Abstract
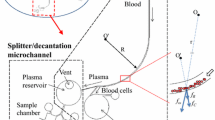
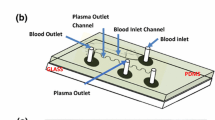
This study presents a compact disk (CD) microfluidic platform for separating human blood plasma from a whole blood sample and then mixing the plasma with a suitable reagent for further analysis purposes. It is shown that the volume of plasma decanted into the plasma reservoir can be precisely controlled through an appropriate control of the disk rotation speed. For example, 0.5 μL of plasma can be deposited in the plasma reservoir by rotating the disk at a speed of 2,600 rpm for 5 s. The performance of three microfluidic CD platforms incorporating square-wave mixing channels with different corner shapes is evaluated both numerically and experimentally. The results show that given the use of a rectangular corner feature and a CD rotation speed of 3,400 rpm, a mixing efficiency of more than 97 % can be obtained within 5 s. The practical feasibility of the proposed platform is demonstrated by performing prothrombin time (PT) tests using whole blood samples acquired from 20 healthy male donors. It is shown that the mean time required to complete the entire PT test (including separation, decanting, mixing and coagulation) is less than 4 min.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn CH, Choi JW, Beaucage G, Nevin JH, Lee JB, Puntambekar A, Lee JY (2004) Disposable smart lab on a chip for point-of-care clinical diagnostics. Proc IEEE 92(1):154–173
Badr IHA, Johnson RD, Madou MJ, Bachas LG (2002) Fluorescent ion-selective optode membranes incorporated onto a centrifugal microfluidics platform. Anal Chem 74(21):5569–5575
Chen X, Cui DF, Liu CC, Li H (2007) Microfluidic chip for blood cell separation and collection based on crossflow filtration. Sens Actuator B-Chem 130:216–221
Chin CD, Linder V, Sia SK (2007) Lab-on-a-chip devices for global health: past studies and future opportunities. Lab Chip 7(1):41–57
Cho YK, Lee JG, Park JM, Lee BS, Lee YS, Ko C (2007) One-step pathogen specific DNA extraction from whole blood on a centrifugal microfluidic device. Lab Chip 7:565–573
Ducree J, Haeberle S, Lutz S, Pausch S, von Stetten F, Zengerle R (2007) The centrifugal microfluidic bio-disk platform. J Micromech Microeng 17(7):S103–S115
Ducrée J, Haeberle S, Brenner T, Glatzel T, Zengerle R (2005) Patterning of flow and mixing in rotating radial microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 2:97–105
Ducrée J, Brenner T, Haeberle S, Glatzel T, Zengerle R (2006) Multilamination of flows in planar networks of rotating microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 2:78–84
Figeys D, Pinto D (2000) Lab-on-a-chip: a revolution in biological and medical sciences. Anal Chem 72(9):330a–335a
Fung YC (1973) Stochastic flow in capillary blood vessels. Microvasc Res 5(1):34–48
Gorkin R, Park J, Siegrist J, Amasia M, Lee BS, Park JM, Kim J, Kim H, Madou M, Cho YK (2010) Centrifugal microfluidics for biomedical applications. Lab Chip 10(14):1758–1773
Grumann M, Geipel A, Riegger L, Zengerle R, Ducrée J (2005) Batch-mode mixing on centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Lab Chip 5(5):560–565
Haeberle S, Zengerle R (2007) Microfluidic platforms for lab-on-a-chip applications. Lab Chip 7(9):1094–1110
Haeberle S, Brenner T, Zengerle R, Ducr´ee J (2006) Centrifugal extraction of plasma from whole blood on a rotating disk. Lab Chip 6:776–781
Hossian S, Ansari MA, Kim KY (2009) Evaluation of the mixing performance of three passive micromixers. Chem Eng J 150:492–501
Huang Y, Joo S, Duhon M, Heller M, Wallace B, Xu X (2002) Dielectrophoretic cell separation and gene expression profiling on microelectronic chip arrays. Anal Chem 74:3362–3371
Huang CT, Li PN, Pai CY, Leu TS, Jen CP (2010) Design and simulation of a microfluidic blood-plasma separation chip using microchannel structures. Sep Sci Technol 45:42–49
Inglis DW, Riehn R, Sturm JC, Austin RH (2006) Microfluidic high gradient magnetic cell separation. J Appl Phys 99:08K101
