Abstract
Background
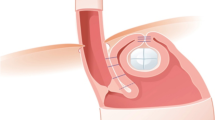
The full-thickness Plicator® (Ethicon Endosurgery, Sommerville, NJ, USA) was developed for endoscopic treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The goal is to restructure the antireflux barrier by delivering transmural pledgeted sutures through the gastric cardia. To date, studies using this device have involved the placement of a single suture to create the plication. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the 12-month safety and efficacy of this procedure using multiple implants to restructure the gastroesophageal (GE) junction.
Methods
A multicenter, prospective, open-label trial was conducted at four tertiary centers. Eligibility criteria included symptomatic GERD [GERD Health-Related Quality-of-Life (GERD-HRQL) questionnaire, off of medication], and pathologic reflux (abnormal 24-h pH) requiring daily proton pump inhibitor therapy. Patients with Barrett’s epithelium, esophageal dysmotility, hiatal hernia >3 cm, and esophagitis (grade III or greater) were excluded. All patients underwent endoscopic full-thickness plication with linear placement of at least two transmural pledgeted sutures in the anterior gastric cardia.
Results
Forty-one patients were treated. Twelve months post treatment, 74% of patients demonstrated improvement in GERD-HRQL scores by ≥50%, with mean decrease of 17.6 points compared with baseline (7.8 vs. 25.4, p < 0.001). Using an intention-to-treat model, 63% of patients had symptomatic improvements of ≥50%, with mean GERD-HRQL decrease of 15.0 (11.0 vs. 26.0, p < 0.001). The need for daily proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy was eliminated in 69% of patients at 12 months on a per-protocol basis, and 59% on an intention-to-treat basis. Adverse events included postprocedure abdominal pain (44%), shoulder pain (24%), and chest pain (17%). No long-term adverse events occurred.
Conclusions
Endoscopic full-thickness plication using multiple Plicator implants can be used safely and effectively to improve GERD symptoms and reduce medication use.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camilleri M, Dubois D, Coulie B, Jones M, Kahrilas PJ, Rentz AM, Sonnenberg A, Stanghellini V, Stewart WF, Tack J, Talley NJ, Whitehead W, Revicki DA (2005) Prevalence and socioeconomic impact of upper gastrointestinal disorders in the United States: results of the US upper gastrointestinal study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:543–552
Farup C, Kleinman L, Sloan S, Ganoczy D, Chee E, Lee C, Revicki D (2001) The impact of nocturnal symptoms associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease on health-related quality of life. Arch Intern Med 161:45–52
Kulig M, Leodolter A, Vieth M, Schulte E, Jaspersen D, Labenz J, Lind T, Meyer-Sabellek W, Malfertheiner P, Stolte M, Willich SN (2003) Quality of life in relation to symptoms in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease–an analysis based on the ProGERD initiative. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 18:767–776
Shaheen N, Ransohoff DF (2002) Gastroesophageal reflux, Barrett esophagus, and esophageal cancer: scientific review. JAMA 287:1972–1981
Lagergren J, Bergstrom R, Lindgren A, Nyren O (1999) Symptomatic gastroesophageal reflux as a risk factor for esophageal adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 340:825–831
Howden CW, Castell DO, Cohen S, Freston JW, Orlando RC, Robinson M (1995) The rationale for continuous maintenance treatment of reflux esophagitis. Arch Intern Med 155:1465–1471
Klinkenberg-Knol EC, Nelis F, Dent J, Snel P, Mitchell B, Prichard P, Lloyd D, Havu N, Frame MH, Roman J, Walan A (2000) Long-term omeprazole treatment in resistant gastroesophageal reflux disease: efficacy, safety, and influence on gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 118:661–669
