Abstract
Background
The two most commonly performed procedures for bariatric surgery include Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) and adjustable gastric banding (AGB). While many studies have commented on short-term, postoperative outcomes of these procedures, few have reported long-term data. The purpose of this study was to compare long-term, postoperative outcomes between RYGB and AGB.
Methods
This was a retrospective, cohort comparing all patients undergoing RYGB or AGB at our institution, from 01/1998 to 08/2012. Patients were followed at 1-, 3-, and 5-year intervals. Adjusted, Cox proportional hazard regression and mixed effects repeated measures modeling were performed to generate cure ratios (CR) and 95 % confidence intervals (CI).
Results
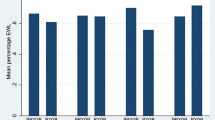
Two thousand four hundred twenty bariatric surgery patients (380 AGB, 2,040 RYGB) were identified by CPT code. Median (range) follow-up for patients was 3 (1–5) years. Preoperatively, RYGB patients were significantly younger, more obese, had higher hemoglobin A1c, and less often suffered from hypertension (HTN), dyslipidemia, and asthma as compared to AGB patients. Postoperatively, RYGB patients experienced significantly longer operating room times, higher incidences of intensive care unit admissions, longer hospital lengths of stay, and increased incidence of small bowel obstruction compared to AGB patients. After adjusting for statistically significant and clinically relevant factors [e.g., age, gender, body mass index, degenerative joint disease (DJD), diabetes, HTN, dyslipidemia, heart disease, apnea, and asthma], RYGB was independently associated with a significantly greater percentage of total body weight loss (p = 0.0065) and greater CR (95 % CI) regarding gastroesophageal reflux disease [2.1(1.4–3.0)], DJD [3.4(2.0–5.6)], diabetes [3.4(2.2–5.4)], apnea [3.1(1.9–5.3)], HTN [5.5(3.4–8.8)], and dyslipidemia [6.3(3.5–11)] compared to AGB.
Conclusion
Our results support previous studies that have observed a greater weight loss associated with RYGB as compared to AGB and provide further evidence toward the long-term sustainability of this weight loss. Additionally, RYGB appears to result in a greater reduction of medical comorbidity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM (2012) Prevalence of obesity in the United States, 2009–2010. United States Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db82.pdf. Accessed 10/12/2013
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (8/3/2010) Cdc vital signs [updated 8/3/2010]. Available www.cdc.gov/vitalsigns/adultobesity/index.html. Accessed 03/10/2014
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (1998) Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: the evidence report. Available www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/obesity/ob-gdlns.pdf. Accessed 10/13/2013
Tice JA, Karliner L, Walsh J, Petersen AJ, Feldman MD (2008) Gastric banding or bypass? A systematic review comparing the two most popular bariatric procedures. Am J Med 121(10):885–893
Nguyen NT, Sloan J, Nguyen XM (2010) Laparoscopic gastric bypass or gastric banding: which operation is best? Adv Surg 44:49–57
Nguyen NT, Slone JA, Nguyen XM, Hartman JS, Hoyt DB (2009) A prospective randomized trial of laparoscopic gastric bypass versus laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for the treatment of morbid obesity: outcomes, quality of life, and costs. Ann Surg 250(4):631–641
Angrisani L, Cutolo PP, Formisano G, Nosso G, Vitolo G (2013) Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding versus Roux-En-Y gastric bypass: 10-year results of a prospective, randomized trial. Surg Obes Relat Dis 9(3):405–413
Angrisani L, Lorenzo M, Borrelli V (2007) Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding versus Roux-En-Y gastric bypass: 5-year results of a prospective randomized trial. Surg Obes Relat Dis 3(2):127–132 (discussion 32–33)
Puzziferri N, Nakonezny PA, Livingston EH, Carmody TJ, Provost DA, Rush AJ (2008) Variations of weight loss following gastric bypass and gastric band. Ann Surg 248(2):233–242
Biertho L, Steffen R, Ricklin T, Horber FF, Pomp A, Inabnet WB, Herron D, Gagner M (2003) Laparoscopic gastric bypass versus laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: a comparative study of 1,200 cases. J Am Coll Surg 197(4):536–544 (discussion 544–545)
Weber M, Muller MK, Bucher T, Wildi S, Dindo D, Horber F, Hauser R, Clavien PA (2004) Laparoscopic gastric bypass is superior to laparoscopic gastric banding for treatment of morbid obesity. Ann Surg 240(6):975–982 (discussion 982–983)
Lee DY, Guend H, Park K, Levine J, Ross RE, McGinty JJ, Teixeira JA (2012) Outcomes of laparoscopic Roux-En-Y gastric bypass versus laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding in adolescents. Obes Surg 22(12):1859–1864
Cottam DR, Atkinson J, Anderson A, Grace B, Fisher B (2006) A case-controlled matched-pair cohort study of laparoscopic Roux-En-Y gastric bypass and lap-band patients in a single us center with 3-year follow-up. Obes Surg 16(5):534–540
Jan JC, Hong D, Pereira N, Patterson EJ (2005) Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding versus laparoscopic gastric bypass for morbid obesity: a single-institution comparison study of early results. J Gastrointest Surg 9(1):30–39 (discussion 40–41)
Jan JC, Hong D, Bardaro SJ, July LV, Patterson EJ (2007) Comparative study between laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding and laparoscopic gastric bypass: single-institution, 5-year experience in bariatric surgery. Surg Obes Relat Dis 3(1):42–50 (discussion 51)
