratio
- CI:
-
confidence interval
References
Earlam R, Cunha-Melo JR (1980) Oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: 1. A critical review of surgery.. Br J Surg 67:381–390
Muller JM, Erasmi H, Stelzner M, Zieren U, Pichlmaier H (1990) Surgical therapy of oesophageal carcinoma. Br J Surg 77:845–857
Swisher SG, Hunt KK, Holmes EC, Zinner MJ, McFadden DW (1995) Changes in the surgical management of esophageal cancer from 1970 to 1993. Am J Surg 169:609–614
Kakegawa T (2003) Forty years’ experience in surgical treatment for esophageal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 8:277–288
Whooley BP, Law S, Murthy SC, Alexandrou A, Wong J (2001) Analysis of reduced death and complication rates after esophageal resection. Ann Surg 233:338–344
Walsh TN, Noonan N, Hollywood D, Kelly A, Keeling N, Hennessy TP (1996) A comparison of multimodal therapy and surgery for esophageal adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 335:462–467
Bailey SH, Bull DA, Harpole DH, Rentz JJ, Neumayer LA, Pappas TN, Daley J, Henderson WG, Krasnicka B, Khuri SF (2003) Outcome after esophagectomy: a ten-year prospective cohort. Ann Thorac Surg 75:217–222
Law S, Wong KH, Kwok KF, Chu KM, Wong J (2004) Predictive factors for postoperative pulmonary complications and mortality after esophagectomy for cancer. Ann Surg 240:791–800
Fang W, Kato H, Tachimori Y, Igaki H, Sato H, Daiko H (2003) Analysis of pulmonary complications after tree-field lymph node dissection for esophageal cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 76:903–908
Fok M, Law SYK, Wong J (1994) Operable esophageal carcinoma: current results from Hong Kong. World J Surg 18:355–360
Hall JC, Tarala RA, Tapper J, Hall JL (1996) Prevention of respiratory complications after abdominal surgery: randomized clinical trial. BMJ 312:148–152
Fagevik Olsen M, Hahn I, Nordgren S, Lonroth H, Lundholm K (1997) Randomized controlled trial of prophylactic chest physiotherapy in major abdominal surgery. Br J Surg 84:1535–1538
Shimada M, Saitoh A, Kano T, Takenaka K, Sugimachi K (1996) The effect of a perioperative steroid pulse on surgical stress in hepatic resection. Int Surg 81:49–51
Matsutani T, Onda M, Sasajima K, Miyashita M (1998) Glucocorticoid attenuates a decrease of antithrombin III following major surgery. J Surg Res 79:158–163
Sato N, Koeda K, Ikeda K, Kimura Y, Aoki K, Iwaya T, Akiyama Y, Ishida K, Saito K, Endo S (2002) Randomized study of the benefits of preoperative corticosteroid administration on the postoperative morbidity and cytokine response in patients undergoing surgery for esophageal cancer. Ann Surg 236:184–190
Luketich JD, Alvelo-Rivera M, Buenaventura PO, Christie NA, McCaughan JS, Litle VR, Schauer PR, Close JM, Fernando HC (2003) Minimally invasive esophagectomy: outcomes in 222 patients. Ann Surg 238:486–495
Taguchi S, Osugi H, Higashino M, Tokuhara T, Takada N, Takemura M, Lee S, Kinoshita H (2003) Comparison of three-field esophagectomy for esophageal cancer incorporating open or thoracoscopic thoracotomy. Surg Endosc 17:1445–1450
Avendano CE, Flume PA, Silvestri GA, King LB, Reed CE (2002) Pulmonary complications after esophagectomy. Ann Thorac Surg 73:922–926
Rizk NP, Bach PB, Schrag D, Bains MS, Turnbull AD, Karpeh M, Brennan MF, Rusch VW (2004) The impact of complications on outcomes after resection for esophageal and gastroesophageal junction carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg 198:42–50
Fujita H, Kakegawa T, Yamana H, Shima I, Toh Y, Tomita Y, Fujii T, Yamasaki K, Higaki K, Noake T, Ishibashi N, Mizutani K (1995) Mortality and morbidity rates, postoperative course, quality of life, and prognosis after extended radical lymphadenectomy for esophageal cancer. Comparison of three-field lymphadenectomy with two-field lymphadenectomy. Ann Surg 222:654–662
Shimada H, Ochiai T, Okazumi S, Matsubara H, Nabeya Y, Miyazawa Y, Arima M, Funami Y, Hayashi H, Takeda A, Gunji Y, Suzuki T, Kobayashi S (2000) Clinical benefits of steroid therapy on surgical stress in patients with esophageal cancer. Surgery 128:791–798
Kohase M, Henriksen-Destefano D, Sehgal PB, Vilcek J (1987) Dexamethasone inhibits feedback regulation of the mitogenic activity of tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, and epidermal growth factor in human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol 132:271–278
Sironi M, Gadina M, Kankova M, Riganti F, Mantovani A, Zandalasini M, Ghezzi P (1992) Differential sensitivity of in vivo TNF and IL-6 production to modulation by anti-inflammatory drugs in mice. Int J Immunopharmac 14:1045–1050
Pasquina P, Tramer MR, Walder B (2003) Prophylactic respiratory physiotherapy after cardiac surgery: systematic review. BMJ 327:1379–1384
Fujita H, Hawahara H, Yamana H, Shirohazu G, Yoshimura Y, Minami T, Negoto Y, Irie H, Shima I, Machi J, Kakegawa T (1988) Mediastinal lymph node dissection procedure during esophageal cancer operation—carefully considered for preserving respiratory function. Jpn J Surg 18:31–34
Fan ST, Lo CM, Liu CL, Lam CM, Yuen WK, Yeung C, Wong J (1999) Hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: toward zero hospital deaths. Ann Surg 229:322–330
Akiyama H, Tsurumaru M, Udagawa H, Kajiyama Y (1994) Radical lymph node dissection for cancer of the thoracic esophagus. Ann Surg 220:364–373
Isono K, Sato H, Nakayama K (1991) Results of a nationwide study on the three-field lymph node dissection of esophageal cancer. Oncology 48:411–420
Kato H, Watanabe H, Tachimori Y, Iizuka T (1991) Evaluation of neck lymph node dissection for thoracic esophageal carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg 51:931–935
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamura, M., Iwahashi, M., Nakamori, M. et al. An analysis of the factors contributing to a reduction in the incidence of pulmonary complications following an esophagectomy for esophageal cancer. Langenbecks Arch Surg 393, 127–133 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-007-0253-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-007-0253-7