Abstract
Background
A recent study demonstrated that high pressure of carbon dioxide (CO2) pneumoperitoneum before liver resection impairs postoperative liver regeneration. This study was aimed to investigate effects of varying insufflation pressures of CO2 pneumoperitoneum on liver regeneration using a rat model.
Methods
180 male Wistar rats were randomly divided into three groups: control group (without preoperative pneumoperitoneum), low-pressure group (with preoperative pneumoperitoneum at 5 mmHg), and high-pressure group (with preoperative pneumoperitoneum at 10 mmHg). After pneumoperitoneum, all rats were subjected to 70 % partial hepatic resection and then euthanized at 0 min, 12 h, and on postoperative days (PODs) 1, 2, 4, and 7. Following outcome parameters were used: liver regeneration (liver regeneration rate, mitotic count, Ki-67 labeling index), hepatocellular damage (serum aminotransferases), oxidative stress [serum malondialdehyde (MDA)], interleukin-6 (IL-6), and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) expression in the liver tissue.
Results
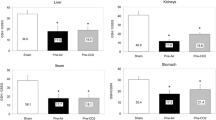
No significant differences were observed for all parameters between control and low-pressure groups. The liver regeneration rate and mitotic count were significantly decreased in the high-pressure group than in control and low-pressure groups on PODs 2 and 4. Postoperative hepatocellular damage was significantly greater in the high-pressure group on PODs 1, 2, 4, and 7 compared with control and/or low-pressure groups. Serum MDA levels were significantly higher in the high-pressure group on PODs 1 and 2, and serum IL-6 levels were significantly higher in the high-pressure group at 12 h and on POD 1, compared with control and/or low-pressure groups. The HGF tissue expression was significantly lower in the high-pressure group at 12 h and on PODs 1 and 4, compared with that in control and/or low-pressure groups.
Conclusions
High-pressure pneumoperitoneum before 70 % liver resection impairs postoperative liver regeneration, but low-pressure pneumoperitoneum has no adverse effects. This study suggests that following laparoscopic liver resection using appropriate pneumoperitoneum pressure, no impairment of liver regeneration occurs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Polychronidis A, Laftsidis P, Bounovas A, Simopoulos C (2008) Twenty years of laparoscopic cholecystectomy: Philippe Mouret—March 17, 1987. JSLS 12(1):109–111
Gagner M, Rheault M, Dubuc J (1992) Laparoscopic partial hepatectomy for liver tumor. Surg Endosc 6:97–98
Lee KF, Chong CN, Wong J, Cheung YS, Wong J, Lai P (2011) Long-term results of laparoscopic hepatectomy versus open hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a case-matched analysis. World J Surg 35(10):2268–2274
Abu HM, Di FF, Syed S, Wiltshire R, Dimovska E, Turner D, Primrose JN, Pearce NW (2013) Assessment of the financial implications for laparoscopic liver surgery: a single-centre UK cost analysis for minor and major hepatectomy. Surg Endosc 27(7):2542–2550
Nguyen KT, Gamblin TC, Geller DA (2009) World review of laparoscopic liver resection: 2,804 patients. Ann Surg 250(5):831–841
Viganò L, Tayar C, Laurent A, Cherqui D (2009) Laparoscopic liver resection: a systematic review. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 16(4):410–421
Nguyen KT, Marsh JW, Tsung A, Steel JJ, Gamblin TC, Geller DA (2011) Comparative benefits of laparoscopic vs open hepatic resection: a critical appraisal. Arch Surg 146(3):348–356
Nitta H, Sasaki A, Fujita T, Itabashi H, Hoshikawa K, Takahara T, Takahashi M, Nishizuka S, Wakabayashi G (2010) Laparoscopy-assisted major liver resections employing a hanging technique: the original procedure. Ann Surg 251(3):450–453
Lin NC, Nitta H, Wakabayashi G (2013) Laparoscopic major hepatectomy: a systematic literature review and comparison of 3 techniques. Ann Surg 257:205–213
Dagher I, O’Rourke N, Geller DA, Cherqui D, Belli G, Gamblin TC, Lainas P, Laurent A, Nguyen KT, Marvin MR, Thomas M, Ravindra K, Fielding G, Franco D, Buell JF (2009) Laparoscopic major hepatectomy: an evolution in standard of care. Ann Surg 250(5):856–860
Pross M, Schulz HU, Flechsig A, Manger T, Halangk W, Augustin W, Lippert H, Reinheckel T (2000) Oxidative stress in lung tissue induced by CO2 pneumoperitoneum in the rat. Surg Endosc 14(12):1180–1184
