Abstract
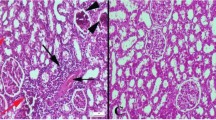
The present study was intended to evaluate hematoprotective and hepato-renal protective effects of Thymus vulgaris against the toxicity induced by thermally oxidized oil. Rabbits were differed into four groups. Group 1, retained as normal control, groups 2–4 received T. vulgaris (2 g/kg ration, thermally oxidized oil (5% of ration), finally T. vulgaris together with thermally oxidized oil respectively. Erythrogram, showed non-significant changes at first month where, thermally oxidized oil group at third month revealed macrocytic hypochromic anemia. Also, a significant leucocytosis, monocytosis, heterophilia, and lymphopenia were perceived. There were a significant excess in malondialdehyde (MDA) level alongside, a significant subside in catalase (CAT) activity. Also the activities of liver enzymes (ALT, AST, and ALP), bilirubin, urea, creatinine, uric acid, triglycerides, cholesterol, and low density lipoprotein (LDL-c) were increased where, there were a significant reduction in serum total proteins, albumin, and high density lipoprotein (HDL-c).These alterations present in lesser level at the end of third month when T. vulgaris added together with the oxidized oil. These changes were correlated to the pathological vagaries. It could be established that using of thermally oxidized sunflower oil caused several toxicological effects on hepatic, renal, and oxidative status. Using of T. vulgaris alleviated the hematotoxicity and hepato-renal toxicity induced by addition of thermally oxidized sunflower oil.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aeschbach R, Loliger J, Scott BC, Murcia A, Butler J, Halliwell B, Aruoma OI (1994) Antioxidant actions of thymol, carvacrol, 6-gingerol, zingerone and hydroxytyrosol. Food Chem Toxicol 32:31–36
Altemimi A, Lakhssassi N, Baharlouei A, Watson DG, Lightfoot DA (2017) Phytochemicals: extraction, isolation, and identification of bioactive compounds from plant extracts. Plants (Basel) 6:42. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants6040042
Ammouche A, Rouaki F, Bitam A, Bellal MM (2002) Effect of ingestion of thermally oxidized sunflower oil on the fatty acid composition and antioxidant enzymes of rat liver and brain in development. Ann Nutr Metab 46:268–275. https://doi.org/10.1159/000066496
Badr MO, Edrees NM, Abdallah AA, El-Deen NA, Neamat-Allah AN, Ismail HT (2011) Anti-tumour effects of Egyptian propolis on Ehrlich ascites carcinoma. Vet Ital 47:341–350
Burenjargal M, Totani N (2009) Cytotoxic compounds generated in heated oil and assimilation of oil in Wistar rats. J Oleo Sci 58:1–7
Chacko C (2011) Repeatedly heated cooking oils alter platelet functions in cholesterol fed Sprague dawley rats. Int J Biol Med Res 2:991–997
Cordatos K (2002) Theory and practice of histological techniques: fifth edition Pathology (Phila), vol 34, p 384. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3025(16)34462-2
Dehghani N, Afsharmanesh M, Salarmoini M, Ebrahimnejad H, Bitaraf A (2018) Effect of pennyroyal, savory and thyme essential oils on Japanese quail physiology. Heliyon 4:e00881–e00881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00881
El-bialy B, Saleh N, Mohamed Abou-Elkhair R (2015) Potential hazards of feeding albino rats on diet containing repeatedly boiled cooking oil: clinicopathological and toxicological studies. Int J Adv Res 3:134–147
El-Murr AI, Abd El Hakim Y, Neamat-Allah ANF, Baeshen M, Ali HA (2019) Immune-protective, antioxidant and relative genes expression impacts of β-glucan against fipronil toxicity in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immun 94:427–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.09.033
El-Nekeety AA, Mohamed SR, Hathout AS, Hassan NS, Aly SE, Abdel-Wahhab MA (2011) Antioxidant properties of oil against aflatoxin-induce oxidative stress in male rats. Toxicon 57:984–991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2011.03.021
Ghidurus M, Turtoi M, Boskou G, Niculita P, Stan V (2010) Nutritional and health aspects related to frying (II). Rom Biotech Lett 15:6467–6472
Goorani S et al (2019a) Hepatoprotective and cytotoxicity properties of aqueous extract of Glycyrrhiza glabra in Wistar rats fed with high-fat diet. Comp Clin Pathol 28:1305–1312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-019-02939-6
Goorani S et al (2019b) The aqueous extract of Allium saralicum R.M. Fritsch effectively treat induced anemia: experimental study on Wistar rats. Orient Pharm Exp Med. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-019-00361-5
