Abstract
Background
Inguinal hernia repair belongs to the most frequently performed surgical procedures. Endoscopic techniques like TAPP and TEP have become standard of care together with the conventional open techniques. Especially in endoscopic techniques, there is a confusing amount of different meshes and fixation techniques with impact on perioperative and long-term outcome. We present the first single-center data on the use of titanized extra lightweight meshes and fibrin glue fixation compared to staple fixation regarding long-term outcome, especially chronic pain.
Materials and methods
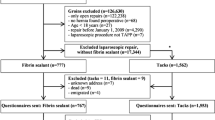
A clinical trial with retrospective analysis of patient- and procedure-related data and questionnaire-based follow-up of TAPP procedures performed in 2012–2014 was conducted in a specialized hernia center. Standard TAPP technique was used with placement of TiMesh extra light (16 g/m2) and either fibrin glue or staple fixation. Procedure- and patient-related data are compared after propensity score matching regarding perioperative complications and long-term outcome.
Results
Of 612 TAPP procedures 372 procedures were included in analysis after propensity score matching. Fibrin glue was used in n = 279 and staple fixation in n = 93 cases. There were significant differences regarding duration of the surgical procedures (p = 0.001) and distribution of mesh size. No differences were noted regarding perioperative complications such as seroma or hematoma formation and need for re-laparoscopy. During a mean follow-up of 32.1 ± 20.6 month with a follow-up rate of 79%, there was no difference in long-term outcome, especially for rate of recurrence (p = 0.112) and development of chronic pain (p = 0.846). The overall rate of recurrence was 3.0% (n = 11), and in 2.4% (n = 9) patients complained of chronic pain.
Conclusion
Inguinal hernia repair using extra lightweight titanized meshes and fibrin glue fixation is safe and feasible compared to staple fixation even in large and combined hernia defects, if mesh size is adjusted to size of hernia defect. The rate of chronic pain was extremely low at 2.4%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tolver MA, Rosenberg J, Juul P, Bisgaard T (2013) Randomized clinical trial of fibrin glue versus tacked fixation in laparoscopic groin hernia repair. Surg Endosc 27:2727–2733
Köckerling F, Simons MP (2018) Current concepts of inguinal hernia repair. Visc Med 34:145–150
Andresen K, Fenger AQ, Burcharth J, Pommergaard HC, Rosenberg J (2017) Mesh fixation methods and chronic pain after transabdominal preperitoneal (TAPP) inguinal hernia surgery: a comparison between fibrin sealant and tacks. Surg Endosc 31:4077–4084
Wirth U, Saller M-L, von Ahnen T, Köckerling F, Schardey HM, Schopf S (2017) Inguinal hernia repair in TAPP technique in a day-case surgery setting—at what price? Chirurg 88:792–798
Fenger AQ, Helvind NM, Pommergaard H-C, Burcharth J, Rosenberg J (2016) Fibrin sealant for mesh fixation in laparoscopic groin hernia repair does not increase long-term recurrence. Surg Endosc 30:986–992
Köckerling F, Bittner R, Kofler M, Mayer F, Adolf D, Kuthe A, Weyhe D (2017) Lichtenstein versus total extraperitoneal patch plasty versus transabdominal patch plasty technique for primary unilateral inguinal hernia repair: a registry-based, propensity score-matched comparison of 57,906 patients. Ann Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/sla.0000000000002541
Niebuhr H, Wegner F, Hukauf M, Lechner M, Fortelny R, Bittner R, Schug-Pass C, Köckerling F (2018) What are the influencing factors for chronic pain following TAPP inguinal hernia repair: an analysis of 20,004 patients from the Herniamed Registry. Surg Endosc 32:1971–1983
Shi Z, Fan X, Zhai S, Zhong X, Huang D (2017) Fibrin glue versus staple for mesh fixation in laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal repair of inguinal hernia: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Surg Endosc 31:527–537
Bittner R, Schmedt C-G, Leibl BJ, Schwarz J (2011) Early postoperative and one year results of a randomized controlled trial comparing the impact of extralight titanized polypropylene mesh and traditional heavyweight polypropylene mesh on pain and seroma production in laparoscopic hernia repair (TAPP). World J Surg 35:1791–1797
Fortelny RH, Petter-Puchner AH, May C, Jaksch W, Benesch T, Khakpour Z, Redl H, Glaser KS (2012) The impact of atraumatic fibrin sealant versus staple mesh fixation in TAPP hernia repair on chronic pain and quality of life: results of a randomized controlled study. Surg Endosc 26:249–254
Bittner R, Gmähle E, Gmähle B, Schwarz J, Aasvang E, Kehlet H (2010) Lightweight mesh and noninvasive fixation: an effective concept for prevention of chronic pain with laparoscopic hernia repair (TAPP). Surg Endosc 24:2958–2964
