Abstract
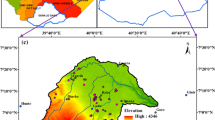
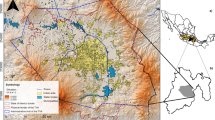
The long-term effect of non-point source pollution on groundwater from agricultural practices is a major concern globally. Non-point source pollutants such as nitrate that occurs through fertilizers and animal waste eventually make their way into the aquifer by infiltrating soil. The goal of this study is to develop an approach for characterization of nitrate concentrations at potential source locations under conditions of geologic uncertainty. A Bayesian framework using the Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) approach is developed to estimate posterior probability distributions of non-point sources by incorporating nitrate concentration data as well as geologic uncertainties. The proposed approach is tested using hypothetical contamination scenarios and then validated using an application case study in North Carolina. Uncertainty existing in geologic formation (i.e., heterogeneous hydraulic conductivity field) is treated as prior and used in evaluating the likelihood function that measures the match between observed and simulated concentrations. The likelihood function computation involves a numerical model that simulates nitrate transport in groundwater from non-point agricultural sources and predicts nitrate concentrations at observation wells. Effectiveness of the MCMC approach is evaluated through a convergence analysis. Comparison among different sampling algorithms is carried out with respect to MCMC convergence diagnostics and making inference. The Bayesian inference analysis methodology developed in this research will help decision makers and water managers to identify potential areas for source containment and decide if further sampling is required.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alabert F (1987) Stochastic imaging of spatial distributions using hard and soft information: unpublished MSc thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, p 197
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration: guidelines for computing crop water requirements. Irrigation and drainage paper No. 56, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy
Allison GB (1988) A review of some of the physical, chemical and isotopic techniques available for estimating groundwater recharge. In: Simmers J (ed) Estimation of natural groundwater recharge. D Reidel, Boston, pp 49–72
Amirabdollahian M, Datta B (2015) Reliability evaluation of groundwater contamination source characterization under uncertain flow field. Int J Environ Sci Dev 6(7):512–518
Aucott WR (1996) Hydrology of the southeastern coastal plain aquifer system in South Carolina and parts of Georgia and North Carolina: U.S. Geological survey professional paper. 1410-E, vii, p 83
Bayes T, Price R (1763) An Essay towards solving a problem in the Chance of. By the late Rev. Mr. Bayes, communicated by Mr. Price, in a letter to John Canton, A. M. F. R. S. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 53(0): 370 418. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstl.1763.0053
Birkinshaw SJ, Ewen J (2000) Nitrogen transformation component for SHETRAN catchment nitrate transport modelling. J Hydrol 230:1–17
Brookes SP, Gelman A (1998) General methods for monitoring convergence of iterative simulations. J Comput Graph Stat 7(4):434–455
Campbell BG, Coes AL, eds, (2010) Groundwater availability in the Atlantic Coastal Plain of North and South Carolina: U.S. Geological survey professional paper 1773, 241 p 7
Carey MA, Lloyd JW (1985) Modelling non-point sources of nitrate pollution of groundwater in the great ouse chalk, UK. J Hydrol 78:83–106
Carle SF, Fogg GE (1996) Transition probability-based indicator geostatistics. Math Geol 28(4):453–476
Carlin BP, Louis TA (2009) Bayesian methods for data analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Carrera J, Alcolea A, Medina A, Hidalgo J, Slooten LJ (2005) Inverse problem in hydrogeology. Hydrogeol J 13(1):206–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-004-0404-7
Chiles JP, Delfiner P (1999) Geostatistics modeling spatial uncertainty. Wiley, New York. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470316993
Christenson E, Serre M (2015) Using remote sensing to calculate plant available nitrogen needed by crops on swine factory farm sprayfields in North Carolina. In: Proceedings of SPIE—the international society for optical engineering. (Vol. 9637). [963704] SPIE. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2195434
Comunian A, Renard P, Strauhaar J, Bayer P (2011) Three-dimensional high resolution fluvio-glacial aquifer analog-part2: geostatistical modeling. J Hydrol 405:10–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.03.037
de Marsily G, Delay F, Gonçalvès J, Renard Ph, Teles V, Violette S (2005) Dealing with spatial heterogeneity. Hydrogeol J13:161–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-004-0432-3
Deutsch CV, Journel AG (1998) GSLIB: geostatistical software library and user’s guide, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Gamerman D, Lopes HF (2006) Markov Chain Monte Carlo: Stochastic Simulation for Bayesian Inference, vol. xvii, 2nd ed., 323 pp., Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, Fla