DeVault KR, Castell DO (2005) Updated guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol 100:190–200
Myrvold HE, Lundell L, Miettinen P, Pedersen SA, Liedman B, Hatlebakk J, Julkunen R, Levander K, Lamm M, Mattson C, Carlsson J, Stahlhammar NO (2001) The cost of long-term therapy for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a randomized trial comparing omeprazole and open anti-reflux surgery. Gut 49:488–494
Leite L, Johnston B, Just R, Castell D (1996) Persistent acid secretion during omeprazole therapy: a study of gastric acid profiles in patients demonstrating failure of omeprazole therapy. Am J Gastroenterol 91:1527–1531
Castell DO, Kahrilas PJ, Richter JE, Vakil NB, Johnson DA, Zuckerman S, Skammer W, Levine JG (2002) Esomeprazole (40 mg) compared with lansoprazole (30 mg) in the treatment of erosive esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol 97:575–583
Sgromo B, Irvine LA, Cuschieri A, Shimi SM (2008) Long-term comparative outcome between laparoscopic total Nissen and Toupet fundoplication: symptomatic relief, patient satisfaction and quality of life. Surg Endosc 22:1048–1053
Strate U, Emmermann A, Fibbe C, Layer P, Zornig C (2008) Laparoscopic fundoplication: Nissen versus Toupet two-year outcome of a prospective randomized study of 200 patients regarding preoperative esophageal motility. Surg Endosc 22:21–30
Guerin E, Betroune K, Closset J, Mehdi A, Lefebvre JC, Houben JJ, Gelin M, Vaneukem P, El Nakadi I (2007) Nissen versus Toupet fundoplication: results of a randomized and multicenter trial. Surg Endosc 21:1985–1990
Bammer T, Hinder R, Klaus A, Klingler P (2001) Five- to eight-year outcome of the first laparoscopic Nissen fundoplications. J Gastrointest Surg 5:42–48
Biertho L, Sebajang H, Anvari M (2006) Effects of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication on esophageal motility: long-term results. Surg Endosc 20:619–623
Khajanchee YS, O’Rourke RW, Lockhart B, Patterson EJ, Hansen PD, Swanstrom LL (2002) Postoperative symptoms and failure after antireflux surgery. Arch Surg 137:1008–1014
Pessaux P, Arnaud JP, Ghavami B, Flament JB, Trebuchet G, Meyer C, Huten N, Tuech JJ, Champault G (2002) Morbidity of laparoscopic fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux: a retrospective study about 1470 patients. Hepatogastroenterology 49:447–450
Rantanen TK, Salo JA, Sipponen JT (1999) Fatal and life-threatening complications in antireflux surgery: analysis of 5,502 operations. Br J Surg 86:1573–1577
Morgenthal CB, Smith CD (2007) Nissen fundoplication: three causes of failure (video). Surg Endosc 21:1006
Herbella FA, Tedesco P, Nipomnick I, Fisichella PM, Patti MG (2007) Effect of partial and total laparoscopic fundoplication on esophageal body motility. Surg Endosc 21:285–288
Oelschlager BK, Lal DR, Jensen E, Cahill M, Quiroga E, Pellegrini CA (2006) Medium- and long-term outcome of laparoscopic redo fundoplication. Surg Endosc 20:1817–1823
Youssef YK, Shekar N, Lutfi R, Richards WO, Torquati A (2006) Long-term evaluation of patient satisfaction and reflux symptoms after laparoscopic fundoplication with Collis gastroplasty. Surg Endosc 20:1702–1705
Biertho L, Sebajang H, Allen C, Anvari M (2006) Does laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication lead to chronic gastrointestinal dysfunction? Surg Endosc 20:1360–1363
Zehetner J, Holzinger F, Breuhahn T, Geppert C, Klaiber C (2006) Five-year results of laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication as the primary surgical repair in GERD patients: is it durable? Surg Endosc 20:220–225
Ozmen V, Oran ES, Gorgun E, Asoglu O, Igci A, Kecer M, Dizdaroglu F (2006) Histologic and clinical outcome after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease and Barrett’s esophagus. Surg Endosc 20:226–229
Granderath FA, Kamolz T, Pointner R (2005) Outcome of laparoscopic redo fundoplication. Surg Endosc 19:863
