Abstract
Purpose
This study was undertaken to examine the effect of gabapentin for preventing hyperalgesia induced by morphine and fentanyl withdrawal in rats.
Methods
To induce hyperalgesia, Sprague Dawley (SD) rats were subcutaneously injected with fentanyl four times at 15-min intervals (60 μg/kg per injection), resulting in total dose of 240 μg/kg over 1 h, and morphine 10 mg/kg twice daily for 7 days. The effect of gabapentin was detected with behavioral tail-flick and paw-withdrawal tests.
Results
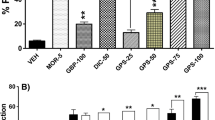
Drug termination produced significant decrease in antinociception thresholds (P < 0.05 vs. saline group), indicating that the rats became sensitive to thermal stimuli. In rats that received combined treatment with fentanyl/morphine and gabapentin (25/50 mg/kg), results demonstrated that there were no significant decreases in antinociception thresholds (vs. saline group) after opioid withdrawal. Gabapentin (50 mg/kg) could also prevent morphine tolerance. The 50% effective dose (ED50) value was 12.5 mg/kg in tail-flick and 13.6 mg/kg in paw-withdrawal tests.
Conclusions
The study showed that gabapentin can significantly prevented opioid-induced hyperalgesia (OIH) induced caused by fentanyl and morphine, suggesting a role for the addition of gabapentin in the perioperative period and during chronic pain treatment as an effective drug to prevent OIH.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angst MS, Clark JD. Opioid-induced hyperalgesia: a qualitative systematic review. Anesthesiology. 2006;104:570–87.
Guntz E, Talla G, Roman A, Dumont H, Segers B, Sosnowski M. Opioid-induced hyperalgesia. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2007;24:205–7.
Li X, Angst MS, Clark JD. A murine model of opioid-induced hyperalgesia. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2001;86:56–62.
Okon TR, George ML. Fentanyl-induced neurotoxicity and paradoxic pain. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2008;35:327–33.
Chia YY, Liu K, Wang JJ, Kuo MC, Ho ST. Intraoperative high dose fentanyl induces postoperative fentanyl tolerance. Can J Anaesth. 1999;46:872–5.
Célèrier E, Rivat C, Jun Y, Laulin JP, Larcher A, Reynier P, Simonnet G. Long-lasting hyperalgesia induced by fentanyl in rats: preventive effect of ketamine. Anesthesiology. 2000;92:465–72.
Waxman AR, Arout C, Caldwell M, Dahan A, Kest B. Acute and chronic fentanyl administration causes hyperalgesia independently of opioid receptor activity in mice. Neurosci Lett. 2009;462:68–72.
Mao J, Price DD, Mayer DJ. Mechanisms of hyperalgesia and morphine tolerance: a current view of their possible interactions. Pain. 1995;62:259–74.
Mayer DJ, Mao J, Holt J, Price DD. Cellular mecha–nisms of neuropathic pain, morphine tolerance, and their interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:7731–6.
Field MJ, Holloman EF, McCleary S, Hughes J, Singh L. Evaluation of gabapentin and S-(+)-3-isobutylgaba in a rat model of postoperative pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997;282:1242–6.
Ross JR, Goller K, Hardy J, Riley J, Broadley K, A’hern R, Williams J. Gabapentin is effective in the treatment of cancer-related neuropathic pain: a prospective, open label study. J Palliat Med. 2005;8:1118–26.
Baillie JK, Power I. The mechanism of action of gabapentin inneuropathic pain. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2006;7:33–9.
Gee NS, Brown JP, Dissanayake VU, Offord J, Thurlow R, Woodruff GN. The novel anticonvulsant drug, gabapentin (Neurontin), binds to the alpha2delta subunit of a calcium channel. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:5768–76.
Dirks J, Fredensborg BB, Christensen D, Fomsgaard JS, Flyger H, Dahl JB. A randomized study of the effects of single-dose gabapentin versus placebo on postoperative pain and morphine consumption after mastectomy. Anesthesiology. 2002;97:560–4.
Van Elstraete AC, Sitbon P, Mazoit JX, Benhamou D. Gabapentin prevents delayed and long-lasting hyperalgesia induced by fentanyl in rats. Anesthesiology. 2008;108:484–94.
Raghavendra V, Tanga FY, DeLeo JA. Attenuation of morphine tolerance, withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia, and associated spinal inflammatory immune responses by propentofylline in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29:327–34.
Wong CS, Hsu MM, Chou R, Chou YY, Tung CS. Intrathecal cyclooxygenase inhibitor administration attenuates morphine antinociceptive tolerance in rats. Br J Anaesth. 2000;85:747–51.