Goorani S, Zangeneh MM, Koohi MK, Seydi N, Zangeneh A, Souri N, Hosseini M-S (2019c) Assessment of antioxidant and cutaneous wound healing effects of Falcaria vulgaris aqueous extract in Wistar male rats. Comp Clin Pathol 28:435–445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2866-3
Goorani S et al (2019d) Hepatoprotective potential of aqueous extract of Allium eriophyllum Boiss in high-fat diet-induced fatty liver diseases. Comp Clin Pathol 28:963–969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2853-8
Goorani S, Zhaleh M, Koohi MK, Seydi N, Rashidi K, Zangeneh MM, Zangeneh A (2019e) The therapeutic potential of aqueous extract of Falcaria vulgaris in the treatment of fatty liver disease: a histopathological and biochemical approach. Comp Clin Pathol 28:955–961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2854-7
Hagh-Nazari L, Goodarzi N, Zangeneh MM, Zangeneh A, Tahvilian R, Moradi R (2017) Stereological study of kidney in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice treated with ethanolic extract of Stevia rebaudiana (bitter fraction). Comp Clin Pathol 26:455–463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-016-2398-7
Hashem M, Neamat-Allah AN, Gheith M (2018a) A study on bovine babesiosis and treatment with reference to hematobiochemical and molecular diagnosis. Slov Vet Res 55:165–173. https://doi.org/10.26873/SVR-643-2018
Hashem MA, Mahmoud EA, Farag MFM (2018b) Clinicopathological and immunological effects of using formalized killed vaccine alone or in combination with propolis against pasteurella multocida challenge in rabbits. Slov Vet Res 55:59–71. https://doi.org/10.26873/SVR-631-2018
Hosseini SA, Meimandipour A, Alami F, Mahdavi A, Mohiti-Asli M, Lotfollahian H, Cross D (2013) Effects of ground thyme and probiotic supplements in diets on broiler performance, blood biochemistry and immunological response to sheep red blood cells. Ital J Anim Sci 12:e19. https://doi.org/10.4081/ijas.2013.e19
Hostetter SJ, Andreasen CB (2004) 4 - Anemia A2 - Cowell, Rick L. In: Veterinary clinical pathology secrets. Mosby, Saint Louis, pp 12–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-56053-633-8.50006-1
IBM (2013) IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows 22 edn. Armonk, IBM Corp., NY
Janakat SM, Al-Khateeb MA (2011) Effect of a popular Middle Eastern food (Falafel) on rat liver. Toxicol Environ Chem 93:360–369. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2010.526611
Kaffashi Elahi R (2012) Preventive effects of turmeric (Curcuma longa Linn.) powder on hepatic steatosis in the rats fed with high fat diet. Life Sci J 9:5462–5468
Khodarahmi M, Azadbakht L (2014) The association between different kinds of fat intake and breast cancer risk in women. Int J Prev Med 5:6–15
Lee K-W, Everts H, Kappert HJ, Yeom K-H, Beynen AC (2003) Dietary carvacrol lowers body weight gain but improves feed conversion in female broiler chickens. J Appl Poultry Res 12:394–399. https://doi.org/10.1093/japr/12.4.394
Leong XF, Aishah A, Nor Aini U, Das S, Jaarin K (2008) Heated palm oil causes rise in blood pressure and cardiac changes in heart muscle in experimental rats. Arch Med Res 39:567–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2008.04.009
Lopez-Varela S, Sanchez-Muniz FJ, Cuesta C (1995) Decreased food efficiency ratio, growth retardation and changes in liver fatty acid composition in rats consuming thermally oxidized and polymerized sunflower oil used for frying. Food Chem Toxicol 33:181–189
Ložienė K, Venskutonis PR, Šipailienė A, Labokas J (2007) Radical scavenging and antibacterial properties of the extracts from different Thymus pulegioides L. chemotypes. Food Chem 103:546–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.08.027
Mahmoud EA (2015) Hemato-biochemical and pathological changes on avian influenza in naturally infected domestic ducks in Egypt. Vet World 8:1177–1182. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2015.1177-1182
Mesembe O, Dr Ibanga I, Osim E (2005) The effects of fresh and thermoxidized palm oil diets on some haematological indices in the rat. Niger J Physiol Sci (ISSN: 0794-859X) Vol 19 Num 1-2 19:86–91. https://doi.org/10.4314/njps.v19i1.32641
Mohseni R, Karimi J, Tavilani H, Khodadadi I, Hashemnia M (2019) Carvacrol downregulates lysyl oxidase expression and ameliorates oxidative stress in the liver of rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis. Indian J Clin Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-019-00845-w