Schopf S, von Ahnen T, von Ahnen M, Schardey HM (2011) Chronic pain after laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal hernia repair: a randomized comparison of light and extralight titanized polypropylene mesh. World J Surg 35:302–310
Jacob DA, Hackl JA, Bittner R, Kraft B, Köckerling F (2015) Perioperative outcome of unilateral versus bilateral inguinal hernia repairs in TAPP technique: analysis of 15,176 cases from the Herniamed Registry. Surg Endosc 29:3733–3740
Köckerling F, Bittner R, Adolf D, Fortelny R, Niebuhr H, Mayer F, Schug-Pass C (2018) Seroma following transabdominal preperitoneal patch plasty (TAPP): incidence, risk factors, and preventive measures. Surg Endosc 32:2222–2231
Miserez M, Peeters E, Aufenacker T, Bouillot JL, Campanelli G, Conze J, Fortelny R, Heikkinen T, Jorgensen LN, Kukleta J, Morales-Conde S, Nordin P, Schumpelick V, Smedberg S, Smietanski M, Weber G, Simons MP (2014) Update with level 1 studies of the European Hernia Society guidelines on the treatment of inguinal hernia in adult patients. Hernia 18:151–163
Antoniou SA, Köhler G, Antoniou GA, Muysoms FE, Pointner R, Granderath FA (2016) Meta-analysis of randomized trials comparing nonpenetrating versus mechanical mesh fixation in laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair. Am J Surg 211:239.e2–249.e2
Köckerling F, Schug-Pass C (2014) What do we know about titanized polypropylene meshes? An evidence-based review of the literature. Hernia 18:445–457
Lonjon G, Porcher R, Ergina P, Fouet M, Boutron I (2017) Potential pitfalls of reporting and bias in observational studies with propensity score analysis assessing a surgical procedure: a methodological systematic review. Ann Surg 265:901–909
Köckerling F, Bittner R, Kraft B, Hukauf M, Kuthe A, Schug-Pass C (2017) Does surgeon volume matter in the outcome of endoscopic inguinal hernia repair? Surg Endosc 31:573–585
Bittner R, Arregui ME, Bisgaard T, Dudai M, Ferzli GS, Fitzgibbons RJ, Fortelny RH, Klinge U, Köckerling F, Kuhry E, Kukleta J, Lomanto D, Misra MC, Montgomery A, Morales-Conde S, Reinpold W, Rosenberg J, Sauerland S, Schug-Pass C, Singh K, Timoney M, Weyhe D, Chowbey P (2011) Guidelines for laparoscopic (TAPP) and endoscopic (TEP) treatment of inguinal hernia [International Endohernia Society (IEHS)]. Surg Endosc 25(9):2773–2843
Köckerling F, Bittner R, Jacob DA, Seidelmann L, Keller T, Adolf D, Kraft B, Kuthe A (2015) TEP versus TAPP: comparison of the perioperative outcome in 17,587 patients with a primary unilateral inguinal hernia. Surg Endosc 29:3750–3760
Scheidbach H, Tannapfel A, Schmidt U, Lippert H, Köckerling F (2004) Influence of titanium coating on the biocompatibility of a heavyweight polypropylene mesh. An animal experimental model. Eur Surg Res 36:313–317
Scheidbach H, Tamme C, Tannapfel A, Lippert H, Köckerling F (2004) In vivo studies comparing the biocompatibility of various polypropylene meshes and their handling properties during endoscopic total extraperitoneal (TEP) patchplasty: an experimental study in pigs. Surg Endosc 18:211–220
Klinge U, Klosterhalfen B (1999) Meshes within the abdominal wall. Chirurg 70:876–887
Klosterhalfen B, Klinge U, Hermanns B, Schumpelick V (2000) Pathology of traditional surgical nets for hernia repair after longterm implantation in humans. Chirurg 71:43–51
Klinge U, Klosterhalfen B, Birkenauer V, Junge K, Conze J, Schumpelick V (2002) Impact of polymer pore size on the interface scar formation in a rat model. J Surg Res 103:208–214
HerniaSurge Group (2018) International guidelines for groin hernia management. Hernia 22:1–165
Funding
Financial support for this study was given by pfm medical AG, Cologne, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was supported by a grant to cover all administrative fees by pfm medical Ag, Cologne. Hans Martin Schardey received reimbursement for travel costs from pfm medical Ag, Cologne and worked as a consultant for pfm medical Ag, Cologne; Johnson & Johnson, Norderstedt; LifeCell Corporation, Branchburg, USA. Ferdinand Köckerling received grants to fund the Herniamed Registry from Johnson & Johnson, Norderstedt; pfm medical, Cologne; Dahlhausen, Cologne; B Braun, Tuttlingen; MenkeMed, Munich and Bard, Karlsruhe. The authors did not receive any payments. Ulrich Wirth, Thomas von Ahnen, Marie Luise Saller and Stefan Schopf have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wirth, U., Saller, M.L., von Ahnen, T. et al. Long-term outcome and chronic pain in atraumatic fibrin glue versus staple fixation of extra light titanized meshes in laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair (TAPP): a single-center experience. Surg Endosc 34, 1929–1938 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-06965-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-06965-x