Abstract
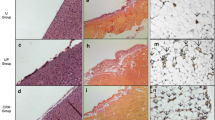
The angiopoietin/Tie-2 system plays an important role in the initiation of angiogenesis. However, the role of angiopoietin/Tie-2 in peritoneal angiogenesis and fibrosis is unclear. In our study we investigated the peritoneal morphologic changes in a uremic peritoneal dialysis (PD) rat model, focusing on the relationship between angiopoietin/Tie-2 and peritoneal angiogenesis. We subjected uremic (subtotal nephrectomy) rats to dialysis, using a standard PD solution, for 10 days, 28 days, or 56 days, and compared them with uremic rats that had not undergone dialysis and control rats. Functional [dialysate-to-plasma (D/P) creatinine; ultrafiltration (UF)] and structural (vessel density and thickness of the submesothelial extracellular matrix) changes of the peritoneum were quantified. Levels of angiopoietin (Ang)-1, Ang-2, Tie-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were examined in the peritoneum by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and related to angiogenesis. The uremic group that had not undergone dialysis was characterized by increased vessel density in the peritoneum compared with that of the control, which correlated with decreased UF and increased D/P creatinine. Progressive angiogenesis and fibrosis were found in the PD groups when compared with the uremic non-dialyzed or control group, accompanied by an increased D/P creatinine that occurred in the PD group after 56 days, while UF decreased. Furthermore, Ang-2 and VEGF levels increased, while Tie-2 level decreased significantly in the uremic non-dialyzed group compare with the control. This tendency was more obvious in the PD groups than in the uremic non-dialyzed or control group, but no difference was found among the PD groups. Both VEGF and Ang-2 correlated positively with vessel density, while Tie-2 correlated negatively. We confirmed angiogenesis and fibrosis changes of the peritoneum as a result of uremic status and PD therapy in the uremic PD rat model. An increased level of Ang-2 and a reduced level of Tie-2 in conditions of uremia and PD therapy correlated with peritoneal angiogenesis and functional deterioration.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krediet RT, Lindholm B, Rippe B (2000) Pathophysiology of peritoneal membrane failure. Perit Dial Int 20 [Suppl 4]:S22–S42
De Vriese AS, Mortier S, Lameire NH (2001) Neoangiogenesis in the peritoneal membrane: does it play a role in ultrafiltration failure? Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:2143–2145
Saxena R (2008) Pathogenesis and treatment of peritoneal membrane failure. Pediatr Nephrol 23:695–703
Ramsauer M, D’Amore PA (2002) Getting Tie(2)d up in angiogenesis. J Clin Invest 110:1615–1617
Koh GY, Kim I, Kwak HJ, Yun MJ, Leem JC (2002) Biomedical significance of endothelial cell specific growth factor, angiopoietin. Exp Mol Med 34:1–11
Pereira BJ, Poutsiaka DD, King AJ, Strom JA, Narayan G, Levey AS, Dinarello CA (1992) In vitro production of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in chronic renal failure, CAPD and HD. Kidney Int 42:1419–1424
Mateijsen MA, van der Wal AC, Hendriks PM, Zweers MM, Mulder J, Struijk DG, Krediet RT (1999) Vascular and interstitial changes in the peritoneum of CAPD patients with peritoneal sclerosis. Perit Dial Int 19:517–525
Chiang SC, Cheng CH, Moulton KS, Kasznica JM, Moulton SL (2000) TNP-470 inhibits intraabdominal adhesion formation. J Pediatr Surg 35:189–196
Tugues S, Fernandez-Varo G, Munoz-Luque J, Ros J, Arroyo V, Rodes J, Friedman SL, Carmeliet P, Jimenez W, Morales-Ruiz M (2007) Antiangiogenic treatment with sunitinib ameliorates inflammatory infiltrate, fibrosis, and portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 46:1919–1926
Margetts PJ, Gyorffy S, Kolb M, Yu L, Hoff CM, Holmes CJ, Gauldie J (2002) Antiangiogenic and antifibrotic gene therapy in a chronic infusion model of peritoneal dialysis in rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:721–728
Kalluri R, Sukhatme VP (2000) Fibrosis and angiogenesis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 9:413–418
Williams JD, Craig KJ, Topley N, Von Ruhland C, Fallon M, Newman GR, Mackenzie RK, Williams GT (2002) Morphologic changes in the peritoneal membrane of patients with renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:470–479
Witzenbichler B, Maisonpierre PC, Jones P, Yancopoulos GD, Isner JM (1998) Chemotactic properties of angiopoietin-1 and -2, ligands for the endothelial-specific receptor tyrosine kinase Tie2. J Biol Chem 273:18514–18521
Valenzuela DM, Griffiths JA, Rojas J, Aldrich TH, Jones PF, Zhou H, McClain J, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Huang T, Papadopoulos N, Maisonpierre PC, Davis S, Yancopoulos GD (1999) Angiopoietins 3 and 4: diverging gene counterparts in mice and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:1904–1909
Davis S, Aldrich TH, Jones PF, Acheson A, Compton DL, Jain V, Ryan TE, Bruno J, Radziejewski C, Maisonpierre PC, Yancopoulos GD (1996) Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning. Cell 87:1161–1169
Suri C, Jones PF, Patan S, Bartunkova S, Maisonpierre PC, Davis S, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD (1996) Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell 87:1171–1180
Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, Bartunkova S, Wiegand SJ, Radziejewski C, Compton D, McClain J, Aldrich TH, Papadopoulos N, Daly TJ, Davis S, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD (1997) Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis. Science 277:55–60
Guo P, Imanishi Y, Cackowski FC, Jarzynka MJ, Tao HQ, Nishikawa R, Hirose T, Hu B, Cheng SY (2005) Up-regulation of angiopoietin-2, matrix metalloprotease-2, membrane type 1 metalloprotease, and laminin 5 gamma 2 correlates with the invasiveness of human glioma. Am J Pathol 166:877–890
Korff T, Kimmina S, Martiny-Baron G, Augustin HG (2001) Blood vessel maturation in a 3-dimensional spheroidal coculture model: direct contact with smooth muscle cells regulates endothelial cell quiescence and abrogates VEGF responsiveness. FASEB J 15:447–457
Roviezzo F, Tsigkos S, Kotanidou A, Bucci M, Brancaleone V, Cirino G, Papapetropoulos A (2005) Angiopoietin-2 causes inflammation in vivo by promoting vascular leakage. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 314:738–744
Takagi H, Koyama S, Seike H, Oh H, Otani A, Matsumura M, Honda Y (2003) Potential role of the angiopoietin/tie2 system in ischemia-induced retinal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:393–402
Selgas R, del Peso G, Bajo MA, Molina S, Cirugeda A, Sanchez-Tomero JA, Castro MJ, Castro MA, Vara F (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels in peritoneal dialysis effluent. J Nephrol 14:270–274
Combet S, Miyata T, Moulin P, Pouthier D, Goffin E, Devuyst O (2000) Vascular proliferation and enhanced expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in human peritoneum exposed to long-term peritoneal dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:717–728
Shibuya M (2008) Vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent and -independent regulation of angiogenesis. BMB Rep 41:278–286
Acknowledgments
The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30600290) and the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (07QA14040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, J., Fang, W., Ni, Z. et al. Peritoneal morphologic changes in a peritoneal dialysis rat model correlate with angiopoietin/Tie-2. Pediatr Nephrol 24, 163–170 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-0944-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-0944-5