Papasavas PK, Keenan RJ, Yeaney WW, Caushaj PF, Gagne DJ, Landreneau RJ (2003) Effectiveness of laparoscopic fundoplication in relieving the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and eliminating antireflux medical therapy. Surg Endosc 17:1200–1205
Chen YK, Raijman I, Ben-Menachem T, Starpoli AA, Liu J, Pazwash H, Weiland S, Shahrier M, Fortajada E, Saltzman JR, Carr-Locke DL (2005) Long-term outcomes of endoluminal gastroplication: a US multicenter trial. Gastrointest Endosc 51:659–667
Schwartz MP, Wellink H, Gooszen HG, Conchillo JM, Samsom M, Smout AJ (2007) Endoscopic gastroplication for the treatment of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a randomised, sham-controlled trial. Gut 56:20–28
Triadafilopoulos G, Di Baise JK, Nostrant TT, Stollman NH, Anderson PK, Wolfe MM, Rothstein RI, Wo JM, Corley DA, Patti MG, Antignano LV, Goff JS, Edmundowicz SA, Castell DO, Rabine JC, Kim MS, Utley DS (2002) The Stretta procedure for the treatment of GERD: 6- and 12-month follow-up of the US open label trial. Gastrointest Endosc 55:149–156
Triadafilopoulos G (2004) Changes in GERD symptom scores correlate with improvement in esophageal acid exposure after the Stretta procedure. Surg Endosc 18:1038–1044
Cohen LB, Johnson DA, Ganz RA, Aisenberg J, Deviere J, Foley TR, Haber GB, Peters JH, Lehman GA (2005) Enteryx implantation for GERD: expanded multicenter trial results and interim post-approval followup to 24 months. Gastrointest Endosc 61:650–658
Deviere J, Costamagna G, Neuhaus H, Voderholzer W, Louis H, Tringali A, Marchese M, Fiedler T, Darb-Esfahani P, Schumacher B (2005) Nonresorbable copolymer implantation for gastroesophageal reflux disease: a randomized sham-controlled multicenter trial. Gastroenterology 128:532–540
Cipolletta L, Rotondano G, Dughera L, Repici A, Bianco MA, De Angelis C, Vingiani AM, Battaglia E (2005) Delivery of radiofrequency energy to the gastroesophageal junction (Stretta procedure) for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Surg Endosc 19:849–853
McClusky DA, Khaitan L, Swafford VA, Smith CD (2007) Radiofrequency energy delivery to the lower esophageal sphincter (Stretta procedure) in patients with recurrent reflux after antireflux surgery: can surgery be avoided? Surg Endosc 21:1207–1211
Tam WC, Schoeman MN, Zhang Q, Dent J, Rigda R, Utley D, Holloway RH (2003) Delivery of radiofrequency energy to the lower oesophageal sphincter and gastric cardia inhibits transient lower oesophageal sphincter relaxations and gastro-oesophageal reflux in patients with reflux disease. Gut 52:479–485
Schiefke I, Zabel-Langhennig A, Neumann S, Feisthammel J, Moessner J, Caca K (2005) Long term failure of endoscopic gastroplication (EndoCinch). Gut 54:752–758
Rothstein R, Filipi C, Caca K, Pruitt R, Mergener K, Torquati A, Haber G, Chen Y, Chang K, Wong D, Deviere J, Pleskow D, Lightdale C, Ades A, Kozarek R, Richards W, Lembo A (2006) Endoscopic full-thickness plication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a randomized, sham-controlled trial. Gastroenterology 131:704–712
Pleskow D, Rothstein R, Kozarek R, Haber G, Gostout C, Lembo A (2006) Endoscopic full-thickness plication for the treatment of GERD: long-term multicenter results. Surg Endosc 21:439–444
Pleskow D, Rothstein R, Kozarek R, Haber G, Gostout C, Lembo A (2008) Endoscopic full-thickness plication for the treatment of GERD: five-year long-term multicenter results. Surg Endosc 22:326–332
Contini S, Bertele A, Nervi G, Zinicola R, Scarpignato C (2002) Quality of life for patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease 2 years after laparoscopic fundoplication. Evaluation of the results obtained during the initial experience. Surg Endosc 16:1555–1560
Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, Dent J, Jones R (2006) The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol 101:1900–1920
Torquati A, Richards WO (2007) Endoluminal GERD treatments: critical appraisal of current literature with evidence-based medicine instruments. Surg Endosc 21:697–706