Kersaudy-Kerhoas M, Dhariwal R, Desmulliez MPY, Jouvet L (2010) Hydrodynamic blood plasma separation in microfluidic channels. Microfluid Nanofluid 8:105–114
Kong MCR, Salin ED (2012) Micromixing by pneumatic agitation on continually rotating centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Microfluid Nanofluid 13:519–525
Kuo JN, Jiang LR (2014) Design optimization of micromixer with square-wave microchannel on compact disk microfluidic platform. Microsyst Technol 20(1):91–99
Kuo JN, Li BS (2014) Lab-on-CD microfluidic platform for rapid separation and mixing of plasma from whole blood. Biomed Microdevices 16:549–558
La M, Park SJ, Kim HW, Park JJ, Ahn KT, Ryew SM, Kim DS (2013) A centrifugal force-based serpentine micromixer (CSM) on a plastic lab-on-a-disk for biochemical assays. Microfluid Nanofluid 15:87–98
Li C, Dong X, Qin J, Lin B (2009) Rapid nanoliter DNA hybridization based on reciprocating flow on a compact disk microfluidic device. Anal Chim Acta 640:93–99
Lu LH, Ryu KS, Liu C (2002) A magnetic microstirrer and array for microfluidic mixing. J Microelectromech Syst 11(5):462–469
Lu C, Xie Y, Yang Y, Cheng MMC, Koh CG, Bai Y, Lee LJ (2007) New valve and bonding designs for microfluidic biochips containing proteins. Anal Chem 79:994–1001
Madou M, Zoval J, Jia G, Kido H, Kim J, Kim N (2006) Lab on a CD. Ann Rev Biomed Eng 8:601–628
McDonald JC, Chabinyc ML, Metallo S, Anderson JR, Stroock AD, Whitesides GM (2002) Prototyping of microfluidic devices in poly (dimethylsiloxane) using solid-object printing. Anal Chem 74:1537–1545
Nguyen NT, Wu Z (2005) Micromixers-a review. J Micromech Microeng 15:R1–R16
Petersson F, Nilsson A, Jönsson H, Laurell T (2005) Carrier medium exchange through ultrasonic particle switching in microfluidic channels. Anal Chem 77:1216–1221
Shih CH, Lu CH, Yuan WL, Chiang WL, Lin CH (2011) Supernatant decanting on a centrifugal platform. Biomicrofluidics 5:013414
Shih CH, Lu CH, Wu JH, Lin CH, Wang JM, Lin CY (2012) Prothrombin time tests on a microfluidic disc analyzer. Sens Actuator B-Chem 161:1184–1190
Shim JS, Browne AW, Ahn CH (2010) An on-chip whole blood/plasma separator with bead-packed microchannel on COC polymer. Biomed Microdevices 12:949–957
Smistrup K, Hansen O, Bruus H, Hansen MF (2005) Magnetic separation in microfluidic systems using microfabricated electromagnets-experiments and simulations. J Magn Magn Mater 293:597–604
Srinivasan V, Pamula VK, Fair RB (2004) An integrated digital microfluidic lab-on-a-chip for clinical diagnostics on human physiological fluids. Lab Chip 4(4):310–315
Steigert J, Brenner T, Grumann M, Riegger L, Lutz S, Zengerle R, Ducree J (2007) Integrated siphon-based metering and sedimentation of whole blood on a hydrophilic lab-on-a-disk. Biomed Microdevices 9:675–679
Toner M, Irimia D (2005) Blood-on-a-chip. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 7:77–103
Van Delinder V, Groisman A (2006) Separation of plasma from whole human blood in a continuous cross-flow in a molded microfluidic device. Anal Chem 78:3765–3771
Yager P, Edwards T, Fu E, Helton K, Nelson K, Tam MR, Weigl BH (2006) Review Article Microfluidic diagnostic technologies for global public health. Nature 442:412–418
Yang SY, Lin JL, Lee GB (2009) A vortex-type micromixer utilizing pneumatically driven membranes. J Micromech Microeng 19(3):035020
Zhang J, Guo Q, Liu M, Yang J (2008) A lab-on-CD prototype for high-speed blood separation. J Micromech Microeng 18:125025
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided to this study by the National Science Council of Taiwan under Grant No. NSC 101-2221-E-150-036. In addition, the access provided to the fabrication equipment used in the present study by the Common Lab for Micro/Nano Science and Technology of National Formosa University is also greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuo, JN., Chen, XF. Decanting and mixing of supernatant human blood plasma on centrifugal microfluidic platform. Microsyst Technol 22, 861–869 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2458-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2458-y