Abstract
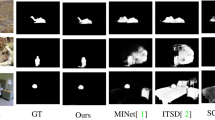
In challenging scenarios (e.g., small objects and cluttered backgrounds), most existing algorithms suffer from inconsistent results with human visual attention. Since fixation prediction can better model the human visual attention mechanism and has a strong correlation with salient objects. Inspired by this, we proposed a fixation guidance network (FGNet) for salient object detection, which innovatively used fixation prediction to guide both salient object detection and edge detection. Firstly, a multi-branch network structure was designed to achieve multi-task detection. Each branch unit significantly learned the extracted features to accomplish the correct prediction. Secondly, given the strong correlation between the fixation and salient objects, a fixation guidance module was employed to guide salient object detection and edge detection for obtaining more accurate detection results. Finally, to full use the complementary relationship between salient features and edge features, we proposed a multi-resolution feature interaction module to achieve mutual optimization within the same feature and between the different features for suppressing noise and enhancing their representations. The experimental results show that our proposed method performed better in challenging scenes and outperformed existing state-of-the-art algorithms in several metrics on four public benchmark datasets.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support this findings of this study are openly available in the following public domain resources: HKU-IS: [29] https://i.cs.hku.hk/~gbli/deep_saliency.html; PASCAL-S [44]: https://academictorrents.com/details/6c49defd6f0e417c039637475cde638d1363037e; DUTS [47]: http://saliencydetection.net/duts/; DUT-OMRON [48]: http://saliencydetection.net/dut-omron/; ECSSD [49]: http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/leojia/projects/hsaliency/.
References
Borji A, Cheng MM, Hou Q, Jiang H, Li J (2014) Salient object detection: a survey. Eprint Arxiv 16(7):3118
Liu N, Han J, Yang M-H (2018) PiCANet: Learning pixel-wise contextual attention for saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 3089–3098
Cheng M-M, Mitra NJ, Huang X, Torr PH, Hu S-M (2014) Global contrast based salient region detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(3):569–582
Luo Z, Mishra A, Achkar A, Eichel J, Li S, Jodoin P (2017) Non-local deep features for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 6593–6601
Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E (1998) A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 20(11):1254–1259
Liu T, Yuan Z, Sun J, Wang J, Zheng N, Tang X, Shum H-Y (2010) Learning to detect a salient object. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33(2):353–367
Achanta R, Estrada F, Wils P, Süsstrunk S (2008) Salient region detection and segmentation. In: Computer vision systems: 6th international conference, ICVS 2008 Santorini, Greece, May 12–15, 2008 Proceedings 6, pp 66–75
Lecun Y, Bottou L (1998) Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc IEEE 86(11):2278–2324
He S, Lau RWH, Liu W, Huang Z, Yang Q (2015) SuperCNN: A superpixelwise convolutional neural network for salient object detection. Int J Comput Vis. 115(3):330–344
Lee G, Tai Y-W, Kim J (2016) Deep saliency with encoded low level distance map and high level features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 660–668
Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T (2015) Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(4):640–651
Chen S, Tan X, Wang B, Hu X (2018) Reverse attention for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 234–250
Guan W, Wang T, Qi J, Zhang L, Lu H (2019) Edge-aware convolution neural network based salient object detection. IEEE Signal Process Lett 26(1):114–118
Jiang H, Wang J, Yuan Z, Wu Y, Zheng N, Li S (2013) Salient object detection: a discriminative regional feature integration approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 2083–2090
Niu Y, Geng Y, Li X, Liu F (2012) Leveraging stereopsis for saliency analysis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 454–461
Borji A, Cheng M-M, Jiang H, Li J (2015) Salient object detection: a benchmark. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5706–5722
Chen X, Zheng A, Li J, Lu F (2017) Look, perceive and segment: finding the salient objects in images via two-stream fixation-semantic CNNs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 1050–1058
Kruthiventi SS, Gudisa V, Dholakiya JH, Venkatesh Babu R (2016) Saliency unified: a deep architecture for simultaneous eye fixation prediction and salient object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 5781–5790
Wang W, Shen J, Dong X, Borji A, Yang R (2019) Inferring salient objects from human fixations. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42(8):1913–1927
Zhang M, Liu T, Piao Y, Yao S, Lu H (2021) Auto-msfnet: search multi-scale fusion network for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM international conference on multimedia, pp 1–10
Wu Z, Su L, Huang Q (2019) Stacked cross refinement network for edge-aware salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 7264–7273
Liu N, Han J, Zhang D, Wen S, Liu T (2015) Predicting eye fixations using convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 362–370
Wang W, Shen J (2018) Deep visual attention prediction. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(5):2368–2378
Kruthiventi SSS, Ayush K, Venkatesh Babu R (2017) Deepfix: A fully convolutional neural network for predicting human eye fixations. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(9):4446–4456
Treisman A, Gelade G (1980) A feature-integration theory of attention. Cogn Psychol 12(1):97–136
Koch C, Ullman S (1987) Shifts in selective visual attention: towards the underlying neural circuitry. Hum Neurobiol 4(4):219–227
Oliva A, Torralba A, Castelhano MS, Henderson JM (2003) Top-down control of visual attention in object detection. In: Proceedings 2003 international conference on image processing (Cat. No. 03CH37429), vol 1, pp 253–256
Bruce NDB, Tsotsos JK (2005) Saliency based on information maximization. In: International conference on neural information processing systems, vol 18
Li G, Yu Y (2015) Visual saliency based on multiscale deep features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 5455–5463
Wang L, Wang L, Lu H, Zhang P, Ruan X (2016) Saliency detection with recurrent fully convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 825–841