von Renteln D, Brey U, Riecken B, Caca K. Endoscopic full-thickness plication (Plicator) with two serially placed implants improves esophagitis, reduces PPI use and esophageal acid exposure. Endoscopy 40:173-178
von Renteln D, Schiefke I, Fuchs KH, Raczynski S, Philipper M, Breithaupt W, Caca K, Neuhaus H (2008) Endoscopic full-thickness plication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease by application of multiple Plicator implants: a multi-center study. Gastrointest Endosc 68:833–844
Campos GM, Peters JH, De Meester TR, Oberg S, Crookes PF, Tan S, De Meester SR, Hagen JA, Bremner CG (1999) Multivariate analysis of factors predicting outcome after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 3:292–300
Pearl J, Marks J (2007) Endoluminal therapies for GERD: are they dead? Surg Endosc 21:1–4
Mainie I, Tutuian R, Agrawal A, Adams D, Castell DO (2006) Combined multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH monitoring to select patients with persistent gastro-oesophageal reflux for laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Br J Surg 93:1483–1487
von Renteln D, Kaehler G, Eickhoff A, Riecken B, Caca K (2008) Gastric full-thickness suturing following NOTES procedures for closure of the access site to the peritoneal cavity. Endoscopy 40:E99–E100
McGee MF, Marks JM, Jin J, Williams C, Chak A, Schomisch SJ, Andrews J, Okada S, Ponsky JL (2008) Complete endoscopic closure of gastric defects using a full-thickness tissue plicating device. J Gastrointest Surg 12:38–45
McGee MF, Marks JM, Onders RP, Chak A, Jin J, Williams CP, Schomisch SJ, Ponsky JL (2008) Complete endoscopic closure of gastrotomy after natural orifice translumenal endoscopic surgery using the NDO Plicator. Surg Endosc 22:214–220
von Renteln D, Riecken B, Walz B, Caca K (2008) Endoscopic GIST resection using FlushKnife ESD and subsequent perforation closure by means of endoscopic full-thickness suturing. Endoscopy 40:E224–E225
von Renteln D, Schmidt A, Riecken B, Caca K (2008) Gastric full-thickness suturing during endoscopic mucosal resection and for treatment of gastric wall defects. Gastrointest Endosc 67:738–744
von Renteln D, Eickhoff A, Kaehler G, Riecken B, Caca K (2009) Endoscopic closure of the NOTES access site to the peritoneal cavity by means of transmural resorbable sutures: an animal survival study. Endoscopy 41:154–159
Rattner D, Kalloo A (2006) ASGE/SAGES Working Group on Natural Orifice Translumenal Endoscopic Surgery. Surg Endosc 20:329–333
MacFadyen BV, Cuschieri A (2005) Endoluminal surgery. Surg Endosc 19:1–3
Conflict of interest statement
The authors Daniel von Renteln, Ingolf Schiefke, Karl-Hermann Fuchs, Susanne Raczynski, Michael Philipper, Wolfram Breithaupt, and Horst Neuhaus declare that they have no conflict of interest including any financial interest in the product being discussed.
Karel Caca declares that he has served in the capacity as a member of the NDO Surgical, Inc. Medical Advisory Board from October 3, 2006, to October 3, 2007 and has received honoraria for speaking and training. Research funding was granted by NDO Surgical, Inc, Mansfield, MA. Research funding contained material support (Plicator device and sutures), financing of the Plicator procedures, and costs for data processing and statistical analysis by QST Consultations, Ltd. (Allendale, MI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Endoscopic full-thickness plication and hernia repair utilizing three implants (WMV 11474 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
von Renteln, D., Schiefke, I., Fuchs, K.H. et al. Endoscopic full-thickness plication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease using multiple Plicator implants: 12-month multicenter study results. Surg Endosc 23, 1866–1875 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0490-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-009-0490-7