Abstract
Background
Rituximab is a chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody that induces sustained remission in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. However, there is no consensus on the optimal regimen and monitoring of rituximab. In other autoimmune diseases, anti-rituximab antibodies (ARA) have been reported in 10–40% of patients, but their clinical relevance remains unclear. In nephrotic syndrome, data are scarce.
Methods
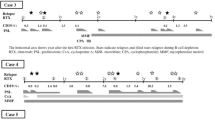
We report a single-center retrospective study with immuno- and pharmacological monitoring of rituximab treatment in children with frequent relapsing (FR) or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome (SDNS). We analyzed the monthly monitoring of 24 children, receiving a dose of rituximab (375 mg/m2) between December 2017 and April 2018 at the Pediatric Nephrology Department of Robert-Debré hospital, Paris.
Results
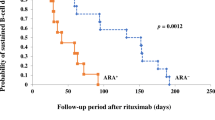
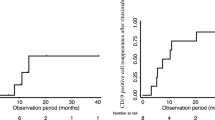
ARA were detected in 7/24 patients (29%), sometimes after the first infusion of rituximab. ARA were present at baseline in two patients previously treated with rituximab. Both displayed no B-cell depletion. ARA were also reported in 5/22 patients during follow-up, with antibodies always detected in the first month following B-cell recovery. An incomplete CD19+CD20− B-cell depletion at M1 (5–25/mm3) and low serum rituximab levels was predictive of developing ARA. The development of de novo ARA during follow-up was not associated with shorter B-cell depletion.
Conclusions
This study shows that ARA are frequent in children with FR/SDNS and that close immuno- and pharmacological monitoring may help personalizing rituximab treatment in patients needing repeated injections.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dossier C, Delbet JD, Boyer O, Daoud P, Mesples B, Pellegrino B, See H, Benoist G, Chace A, Larakeb A, Hogan J, Deschênes G (2019) Five-year outcome of children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: the NEPHROVIR population-based cohort study. Pediatr Nephrol 34:671–678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-4149-2
Johnson PW, Glennie MJ (2001) Rituximab: mechanisms and applications. Br J Cancer 85:1619–1623. https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2001.2127
Benz K, Dötsch J, Rascher W, Stachel D (2004) Change of the course of steroid dependent nephrotic syndrome after rituximab therapy. Pediatr Nephrol 19:794–797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-004-1434-z
Ravani P, Rossi R, Bonanni A, Quinn RR, Sica F, Bodria M, Pasini A, Montini G, Edefonti A, Belingheri M, De Giovanni D, Barbano G, Degl'Innocenti L, Scolari F, Murer L, Reiser J, Fornoni A, Ghiggeri GM (2015) Rituximab in children with steroid-dependant nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter, open-label, noninferiority, randomized controlled trial. J Am Soc Nephrol 26:2259–2266. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2014080799
Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K, Mori R, Tuchida N, Kamei K, Miura K, Aya K, Nakanishi K, Ohtomo Y, Takahashi S, Tanaka R, Kaito HH, Ishikura K, Ito S, Ohashi Y, Rituximab for Childhood-onset Refractory Nephrotic Syndrome (RCRNS) Study Group (2014) Rituximab for childhood-onset, complicated, frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 384:1273–1281. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60541-9
Basu B, Sander A, Roy B, Preussler S, Barua S, Mahapatra TKS, Schaefer F (2018) Efficacy of rituximab vs tacrolimus in pediatric corticosteroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr 172:757–764. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2018.1323
Albert D, Dunham J, Khan S, Stansberry J, Kolasinski S, Tsai D, Pullman-Mooar S, Barnack F, Striebich C, Looney RJ, Prak ET, Kimberly R, Zhang Y, Eisenberg R (2008) Variability in the biological response to anti-CD20 B cell depletion in systemic lupus erythaematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 67:1724–1731. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2007.083162
Li T, Zhang LJ, Zhang QX, Yang CS, Zhang C, Li YJ, Shi FD, Yang L (2018) Anti-rituximab antibody in patients with NMOSDs treated with low dose rituximab. J Neuroimmunol 316:107–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2017.12.021
Einarsson JT, Evert M, Geborek P, Saxne T, Lundgren M, Kapetanovic MC (2017) Rituximab in clinical practice: dosage, drug adherence, Ig levels, infections, and drug antibodies. Clin Rheumatol 36:2743–2750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3848-6
Wincup C, Menon M, Smith E, Schwartz A, Isenberg D, Jury EC, Mauri C, ABIRISK Consortium (2019) Presence of anti-rituximab antibodies predicts infusion-related reactions in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 78:1140–1142. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215200
Ahn YH, Kang HG, Lee JM, Choi HJ, Ha IS, Cheong HI (2014) Development of antirituximab antibodies in children with nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 29:1461–1464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2794-7
Vendramin C, Thomas M, Westwood JP, McGuckin S, Scully M (2019) Rituximab-induced acute and delayed serum sickness in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: the role of anti-rituximab antibodies. Br J Haematol 184:858–861. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.15177