Liu N, Han J (2016) Dhsnet: Deep hierarchical saliency network for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 678–686
Pang Y, Zhao X, Zhang L, Lu H (2020) Multi-scale interactive network for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 9413–9422
Kroner A, Senden M, Driessens K, Goebel R (2020) Contextual encoder-decoder network for visual saliency prediction. Neural Netw 129:261–270
Zhao J-X, Liu J-J, Fan D-P, Cao Y, Yang J, Cheng M-M (2019) Egnet: Edge guidance network for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 8779–8788
Zhou H, Xie X, Lai J-H, Chen Z, Yang L (2020) Interactive two-stream decoder for accurate and fast saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 9141–9150
Wang W, Zhao S, Shen J, Hoi SC, Borji A (2019) Salient object detection with pyramid attention and salient edges. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 1448–1457
Yuan J, Wei J, Wattanachote K, Zeng K, Luo X, Xu Q, Gong Y (2022) Attention-based bi-directional refinement network for salient object detection. Appl Intell 52(12):14349–14361
Wang Z, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Wang Z, Coleman S, Kerr D (2022) TF-SOD: a novel transformer framework for salient object detection. Neural Comput Appl 34(14):11789–11806
Zhang L, Wu J, Wang T, Borji A, Wei G, Lu H (2020) A multistage refinement network for salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:3534–3545
Chen Z, Xu Q, Cong R, Huang Q (2020) Global context-aware progressive aggregation network for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol 34, pp 10599–10606
Hou Q, Cheng M-M, Hu X, Borji A, Tu Z, Torr PH (2017) Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 3203–3212
Li Z, Lang C, Chen Y, Liew J, Feng J (2019) Deep reasoning with multi-scale context for salient object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:1901.08362
Li G, Yu Y (2016) Deep contrast learning for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 478–487
Li Y, Hou X, Koch C, Rehg JM, Yuille AL (2014) The secrets of salient object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 280–287
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 770–778
Wu Z, Su L, Huang Q (2019) Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 3907–3916
Wang L, Lu H, Wang Y, Feng M, Wang D, Yin B, Ruan X (2017) Learning to detect salient objects with image-level supervision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 136–145
Judd T, Ehinger K, Durand F, Torralba A (2010) Learning to predict where humans look. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 2106–2113
Yan Q, Xu L, Shi J, Jia J (2013) Hierarchical saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 1155–1162
Borji A, Itti L (2012) State-of-the-art in visual attention modeling. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(1):185–207
Borji A, Itti L (2012) Exploiting local and global patch rarities for saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 478–485
Sprague N, Ballard D (2003) Eye movements for reward maximization. Neural Inf Process Syst 16:1467–1474
Liu N, Han J, Liu T, Li X (2016) Learning to predict eye fixations via multiresolution convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(2):392–404
Pan J, Sayrol E, Giro-i-Nieto X, McGuinness K, O’Connor NE (2016) Shallow and deep convolutional networks for saliency prediction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 598–606
Wang W, Lai Q, Fu H, Shen J, Ling H, Yang R (2021) Salient object detection in the deep learning era: an in-depth survey. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 44(6):3239–3259
Wang T, Zhang L, Wang S, Lu H, Yang G, Ruan X, Borji A (2018) Detect globally, refine locally: a novel approach to saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 3127–3135
Zhang L, Dai J, Lu H, He Y, Wang G (2018) A bi-directional message passing model for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 1741–1750
Wei J, Wang S, Wu Z, Su C, Huang Q, Tian Q (2020) Label decoupling framework for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 13025–13034
Wei J, Wang S, Huang Q (2020) F\(^3\)net: Fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, vol 34, pp 12321–12328
Chen S, Tan X, Wang B, Lu H, Hu X, Fu Y (2020) Reverse attention-based residual network for salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:3763–3776
Feng M, Lu H, Yu Y (2020) Residual learning for salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:4696–4708
Liu N, Zhang N, Wan K, Shao L, Han J (2021) Visual saliency transformer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 4722–4732
Xu B, Liang H, Liang R, Chen P (2021) Locate globally, segment locally: a progressive architecture with knowledge review network for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on artificial intelligence, vol 35, pp 3004–3012
Wu Z, Li S, Chen C, Hao A, Qin H (2022) Recursive multi-model complementary deep fusion for robust salient object detection via parallel sub-networks. Pattern Recogn 121:108212
Wu Y-H, Liu Y, Zhang L, Cheng M-M, Ren B (2022) EDN: Salient object detection via extremely-downsampled network. IEEE Trans Image Process 31:3125–3136
Zhuge M, Fan D-P, Liu N, Zhang D, Xu D, Shao L (2023) Salient object detection via integrity learning. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 45(3):3738–3752
Zhang X, Zhou X, Lin M, Sun J (2018) Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 6848–6856
Howard A, Sandler M, Chu G, Chen L-C, Chen B, Tan M, Wang W, Zhu Y, Pang R, Vasudevan V, et al (2019) Searching for mobilenetv3. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp 1314–1324
Fan D-P, Zhang J, Xu G, Cheng M-M, Shao L (2022) Salient objects in clutter. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 45(2):2344–2366
Jiang M, Huang S, Duan J, Zhao Q (2015) Salicon: Saliency in context. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp 1072–1080
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Grant No. 2019A1515011078) and National Science Foundation Grant of China (Grant No. 61772149). The corresponding author is Yongyi Gong.
Funding
This work was funded by Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Grant No. 2019A1515011078) and National Science Foundation Grant of China (Grant No. 61772149).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, J., Xiao, L., Wattanachote, K. et al. FGNet: Fixation guidance network for salient object detection. Neural Comput & Applic 36, 569–584 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-09028-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-023-09028-4