Abstract
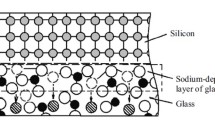
In this paper a novel process to bond and, at the same time, to electrically connect a silicon wafer to a glass wafer is presented. It consists of a low temperature anodic bonding process between silicon and glass by using a glass wafer with etched channels in order to contain metal tracks. The glass-to-silicon anodic bonding process at low temperatures (not exceeding 300°C) assures a strong mechanical link (Berthold et al. in Transducers 1999, June:7–10, 1999). The electrical contacts between the metal pads on the backside of a silicon wafer and the metal pads on the glass wafer are achieved by sintering and diffusion of metals due to a kind of thermo compression bonding. This bonding method permits a high vertical control due to a well-controlled etching of the cavity depth and to the thickness precision of both metallization (pads on silicon wafers and metal tracks on glass wafer). This IC-processing compatible approach opens up the way to a new electrical connection concept keeping, at the same time, a strong mechanical bond between glass and silicon wafers for an easier fabrication of a more complex micro-system.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berthold A, Nicola L, Sarro PM, Vellekoop MJ (1999) A novel technological process for glass-to-glass anodic bonding, Transducers 1999, June 7–10
Raley NF, Davidson JC, Balch JW (1995) Examination of glass-silicon and glass-glass bonding techniques for microfluidic systems. Proc of SPIE 2639:40–45
Wang HY, Foote RS, Jacobson SC, Schneibel JH, Ramsey JM (1997) Low temperature bonding for microfabrication of chemical analysis devices. Sensor Actuator B 45:199–207
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank A. Gaillard and N.T. Tran for their technical support, Advanced Technology Centre of BAE SYSTEMS (Bristol, UK) for the fabrication of flow sensors and the European Community for supporting this research in the AEROMEMS II project. The AEROMEMS II project is a collaboration between BAE SYSTEMS, Dassault, Airbus Deutschland GmbH, EADS-Military, Snecma, ONERA, DLR, LPMO, National Technical University of Athens, University of Manchester, LML, University of Warwick, Technical University of Berlin, University of Cranfield and Auxitrol.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brida, S., Metivet, S., Petit, D. et al. Mechanical and electrical bonding between silicon wafer and glass wafer with etched channels containing metal tracks. Microsyst Technol 12, 59–62 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-005-0004-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-005-0004-z