Moradi R, Hajialiani M, Salmani S, Almasi M, Zangeneh A, Zangeneh MM (2019) Effect of aqueous extract of Allium saralicum R.M. Fritsch on fatty liver induced by high-fat diet in Wistar rats. Comp Clin Pathol 28:1205–1211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2834-y
Nakatani N (2000) Phenolic antioxidants from herbs and spices. Biofactors 13:141–146
Narasimhamurthy K, Raina PL (1999) Long term feeding effects of heated and fried oils on lipids and lipoproteins in rats. Mol Cell Biochem 195:143–153
Neamat-Allah AN (2015) Immunological, hematological, biochemical, and histopathological studies on cows naturally infected with lumpy skin disease. Vet World 8:1131–1136. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2015.1131-1136
Neamat-Allah AN, Damaty HM (2016) Strangles in Arabian horses in Egypt: clinical, epidemiological, hematological, and biochemical aspects. Vet World 9:820–826. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2016.820-826
Neamat-Allah ANF, Mahmoud EA (2019) Assessing the possible causes of hemolytic anemia associated with lumpy skin disease naturally infected buffaloes. Comp Clin Pathol 28:747–753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-019-02952-9
Neamat-Allah ANF, AeI E-M, Abd El-Hakim Y (2019a) Dietary supplementation with low molecular weight sodium alginate improves growth, haematology, immune reactions and resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in Clarias gariepinus. Aquac Res 50:1547–1556. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.14031
Neamat-Allah ANF, Mahmoud EA, Abd El Hakim Y (2019b) Efficacy of dietary nano-selenium on growth, immune response, antioxidant, transcriptomic profile and resistance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus against Streptococcus iniae infection. Fish Shellfish Immun 94:280–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.09.019
Oarada M, Miyazawa T, Kaneda T (1986) Distribution of 14C after oral administration of [U-14C]labeled methyl linoleate hydroperoxides and their secondary oxidation products in rats. Lipids 21:150–154. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02534437
Oliver SJ (2013) The role of traditional medicine practice in primary health care within aboriginal Australia: a review of the literature. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed 9:46–46. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-4269-9-46
Perumalla Venkata R, Subramanyam R (2016) Evaluation of the deleterious health effects of consumption of repeatedly heated vegetable oil. Toxicol Rep 3:636–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2016.08.003
Prasanna R, Ashraf EA, Essam MA (2017) Chamomile and oregano extracts synergistically exhibit antihyperglycemic, antihyperlipidemic, and renal protective effects in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 95:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2016-0189
Rouaki F, Mazari A, Kanane A, Errahmani MB, Ammouche A (2013) Cardiotoxicity induced by dietary oxidized sunflower oil in rats: pro- and antioxidant effects of alpha-tocopherol. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 83:367–376. https://doi.org/10.1024/0300-9831/a000178
Saleh N, Allam T, Abd El-latif A, Ghazy E (2014) The effects of dietary supplementation of different levels of thyme (Thymus vulgaris) and ginger (Zingiber officinale) essential oils on performance, hematological, biochemical and immunological parameters of broiler chickens. Global Veterinaria 12:736–744
Salem FS, Badr MO, Neamat-Allah AN (2011) Biochemical and pathological studies on the effects of levamisole and chlorambucil on Ehrlich ascites carcinoma-bearing mice. Vet Ital 47:89–95
Shastry CS, Ambalal PN, Himanshu J, Aswathanarayana BJ (2011) Evaluation of effect of reused edible oils on vital organs of Wistar rats. Nitte Univ J Health Sci 1:10–15
Shati AA, Elsaid FG (2009) Effects of water extracts of thyme (Thymus vulgaris) and ginger (Zingiber officinale roscoe) on alcohol abuse. Food Chem 47:1945–1949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2009.05.007
Srivastava S, Singh M, George J, Bhui K, Shukla Y (2010) Genotoxic and carcinogenic risks associated with the consumption of repeatedly boiled sunflower oil. J Agric Food Chem 58:11179–11186. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf102651n
Stockham SL, Scott MA (2013) Fundamentals of veterinary clinical pathology 2nd edition, Kindle Edition edn. Wiley-Blackwell, Hoboken