Schäfer M, Sägesser H, Reichen J, Krähenbühl L (2001) Alterations in hemodynamics and hepatic and splanchnic circulation during laparoscopy in rats. Surg Endosc 15:1197–1201
Eleftheriadis E, Kotzampassi K, Papanotas K, Heliadis N, Sarris K (1996) Gut ischemia, oxidative stress, and bacterial translocation in elevated abdominal pressure in rats. World J Surg 20:11–16
Polat C, Aktepe OC, Akbulut G, Yilmaz S, Arikan Y, Dilek ON, Gokce O (2003) The effects of increased intra-abdominal pressure on bacterial translocation. Yonsei Med J 44(2):259–264
Smith HS (2011) Carbon dioxide embolism during pneumoperitoneum for laparoscopic surgery: a case report. AANA J 79:371–373
Eiriksson K, Fors D, Rubertsson S, Arvidsson D (2011) High intra-abdominal pressure during experimental laparoscopic liver resection reduces bleeding but increases the risk of gas embolism. Br J Surg 98(6):845–852
Gutt CN, Schmandra TC (1999) Portal venous flow during CO2 pneumoperitoneum in the rat. Surg Endosc 13:902–905
Schmandra TC, Kim ZG, Gutt CN (2001) Effect of insufflation gas and intraabdominal pressure on portal venous flow during pneumoperitoneum in the rat. Surg Endosc 15:405–408
Jakimowicz J, Stultiëns G, Smulders F (1998) Laparoscopic insufflation of the abdomen reduces portal venous flow. Surg Endosc 12(2):129–132
Richter S, Olinger A, Hildebrandt U, Menger MD, Vollmar B (2001) Loss of physiologic hepatic blood flow control (“hepatic arterial buffer response”) during CO2 pneumoperitoneum in the rat. Anesth Analg 93:872–877
Schmidt SC, Schumacher G, Klage N, Chopra S, Neuhaus P, Neumann U (2010) The impact of carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum on liver regeneration after liver resection in a rat model. Surg Endosc 24:1–8
Avital S, Itash R, Szomstein S, Rosenthal R, Inbar R, Sckornik Y, Weinbroum A (2009) Correlation of CO2 pneumoperitoneal pressures between rodents and humans. Surg Endosc 23(1):50–54
Perrin M, Fletcher A (2004) Laparoscopic abdominal surgery. Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain 4(4):107–110
Matsumoto T, Tsuboi S, Dolgor B, Bandoh T, Yoshida T, Kitano S (2001) The effect of gases in the intraperitoneal space on cytokine response and bacterial translocation in a rat model. Surg Endosc 15:80–84
Martins PNA, Theruvath TP, Neuhaus P (2007) Rodent models of partial hepatectomies. Liver Int 28:3–11
Okano T, Ohwada S, Nakasone Y, Sato Y, Ogawa T, Tago K, Morishita Y (2001) Blood transfusion causes deterioration in liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in rats. J Surg Res 101(2):157–165
Endo Y, Ohta M, Sasaki A et al (2007) A comparative study of the long-term outcomes after laparoscopy-assisted and open left lateral hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 19:171–174
Güven HE, Oral S (2007) Liver enzyme alterations after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J Gastrointest Liver Dis 16:391–394
Glantzounis GK, Tselepis AD, Tambaki AP, Trikalinos TA, Manataki AD, Galaris DA, Tsimoyiannis EC, Kappas AM (2001) Laparoscopic surgery-induced changes in oxidative stress markers in human plasma. Surg Endosc 15:1315–1319
Eryılmaz HB, Memis D, Sezer A, Inal MT (2012) The effects of different insufflation pressures on liver functions assessed with LiMON on patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Sci World J. doi:10.1100/2012/172575 (Epub 24 April 2012)
Morino M, Giraudo G, Festa V (1998) Alterations in hepatic function during laparoscopic surgery: an experimental clinical study. Surg Endosc 12:968–972
Ferrari R (1994) Oxygen-Free radicals at myocardial level: effects of ischemia and reperfusion. Adv Exp Med Biol 366:99–111
Kloner RA, Przyklenk K, Whittaker P (1989) Deleterious effects of oxygen radicals in ischemia/reperfusion. Resolved and unresolved issues. Circulation 80:1115–1127
Foschi D, Castoldi L, Lesma A, Musazzi M, Benevento A, Trabucchi E (1993) Effects of ischaemia and reperfusion on liver regeneration in rats. Eur J Surg 59:393–398
Camargo CA Jr, Madden JF, Gao W, Selvan RS, Clavien PA (1997) Interleukin-6 protects liver against warm ischemia/reperfusion injury and promotes hepatocyte proliferation in the rodent. Hepatology 26(6):1513–1520
