Abstract
Background
Laparoscopic antireflux surgery has become an established method of treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. This study compares the long-term outcome of total (Nissen) and partial (Toupet) fundoplication, performed in a single institution, by evaluating symptoms and quality of life.
Methods
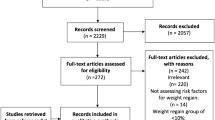
266 patients who underwent laparoscopic Nissen or Toupet fundoplication completed a preoperative reflux symptom questionnaire. Postsurgery symptom evaluation, patient satisfaction and quality of life in reflux and dyspepsia (QOLRAD) questionnaires were sent to these patients in December 2004. The two groups were compared for each item nonparametrically.
Results
Completed questionnaires were received from 161 patients (61%) of whom 99 had a laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication and 62 laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication. Both procedures were equivalent in improving reflux symptom scores in the long term, 79/99 (80%) and 56/62 (90%) were either symptom free or had obtained significant symptomatic relief. Both groups had equivalent QoL scores on the QOLRAD questionnaire. An equivalent number of patients (86% and 83.9% after Nissen and Toupet, respectively) were sufficiently satisfied to recommend antireflux surgery to a friend or relative complaining of reflux symptoms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, in patients who have returned the questionnaire, long-term satisfaction, general symptom scores, and quality of life are equivalent after laparoscopic Nissen (complete) or Toupet (partial) fundoplication. There is however, a significant increased prevalence of persistent heartburn after laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nissen R (1961) Gastropexy and ‘fundoplication’ in surgeical treatment of hiatal hernia. Am J Dig Dis 6:954–961
Toupet A (1963) Technique d’oesophago-gastroplastie avec phrenogastrpexie appliqué dans la cure radicale des hernies hiatales et comme complement de l’operation d’Heller dans les cardiospasmes. Mem Acad Chir Paris 89:384–389
Boutelier P, Jansson G (1982) An alternative fundoplicative maneuver for gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Surg 143:260–264
Mosnier H, Leport J, Aubert A, Kianmanesh R, et al. (1995) Laparoscopic posterior fundoplication in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux. J Am Coll Surg 81:220–224
Cuschieri A, Hunter J, Wolf B, et al. (1993) Multicentre evaluation of laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Preliminary report. Surg Endosc 7:505–510
Dallemagne B, Weerts JM, Jehaes C, et al. (1996) Causes of failures in laparoscopic antireflux operations. Surg Endosc 10:305–310
Watson A, De Beaux AC (2001) Complications of laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Surg Endosc 15:344–352
Jobe BA, Wallace J (1997) Evaluation of laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication as a primary repair for all patients with medically resistant gastroesophageal reflux. Surg Endosc 11:1080–1083
Fernando HC, Luketich JD, Christie NA, et al. (2002) Outcomes of Laparoscopic Toupet compared to Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Surg Endosc 16:905–908
Korolija D, Sauerland S, Wood-Dauphinee S, et al. (2004). Evaluation of quality of life after laparoscopic surgery: Evidence-based guidelines of the European Association for Endoscopic Surgery. Surg Endosc 18(6):879–897
Catarci M, Gentileschi P, Papi C, et al. (2004) Evidence-based appraisal of antireflux fundoplication. Ann Surg 239:325–337
Kamolz T, Granderath FA, Bammer T, et al. (2001) Psychological intervention influences the outcome of laparoscopic antireflux surgery in patients with stress-related symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 36(8):800–805
Peters J (2001) Society of American Gastrointestinal Endoscopic Surgeons. SAGES Scientific session and postgraduate course, April 18–21, St Louis, Missouri
Anderson JR (2006) In: Griffin SM, Raimes SAA Oesophago-gastric surgery companion to specialist surgical practice. Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 345–363
Kamolz T, Granderath FA, Pointner R, et al. (2002) Postprandial bloating after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: a cause of comorbidity? Can J Surg 45(4):306–307
Velanovich V (2003) Medication usage and additional esophageal procedures after antireflux surgery. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 13(3):161–164
Lord RV, Kaminski A, Oberg S, et al. (2002) Absence of gastroesophageal reflux disease in a majority of patients taking acid suppression medications after Nissen fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 6(1):3–9; discussion
Zornig C, Strate U, Emmermann A, et al. (2002) Nissen vs. Toupet laparoscopic fundoplication. Surg Endosc 16:758–766
Stewart GD, Watson AJ, Lamb PJ, et al. (2004) Comparison of three different procedures for antireflux surgery. Br J Surg 91(6):724–729
Laws HL, Clements RH, Swillie CM (1997) A randomized, prospective comparison of the Nissen fundoplication versus the Toupet fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg 225:647–654
Watson DI, Jamieson GG, Pike GK, et al. (1999) Prospective randomized double-blind trial between laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication and anterior partial fundoplication. Br J Surg 86:123–130
Khajanchee YS, O’Rourke RW, Lockhart B, et al. (2002) Postoperative symptoms and failure after antireflux surgery. Arch Surg 137(9):1008–1013; discussion 1013–1014
Kamolz T, Bammer T, Wykypiel H, et al. (2000) Quality of life and surgical outcome after laparoscopic Nissen and Toupet fundoplication: one-year follow-up. Endoscopy 32(5):363–368
Wise JL, Murray JA (2007) Utlising multichannel intraluminal impedance for diagnosing GERD: a review. Dis Esophagus 20:83–88
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sgromo, B., Irvine, L., Cuschieri, A. et al. Long-term comparative outcome between laparoscopic total Nissen and Toupet fundoplication: Symptomatic relief, patient satisfaction and quality of life. Surg Endosc 22, 1048–1053 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9671-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9671-4