Gayer CJ (2011) Introduction to Markov Chain Monte Carlo: Handbook of Markov Chain Monte Carlo, May 2011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1201/b10905-2
Gelfand AE, Smith AFM (1990) Sampling-based approaches to calculating marginal densities. J Am Stat Assoc 85:398–409
Gelman A, Hill J (2007) Data analysis using regression and multi-level/hierarchical models. Cambridge University Press, New York
Gelman A, Rubin DB (1992) Inference from iterative simulation using multiple sequences (with discussion). Stat Sci 7:457–511
Gelman A, Carlin Jb, Stern Hs, Rubin Db (1995) Bayesian data analysis. In: Chatfield C, Zidek Jv (eds) Texts in statistical science series. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Gorelick SM, Evans B, Remson I (1983) Identifying sources of groundwater pollution: an optimization approach. Water Resour Res 19(3):779–790. https://doi.org/10.1029/wr019i003p00779
Hamra G, MacLehose R, Richardson D (2013) Markov chain Monte Carlo: an introduction for epidemiologists. Int J Epidemiol 42(2):627–634. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyt043
Hastings WK (1970) Monte Carlo sampling methods using Markov chains and their applications. Biometrika 57:97–109
Hazart A, Giovannelli JF, Dubost S, Chatellier L (2007) Contaminant source estimation in a two-layers porous environment using a Bayesian approach. In: IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium
Huang CL, Hu B, Li X, Ye M (2011) Using data assimilation method to calibrate a heterogeneous conductivity field and improve solute transport prediction with an unknown contamination source. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 23(8):1155–1167
Jiang S, Fan J, Xia X, Li X, Zhang R (2018) An effective Kalman filter-based method for groundwater pollution source identification and plume morphology characterization. J Water 10(8):1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10081063
Jin X, Mahinthakumar G, Zechman E, Ranjithan RS (2009) A genetic algorithm-based procedure for 3D source identification at the Borden emplacement site. J Hydro inf 11(1):51–64
Journel AG, Huijbregts CJ (1978) Mining geostatistics. Academic Press, London
Jyrkama MI, Sykes JF, Normani SD (2002) Recharge estimation for transient ground water modeling. Ground Water 40(6):638–648
Kéry M, Gardner B, Monnerat C (2010) Predicting species distributions from checklist data using site-occupancy models. J Biogeogr 37:1851–1862. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2699.2010.02345.x
Laftouhi NE, Vanclooster M, Jalal M, Witam O, Aboufirassi M, Bahir M, Persoons E´ (2003) Groundwater nitrate pollution in the Essaouira Basin (Morocco). Comptes Rendus Geosci 335:307–317
Langousis A, Kaleris V, Kokosi A, Mamounakis G (2018) Markov based transition probability geostatistics in groundwater applications: assumptions and limitations. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-017-1504-y
Le Ravalec-Dupin M (2005) Inverse stochastic modeling of flow in porous media: application to reservoir characterization. Editions Technip, Paris. ISBN 2710808641
Ledoux E, Gomez E, Monget JM, Viavattene C, Viennot P, Ducharne A, Benoit M, Mignolet C, Schott C, Mary B (2007) Agriculture and groundwater nitrate contamination in the Seine basin. The STICS—MODCOU modelling chain. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.12.002 in press
Lee CH, Chen WP, Lee RH (2007) Estimation of groundwater recharge using water balance coupled with base- flow-record estimation and stable-base-flow analysis. Environ Geol 51:869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0561-1
Leon HS (1984) Duplin county places, past and present: a guide to duplin county, North Carolina
Liu X, Cardiff MA, Kitanidis PK (2010) Parameter estimation in nonlinear environmental problems. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 24:1003–1022
Lynch SM (2007) Introduction to applied Bayesian statistics and estimation for social scientists. Springer, New York
Mahinthakumar G, Sayeed M (2005) Hybrid genetic algorithm—Local search methods for solving groundwater source identification inverse problems. J Water Resour Plann Manage 131(1):45–57
Mantoglou A, Wilson JL (1982) The turning bands method for simulation of random fields using line generation by a spectral method. Water Resour Res 18(5):1379–1394
Maurer EP, Wood AW, Adam JC, Lettenmaier DP, Nijssen B (2002) A long-term hydrologiclly-based data set of land surface fluxes and states for the conterminous united states. J Climate 15:3237–3251
Messier KP, Kane E, Bolich R, Serre ML (2014) Nitrate variability in groundwater of North Carolina using monitoring and private well data models. Environ Sci Technol 48:10804–10812
Mew T, and Spruill T (2000) Determination of aquifer recharge, ground-water flow and basin discharge—methods and examples [abs.]. In: Proceedings of the cross-discipline ecosystem modeling and analysis workshop, August 15–17, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina
Mew HE, Hirth DK, Lewis DV, Daniels RB, Keyworth AJ (2002) Methodology for compiling ground water recharge maps in the piedmont and coastal plain provinces of North Carolina. groundwater bulletin number 25, N.C. Department of Environment and Natural Resources, pp 1–76