Usami M, Furuchi K, Shiroiwa H, Saitoh Y (1994) Effect of repeated portal-triad cross-clamping during partial hepatectomy on hepatic regeneration in normal and cirrhotic rats. J Surg Res 57(5):541–548
Hazebroek EJ, Haitsma JJ, Lachmann B, Steyerberg EW, de Bruin RW, Bouvy ND, Bonjer HJ (2002) Impact of carbon dioxide and helium insufflation on cardiorespiratory function during prolonged pneumoperitoneum in an experimental rat model. Surg Endosc 16:1073–1078
Nickkholgh A, Barro-Bejarano M, Liang R, Zorn M, Mehrabi A, Gebhard MM, Büchler MW, Gutt CN, Schemmer P (2008) Signs of reperfusion injury following CO2 pneumoperitoneum: an in vivo microscopy study. Surg Endosc 22:122–128
Kaya Y, Aral W, Coskun T, Erkasap N, Var A (2002) Increased intraabdominal pressure impairs liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in rats. J Surg Res 108:250–257
Yagmurdur MC, Basaran O, Ozdemir H, Gur G, Turan M, Karakayali H, Haberal M (2004) The impact of transient elevation of intraabdominal pressure on liver regeneration in the rat. J Investig Surg 17:315–322
Gagner M (2010) High-pressure carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum before major liver resection in a rat model is not realistic and cannot be transposed to humans when studying liver regeneration. Surg Endosc 25:988–989
Sammour T, Mittal A, Loveday BP, Kahokehr A, Phillips AR, Windsor JA, Hill AG (2009) Systematic review of oxidative stress associated with pneumoperitoneum. Br J Surg 96:836–850
Xu GS, Liu HN, Li J, Wu XL, Dai XM, Liu YH (2009) Hepatic injury induced by carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum in experimental rats. World J Gastroenterol 15(24):3060–3064
Biffl WL, Moore EE, Moore FA, Peterson VM (1996) Interleukin-6 in the injured patient marker of injury or mediator of inflammation? Ann Surg 224:647–664
Xing Z, Gauldie J, Cox G, Baumann H, Jordana M, Lei XF, Achong MK (1998) IL-6 is an antiinflammatory cytokine required for controlling local or systemic acute inflammatory responses. J Clin Investig 101:311–320
Otsuka Y, Katagiri T, Ishii J, Maeda T, Kubota Y, Tamura A, Tsuchiya M, Kaneko H (2013) Gas embolism in laparoscopic hepatectomy: what is the optimal pneumoperitoneal pressure for laparoscopic major hepatectomy? J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 20:137–140
Are C, Fong Y, Geller DA (2005) Laparoscopic liver resection. Adv Surg 39:57–75
Buell JF, Koffron AJ, Thomas MJ, Rudich S, Abecassis M, Woodle ES (2005) Laparoscopic liver resection. J Am Coll Surg 200:472–480
Cannon RM, Brock GN, Marvin MR, Buell JF (2011) Laparoscopic liver resection: an examination of our first 300 patients. J Am Coll Surg 213:501–507
Leister I, Schüler P, Vollmar B, Füzesi L, Kahler E, Becker H, Markus PM (2004) Microcirculation and excretory function of the liver under conditions of carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum. Surg Endosc 18:1358–1363
Junghans T, Böhm B, Meyer E (2000) Influence of nitrous oxide anesthesia on venous gas embolism with carbon dioxide and helium during pneumoperitoneum. Surg Endosc 14:1167–1170
Nesek-Adam V, Rasić Z, Vnuk D, Schwarz D, Rasić D, Crvenković D (2010) Ischemic preconditioning decreases laparoscopy induced oxidative stress in the liver. Coll Antropol 34:571–576
Cevrioglu AS, Yilmaz S, Koken T, Tokyol C, Yilmazer M, Fenkci IV (2004) Comparison of the effects of low intra-abdominal pressure and ischaemic preconditioning on the generation of oxidative stress markers and inflammatory cytokines during laparoscopy in rats. Hum Reprod 19:2144–2151
Avraamidou A, Marinis A, Asonitis S, Perrea D, Polymeneas G, Voros D, Argyra E (2012) The impact of ischemic preconditioning on hemodynamic, biochemical and inflammatory alterations induced by intra-abdominal hypertension: an experimental study in a porcine model. Langenbecks Arch Surg 397:1333–1341
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Ms. Mayumi Takeda for her technical assistance.
Disclosures
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. No financial support was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Komori, Y., Iwashita, Y., Ohta, M. et al. Effects of different pressure levels of CO2 pneumoperitoneum on liver regeneration after liver resection in a rat model. Surg Endosc 28, 2466–2473 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3498-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-014-3498-6