Sun YX, Liu JC, Liu DY (2011) Phytochemicals and bioactivities of Anemone raddeana Regel: a review. Pharmazie 66:813–821
Tennant BC, Center SA (2008) Chapter 13 - Hepatic function A2 - Kaneko, J. Jerry. In: Harvey JW, Bruss ML (eds) Clinical biochemistry of domestic animals (6th). Academic Press, San Diego, pp 379–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-370491-7.00013-1
Toghyani M, Tohidi M, Gheisari A, Tabeidian S (2010) Performance, immunity, serum biochemical and hematological parameters in broiler chicks fed dietary thyme as alternative for an antibiotic growth promoter. Afr J Biotechnol 9:6819–6825
Totani N, Ojiri Y (2007) Mild ingestion of used frying oil damages hepatic and renal cells in Wistar rats. J Oleo Sci 56:261–267
Tousson E, El-Moghazy M, El-Atrsh E (2011) The possible effect of diets containing Nigella sativa and Thymus vulgaris on blood parameters and some organs structure in rabbit. Toxicol Ind Health 27:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233710381891
Zangeneh MM, Farzaei MH, Goodarzi N, Zangeneh A (2018a) Protection of CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity by Trachyspermum ammi essential oil in mice. Comp Clin Pathol 27:1367–1374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2748-8
Zangeneh MM, Goodarzi N, Zangeneh A, Tahvilian R, Najafi F (2018b) Amelioration of renal structural changes in STZ-induced diabetic mice with ethanolic extract of Allium saralicum R.M. Fritsch Comp Clin Pathol 27:861–867. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2674-9
Zangeneh MM, Zangeneh A, Almasi M, Tahvilian R, Hosseini F, Moradi R (2018c) A comparative study of hepatoprotective effect of Inula britannica L aqueous extract and glibenclamide in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Comp Clin Pathol 27:1649–1657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2789-z
Zangeneh MM et al (2018d) Nephroprotective activity of Alyssum meniocoides Boiss aqueous extract on streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephrotoxicity in male mice. Comp Clin Pathol 27:1147–1154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2712-7
Zangeneh MM, Zangeneh A, Bahrami E, Almasi M, Amiri-Paryan A, Tahvilian R, Moradi R (2018e) Evaluation of hematoprotective and hepatoprotective properties of aqueous extract of Ceterach officinarum DC against streptozotocin-induced hepatic injury in male mice. Comp Clin Pathol 27:1427–1436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2754-x
Zangeneh MM, Zangeneh A, Tahvilian R, Moradi R (2018f) Evaluation of the nephroprotective effect of Glycyrrhiza glabra L aqueous extract on CCl4-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Comp Clin Pathol 27:1119–1126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2707-4
Zangeneh MM, Zangeneh A, Tahvilian R, Moradi R, Tehrani PR (2018g) Preclinical evaluation of hematoprotective and nephroprotective activities of Bellis perennis L aqueous extract on CCl4-induced renal injury in mice. Comp Clin Pathol 27:1557–1566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2773-7
Zangeneh MM, Zangeneh A, Tahvilian R, Moradi R, Zhaleh H, Amiri-Paryan A, Bahrami E (2018h) Hepatoprotective and hematoprotective effects of Falcaria vulgaris aqueous extract against CCl4-induced hepatic injury in mice. Comp Clin Pathol 27:1359–1365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2747-9
Zangeneh MM, Salmani S, Zangeneh A, Khedri R, Zarei MS (2019) Histopathological and biochemical effects of aqueous extract of Tragopogon graminifolius on the liver tissues of Wistar rats fed with high-fat diet. Comp Clin Pathol 28:1197–1203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2828-9
Acknowledgments
Grateful thanks to Prof. Dr. Mustafa A Selim, Department of pathology, Veterinary Medicine at Zagazig University for his effort in reading the histopathology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
None.
Ethical approval
Analysis was managed in accordance with the standards set by Animal Health Research Ethics Training Initiative, Egypt, and experimental protocols were approved by the official animal ethics agency.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdallah, A.A.M., Nasr El-Deen, N.A.M., Neamat-Allah, A.N.F. et al. Evaluation of the hematoprotective and hepato-renal protective effects of Thymus vulgaris aqueous extract on thermally oxidized oil-induced hematotoxicity and hepato-renal toxicity. Comp Clin Pathol 29, 451–461 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-019-03078-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-019-03078-8