Bowne WB, Julliard K, Castro AE, Shah P, Morgenthal CB, Ferzli GS (2006) Laparoscopic gastric bypass is superior to adjustable gastric band in super morbidly obese patients: a prospective comparative analysis. Arch Surg 141(7):683–689
Boza C, Gamboa C, Awruch D, Perez G, Escalona A, Ibanez L (2010) Laparoscopic Roux-En-Y gastric bypass versus laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: 5 years of follow-up. Surg Obes Relat Dis 6(5):470–475
Romy S, Donadini A, Giusti V, Suter M (2012) Roux-En-Y gastric bypass vs gastric banding for morbid obesity: a case-matched study of 442 patients. Arch Surg 147(5):460–466
Spivak H, Abdelmelek MF, Beltran OR, Ng AW, Kitahama S (2012) Long-term outcomes of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding and laparoscopic Roux-En-Y gastric bypass in the United States. Surg Endosc 26(7):1909–1919
O’Brien PE, MacDonald L, Anderson M, Brennan L, Brown WA (2013) Long-term outcomes after bariatric surgery: 15-year follow-up of adjustable gastric banding and a systematic review of the bariatric surgical literature. Ann Surg 257(1):87–94
Zuegel NP, Lang RA, Huttl TP, Gleis M, Ketfi-Jungen M, Rasquin I, Kox M (2012) Complications and outcome after laparoscopic bariatric surgery: Lagb versus Lrygb. Langenbeck’s Arch Surgy/Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Chirurgie 397(8):1235–1241
Saunders J, Ballantyne GH, Belsley S, Stephens DJ, Trivedi A, Ewing DR, Iannace VA, Capella RF, Wasileweski A, Moran S, Schmidt HJ (2008) One-year readmission rates at a high volume bariatric surgery center: laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding, laparoscopic gastric bypass, and vertical banded gastroplasty-Roux-En-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg 18(10):1233–1240
Lancaster RT, Hutter MM (2008) Bands and bypasses: 30-day morbidity and mortality of bariatric surgical procedures as assessed by prospective, multi-center risk-adjusted Acs-Nsqip data. Surg Endosc 22(12):2554–2563
Saunders JK, Ballantyne GH, Belsley S, Stephens D, Trivedi A, Ewing DR, Iannace V, Capella RF, Wasielewski A, Moran S, Schmidt HJ (2007) 30-Day readmission rates at a high volume bariatric surgery center: laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding, laparoscopic gastric bypass, and vertical banded gastroplasty-Roux-En-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg 17(9):1171–1177
Stephens DJ, Saunders JK, Belsley S, Trivedi A, Ewing DR, Iannace V, Capella RF, Wasielewski A, Moran S, Schmidt HJ, Ballantyne GH (2008) Short-term outcomes for super–super obese (Bmi ≥ 60 Kg/m2) patients undergoing weight loss surgery at a high-volume bariatric surgery center: laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding, laparoscopic gastric bypass, and open tubular gastric bypass. Surg Obes Relat Dis 4(3):408–415
Davies SW, Efird JT, Guidry CA, Penn RI, Sawyer RG, Schirmer BD, Hallowell PT (2014) Long-term diabetic response to gastric bypass. J Surg Res 190(2):498–503
Cummings DE (2009) Endocrine mechanisms mediating remission of diabetes after gastric bypass surgery. Int J Obes 33(Suppl 1):S33–S40
Beckman LM, Beckman TR, Earthman CP (2010) Changes in gastrointestinal hormones and leptin after Roux-En-Y gastric bypass procedure: a review. J Am Diet Assoc 110(4):571–584
Chronaiou A, Tsoli M, Kehagias I, Leotsinidis M, Kalfarentzos F, Alexandrides TK (2012) Lower ghrelin levels and exaggerated postprandial peptide-Yy, glucagon-like peptide-1, and insulin responses, after gastric fundus resection, in patients undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a randomized clinical trial. Obes Surg 22(11):1761–1770
Ernst B, Thurnheer M, Wilms B, Schultes B (2009) Differential changes in dietary habits after gastric bypass versus gastric banding operations. Obes Surg 19(3):274–280
Tichansky DS, Boughter JD Jr, Madan AK (2006) Taste change after laparoscopic Roux-En-Y gastric bypass and laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2(4):440–444
Scholtz S, Miras AD, Chhina N, Prechtl CG, Sleeth ML, Daud NM, Ismail NA, Durighel G, Ahmed AR, Olbers T, Vincent RP, Alaghband-Zadeh J, Ghatei MA, Waldman AD, Frost GS, Bell JD, le Roux CW, Goldstone AP (2013) Obese patients after gastric bypass surgery have lower brain-hedonic responses to food than after gastric banding. Gut 63:891–902
Oliak D, Ballantyne GH, Weber P, Wasielewski A, Davies RJ, Schmidt HJ (2003) Laparoscopic Roux-En-Y gastric bypass: defining the learning curve. Surg Endosc 17(3):405–408
Salem L, Devlin A, Sullivan SD, Flum DR (2008) Cost-effectiveness analysis of laparoscopic gastric bypass, adjustable gastric banding, and nonoperative weight loss interventions. Surg Obes Relat Dis 4(1):26–32
Ternovits CA, Tichansky DS, Madan AK (2006) Band versus bypass: randomization and patients’ choices and perceptions. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2(1):6–10
Campbell J, McGarry LA, Shikora SA, Hale BC, Lee JT, Weinstein MC (2010) Cost-effectiveness of laparoscopic gastric banding and bypass for morbid obesity. Am J Manag Care 16(7):174–187
Disclosures
Stephen W. Davies, Christopher A. Guidry, and Robert G. Sawyer were supported by NIH Grant 5T32AI078875-05. Jimmy T. Efird, Rachel I. Penn, Bruce D. Schirmer, and Peter T. Hallowell have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davies, S.W., Efird, J.T., Guidry, C.A. et al. Twenty-first century weight loss: banding versus bypass. Surg Endosc 29, 947–954 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3758-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3758-5