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J. A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain. 1988;32:77–88.
Rode F, Broløs T, Blackburn-Munro G, Bjerrum OJ. Venlafaxine compromises the antinociceptive actions of gabapentin in rat models of neuropathic and persistent pain. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2006;187:364–75.
LaBuda CJ, Little PJ. Pharmacological evaluation of the selective spinal nerve ligation model of neuropathic pain in the rat. J Neurosci Methods. 2005;144:175–81.
Goa KL, Sorkin EM. Gabapentin: a review of its pharmacological properties and clinical potential in epilepsy. Drugs. 1993;46:409–27.
Shy M, Chakrabarti S, Gintzler AR. Plasticity of adenylyl cyclase-related signaling sequelae after long-term morphine treatment. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;73:868–79.
Galeotti N, Stefano GB, Guarna M, Bianchi E, Ghelardini C. Signaling pathway of morphine induced acute thermal hyperalgesia in mice. Pain. 2006;123:294–305.
Mao J, Price DD, Phillips LL, Lu J, Mayer DJ. Increases in protein kinase C gamma immunoreactivity in the spinal cord dorsal horn of rats with painful mononeuropathy. Neurosci Lett. 1995;198:75–8.
Van Elstraete AC, Sitbon P, Mazoit JX, Conti M, Benhamou D. Protective effect of prior administration of magnesium on delayed hyperalgesia induced by fentanyl in rats. Can J Anaesth. 2006;53:1180–5.
Yoshikawa M, Nakayama H, Ueno S, Hirano M, Hatanaka H, Furuya H. Chronic fentanyl treatments induce the up-regulation of μ opioid receptor mRNA in rat pheochromocytoma cells. Brain Res. 2000;859:217–23.
Celerier E, Laulin JP, Corcuff JB, Le Moal M, Simonnet G. Progressive enhancement of delayed hyperalgesia induced by repeated heroin administration: a sensitization process. J Neurosci. 2001;21:4074–80.
Maneuf YP, McKnight AT. Block by gabapentin of the facilitation of glutamate release from rat trigeminal nucleus following activation of protein kinase C or adenylyl cyclase. Br J Pharmacol. 2001;134:237–40.
Shimoyama M, Shimoyama N, Hori Y. Gabapentin affects glutamatergic excitatory neurotransmission in the rat dorsal horn. Pain. 2000;85:405–14.
Maneuf YP, McKnight AT. Block by gabapentin of the facilitation of glutamate release from rat trigeminal nucleus following activation of protein kinase C or adenylyl cyclase. Br J Pharmacol. 2001;134:237–40.
Singh L, Field MJ, Ferris P, Hunter JC, Oles RJ, Williams RG, Woodruff GN. The antiepileptic agent gabapentin (Neurontin) possesses anxiolytic-like and antinociceptive actions that are reversed by D-serine. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 1996;127:1–9.
Partridge BJ, Chaplan SR, Sakamoto E, Yaksh TL. Characterization of the effects of gabapentin and 3-isobutyl-gammaaminobutyric acid on substance P-induced thermal hyperalgesia. Anesthesiology. 1998;88:196–205.
Eckhardt K, Ammon S, Hofmann U, Riebe A, Gugeler N, Mikus G. Gabapentin enhances the analgesic effect of morphine in healthy volunteers. Anesth Analg. 2000;91:185–91.
Matthews EA, Dickenson AH. A combination of gabapentin and morphine mediates enhanced inhibitory effects on dorsal horn neuronal responses in a rat model of neuropathy. Anesthesiology. 2002;96:633–40.
De la O-Arciniega M, Díaz-Reval MI, Cortés-Arroyo AR, Domínguez-Ramírez AM, López-Muñoz FJ. Anti-nociceptive synergism of morphine and gabapentin in neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2009;92:457–64.
Hansen C, Gilron I, Hong M. The effects of intrathecal gabapentin on spinal morphine tolerance in the rat tail-flick and paw pressure tests. Anesth Analg. 2004;99:1180–4.
Lin JA, Lee MS, Wu CT, Yeh CC, Lin SL, Wen ZH, Wong CS. Attenuation of morphine tolerance by intrathecal gabapentin is associated with suppression of morphine-evoked excitatory amino acid release in the rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 2005;1054:167–73.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Mr. Wang-Di and Ms. Wu-Jinjin for the behavioral work. The author also thanks Zhao-Wei and Hu Shan-shan for their technical assistance during this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, X., Wei, W. Role of gabapentin in preventing fentanyl- and morphine-withdrawal-induced hyperalgesia in rats. J Anesth 26, 236–241 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-011-1272-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-011-1272-7