Maloney DG, Grillo-López AJ, White CA, Bodkin D, Schilder RJ, Neidhart JA, Janakiraman N, Foon KA, Liles TM, Dallaire BK, Wey K, Royston I, Davis T, Levy R (1997) IDEC-C2B8 (Rituximab) anti CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy in patients with relapsed low-grade non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Blood Sep 90:2188–2195
Looney RJ, Anolik JH, Campbell D, Felgar RE, Young F, Arend LJ, Sloand JA, Rosenblatt J, Sanz I (2004) B cell depletion as a novel treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus: a phase I/II dose-escalation trial of rituximab. Arthritis Rheum 50:2580–2589. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.20430
Pijpe J, van Imhoff GW, Spijkervet FK, Roodenburg JL, Wolbink GJ, Mansour K, Vissink A, Kallenberg CG, Bootsma H (2005) Rituximab treatment in patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome: an open-label phase II study. Arthritis Rheum 52:2740–2750. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.21260
Smith KG, Jones RB, Burns SM, Jayne DR (2006) Long-term comparison of rituximab treatment for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus and vasculitis: Remission, relapse, and re-treatment. Arthritis Rheum 54:2970–2982. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22046
Keystone E, Fleischmann R, Emery P, Furst DE, van Vollenhoven R, Bathon J, Dougados M, Baldassare A, Ferraccioli G, Chubick A, Udell J, Cravets MW, Agarwal S, Cooper S, Magrini F (2007) Safety and efficacy of additional courses of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 56:3896–3908. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.23059
Fujinaga S, Nishino T, Endo S, Umeda C, Watanabe Y, Nakagawa M (2020) Unfavorable impact of anti-rituximab antibodies on clinical outcomes in children with complicated steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 35:2003–2008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-020-04629-w
Fujinaga S, Nishino T (2018) Is cytokine-release syndrome the cause of rituximab treatment-related infusion reactions in children with nephrotic syndrome? Impact of anti-rituximab antibodies. Pediatr Nephrol 33:1097–1098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-3960-0
Chan EY, Webb H, Yu E, Ghiggeri GM, Kemper MJ, Ma AL, Yamamura T, Sinha A, Bagga A, Hogan J, Dossier C, Vivarelli M, Liu ID, Kamei K, Ishikura K, Saini P, Tullus K (2020) Both the rituximab dose and maintenance immunosuppression in steroid-dependent/frequently-relapsing nephrotic syndrome have important effects on outcomes. Kidney Int 97:393–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2019.09.033
Kamei K, Ishikura K, Sako M, Aya K, Tanaka R, Nozu K, Kaito H, Nakanishi K, Ohtomo Y, Miura K, Takahashi S, Morimoto T, Kubota W, Ito S, Nakamura H, Iijima K, Rituximab for Childhood-Onset Refractory Nephrotic Syndrome (RCRNS) Study Group (2017) Long-term outcome of childhood-onset complicated nephrotic syndrome after a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of rituximab. Pediatr Nephrol 32:2071–2078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3718-0
Boyer-Suavet S, Andreani M, Cremoni M, Brglez V, Benzaken S, Bernard G, Nachman P, Esnault V, Seitz-Polski B (2019) Rituximab bioavailability in primary membranous nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 34:1423–1425. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfz041
Cartron G, Dacheux L, Salles G, Solal-Celigny P, Bardos P, Colombat P, Watier H (2002) Therapeutic activity of humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and polymorphism in IgG Fc receptor FcgammaRIIIa gene. Blood 99:754–758. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.v99.3.754
Kamei K, Ito S, Nozu K, Fujinaga S, Nakayama M, Sako M, Saito M, Yoneko M, Iijima K (2009) Single dose of rituximab for refractory steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome in children. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1321–1328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1191-0
Fujinaga S, Sakuraya K (2018) Single infusion of low-dose ofatumumab in a child with complicated nephrotic syndrome with anti-rituximab antibodies. Pediatr Nephrol Mar 33(3):527–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3866-2
Wang CS, Liverman RS, Garro R, George RP, Glumova A, Karp A, Jernigan S, Warshaw B (2017) Ofatumumab for the treatment of childhood nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 32:835–841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3621-8
Dossier C, Prim B, Moreau C, Kwon T, Maisin A, Nathanson S, De Gennes C, Barsotti K, Bourrassi A, Hogan J, Deschênes G (2020) A global antiB cell strategy combining obinutuzumab and daratumumab in severe pediatric nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-020-04811-0
Boyer S, Benzaken S, Bernard G, Esnault V, Seitz-Polski B (2017) Réactivité croisée des anticorps anti-rituximab neutralisants avec les anti-CD20 de troisième génération : une alternative thérapeutique dans la glomérulopathie extramembraneuse? Oral communication. Nephrol Ther 5:267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nephro.2017.08.040
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertrand, Q., Mignot, S., Kwon, T. et al. Anti-rituximab antibodies in pediatric steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 37, 357–365 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-021-05069-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-021-05069-w