Michalak AM, Kitanidis PK (2004) Estimation of historical groundwater contaminant distribution using the adjoint state method applied to geostatistical inverse modeling. Water Resour Res 40:W08302. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004wr003214
Mirghani BY, Mahinthakumar KG, Tryby ME, Ranjithan RS, Zechman EM (2009) A parallel evolutionary strategy based simulation–optimization approach for solving groundwater source identification problems. Adv Water Resour 32(9):1373–1385
Mueller DK, Helsel DR (1996) Nutrients in the Nation’s Waters—Too Much of a Good Thing? Circular 1136. U.S. Geological Survey
Neal RM (2003) Slice sampling. Ann Stat 31(3):705–767. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1056562461
Neal RM (2011) MCMC Using Hamiltonian Dynamics. In: Brooks S, Gelman A, Jones GL, Meng XL (eds) Handbook of Markov Chain Monte Carlo. Chapman and Hall/CRC, Boca Raton. ISBN 0470177934
Painter S (1996) Stochastic interpolation of aquifer properties using fractional Levy motion. Water Resour Res 32:1323–1332
Roberts GO, Rosenthal JS (2001) Optimal scaling for various metropolis-hastings algorithms. Stat Sci 16:351–367
Rushton KR, Ward C (1979) The estimation of groundwater recharge. J Hydrol 41:345–361
Smith B (2001) Bayesian output analysis program (BOA) (Version 1.0.0) [Computer software]. Iowa City, IA: University of Iowa, College of Public Health
Smith TJ, Marshall LA (2008) Bayesian methods in hydrologic modeling: a study of recent advancements in Markov chain Monte Carlo techniques. Water Resour Res 44:W00B05. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007wr006705
Srivastava D, Singh R (2015) Groundwater system modeling for simultaneous identification of pollution sources and parameters with uncertainty characterization, Springer. Eur Water Resour Assoc 29(13):4607–4627
Sun NZ (1999) Inverse problems in groundwater modeling: theory and applications of transport in porous media. Springer, Netherlands. ISBN 978-0-7923-2987-9
Sun AY, Ritzi RW, Sims DW (2008) Characterization and modeling of spatial variability in a complex alluvial aquifer: implications on solute transport. Water Resour Res 44:W04402. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007WR006119
Tarantola A (2005) Inverse problem theory and methods for model parameter estimation. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia. ISBN 0-89871-572-5
Tompson AFB, Ababou R, Gelhar LW (1989) Implementation of the three-dimensional turning bands random field generator. Water Resour Res 25(10):2227–2243
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) (1986) Urban Hydrology for Small Watershed: TR-55. USDA Technical Release 55
US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2012) Basic information about nitrate in drinking water. http://water.epa.gov/drink/contaminants/basicinformation/nitrate.cfm. Accessed 1 Novemb 2012
Vrugt JA, ter Braak CJF, Clark MP, Hyman JM, Robinson BA (2008) Treatment of input uncertainty in hydrologic modeling: doing hydrology backward with Markov Chain Monte Carlo simulation. Water Resour Res 44:W00B09. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007wr006720
Wang H, Jin X (2013) Characterization of groundwater contaminant source using Bayesian method. Stochastic Environ Res Risk Assess 27(4):867–876. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-012-0622-9
Web soil survey, Accessed 13th Jan 2016. http://websoilsurvey.nrcs.usda.gov/app/
Weissmann GS, Fogg GE (1999) Multi-scale alluvial fan heterogeneity modeled with transition probability geostatistics in a sequence stratigraphic framework. J Hydrol 226:48–65
Yan H, Wang SQ, Billesbach DP, Oechel W (2012) Global estimation of evapotranspiration using a leaf area index-based surface energy and water balance model. Remote Sens Environ 124(2012):581–595
Zeng L, Shi L, Zhang D, Wu L (2012) A sparse grid based Bayesian method for contaminant source identification. Adv Water Resour 37:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2011.09.011
Zheng Y, Han F (2016) Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) uncertainty analysis for watershed water quality modeling and management. Stoch Environ Res Risk A 30(1):293–308
Zhou HY, Gomez-Hernandez Li LP (2014) Inverse methods in hydrogeology: evolution and recent trends. Adv Water Resour 63:22–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2013.10.014
Zimmerman DA, de Marsily G, Gotaway CA, Marietta MG, Axness CL, Beauheim R, Bras R, Carrera J, Dagan G, Davies PB, Gallegos D, Galli A, Gomez-Hernandez J, Grindrod P, Gutjahr AL, Kitanidis P, Lavenue AM, McLaughlin D, Neuman SP, Ramarao BS, Ravenne C, Rubin Y (1998) A comparison of seven geostatistically-based inverse approaches to estimate transmissivities for modeling advective transport by groundwater flow. Water Resour Res 34(6):1373–1413
Acknowledgements
This research is supported in part by the Research and Innovation Seed Funding (RISF) from North Carolina State University. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the North Carolina State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayub, R., Messier, K.P., Serre, M.L. et al. Non-point source evaluation of groundwater nitrate contamination from agriculture under geologic uncertainty. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 33, 939–956 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-019-01669-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-019-01669-z