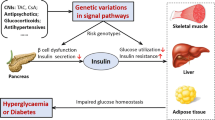
Abstract
Diabetes is known to increase susceptibility to hypertension due to increase in inflammation, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction, leading to vascular stiffness. The polytherapy might lead to several drug–drug interactions (DDIs), which cause certain life-threatening complications such as diabetic nephropathy and hypoglycaemia. So, in this review we focused on drug–drug interactions and impact of genetic factors on drug responses for better disease management. Drug–drug interactions (DDIs) may act either synergistically or antagonistically. For instance, a combination of metformin with angiotensin II receptor antagonist or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) synergistically improves glucose absorption, whereas the same hypertensive drug combination with sulphonylurea might cause severe hypoglycaemia sometimes. Thiazolidinediones (TDZs) can cause fluid retention and heart failure when taken alone, but a combination of angiotensin II receptor antagonist with TZDs prevents these side effects. Interindividual genetic variation affects the DDI response. We found two prominent genes, GLUT4 and PPAR-γ, which are common targets for most of the drug. So, all of these findings established a connection between drug–drug interaction and genetics, which might be used for effective disease management.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- HTN:
-
Hypertension
- DDIs:
-
Drug–drug interactions
- IDF:
-
International Diabetes Federation
- RAAS:
-
Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system
- ADA:
-
American Diabetes Association
- ACEIs:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
- ARBs:
-
Angiotensin receptor blockers
- PPIs:
-
Proton pump inhibitors
- AMPK:
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- OCT1:
-
Organic cation transporter 1
- OCT2:
-
Organic cation transporter 2
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- CAMKK2:
-
Calmodulin kinase kinase 2
- GLUT 4:
-
Glucose transporter-4
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
- IRS-1:
-
Insulin receptor substrate-1
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3 kinase
- SUR1:
-
Sulphonylurea receptor
- IR:
-
Insulin receptor
- AT1:
-
Angiotensin II type 1
- AT2:
-
Angiotensin II type 2
- TDZs:
-
Thiazolidinediones
- PPRE:
-
PPARγ response elements
- RXR:
-
Retinoid X receptor
- PAX6:
-
Paired box protein-6
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- SGLT2:
-
Sodium–glucose co-transporter-2
- SGLT2Is:
-
Sodium–glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors
- NKCC2:
-
Sodium–potassium–chloride co-transporters
- CCB:
-
Calcium channel blockers
References
Abdul-Ghani MA, Norton L, Defronzo RA (2011) Role of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT 2) inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev 32(4):515–531. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2010-0029. (Epub 2011 May 23 PMID: 21606218)
American Diabetes Association, What are my options? https://diabetes.org/healthy-living/medication-treatments/oral-medication/what-are-my-options (Accessed 4 Aug 2022)
Arauz-Pacheco C, Ramirez LC, Rios JM, Raskin P (1990) Hypoglycemia induced by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes receiving sulfonylurea therapy. American J Med 89(6):811–813
Benson SC, Pershadsingh HA, Ho CI, Chittiboyina A, Desai P, Pravenec M, Qi N, Wang J, Avery MA, Kurtz TW (2004) Identification of telmisartan as a unique angiotensin II receptor antagonist with selective PPARgamma-modulating activity. Hypertension 43(5):993–1002. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000123072.34629.57. (Epub 2004 Mar 8 PMID: 15007034)
Berger J, Bailey P, Biswas C, Cullinan CA, Doebber TW, Hayes NS, Saperstein R, Smith RG, Leibowitz MD (1996) Thiazolidinediones produce a conformational change in peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor-gamma: binding and activation correlate with antidiabetic actions in db/db mice. Endocrinology 137(10):4189–4195. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.137.10.8828476. (PMID: 8828476)
Boros LG et al (2015) Targeted 13C-labeled tracer fate associations for drug efficacy testing in cancer. In: Mazurek S, Shoshan M (eds) Tumor cell metabolism. Springer, Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-1824-5_15
Bushardt RL, Massey EB, Simpson TW, Ariail JC, Simpson KN (2008) Polypharmacy: misleading, but manageable. ClinInterv Aging 3(2):383–389. https://doi.org/10.2147/cia.s2468. (PMID: 18686760)
Carmosino M, Rizzo F, Ferrari P, Torielli L, Ferrandi M, Bianchi G, Svelto M, Valenti G (2011) NKCC2 is activated in Milan hypertensive rats contributing to the maintenance of salt-sensitive hypertension. Pflugers Arch 462(2):281–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-011-0967-9. (Epub 2011 May 7 PMID: 21553016)
Custodio JM, Wu CY, Benet LZ (2008) Predicting drug disposition, absorption/elimination/transporter interplay and the role of food on drug absorption. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60(6):717–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2007.08.043. (Epub 2007 Nov 28 PMID: 18199522)
de Oliveira Alvim R, Santos PC, Nascimento RM, Coelho GL, Mill JG, Krieger JE, Pereira AC (2012) BDKRB2 +9/−9 polymorphism is associated with higher risk for diabetes mellitus in the Brazilian general population. Exp Diabetes Res 2012:480251. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/480251 (Epub 2012 Nov 29. PMID: 23243416)
Delahanty LM, Pan Q, Jablonski KA, Watson KE, McCaffery JM, Shuldiner A, Kahn SE, Knowler WC, Florez JC, Franks PW, Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group (2012) Genetic predictors of weight loss and weight regain after intensive lifestyle modification, metformin treatment, or standard care in the Diabetes Prevention Program. Diabetes Care 35(2):363–366. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-1328. (Epub 2011 Dec 16. PMID: 22179955)
El-Mir MY, Nogueira V, Fontaine E, Avéret N, Rigoulet M, Leverve X (2000) Dimethylbiguanide inhibits cell respiration via an indirect effect targeted on the respiratory chain complex I. J Biol Chem 275(1):223–228. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.1.223. (PMID: 10617608)
Ernst FR, Grizzle AJ (2001) Drug-related morbidity and mortality: updating the cost-of-illness model. J Am Pharm Assoc (wash). 41(2):192–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1086-5802(16)31229-3. (PMID: 11297331)
Fioretto P, Giaccari A, Sesti G (2015) Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin, a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, in diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Diabetol 17(14):142. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-015-0297-x. (PMID: 26474563)
Frishman W, Silverman R (1979) Clinical pharmacology of the new beta-adrenergic blocking drugs. Part 2. Physiologic and metabolic effects. Am Heart J 97(6):797–807. https://doi.org/10.1016/0002-8703(79)90016-4 (PMID: 34990)
Ganesh J, Viswanathan V (2011) Management of diabetic hypertensives. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 15:S374–S379. https://doi.org/10.4103/2230-8210.86982
Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, Blonde L, Bloomgarden ZT, Bush MA, Dagogo-Jack S, Davidson MB, Einhorn D, Garvey WT, Grunberger G, Handelsman Y, Hirsch IB, Jellinger PS, McGill JB, Mechanick JI, Rosenblit PD, Umpierrez GE, Davidson MH (2013) American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists’ comprehensive diabetes management algorithm 2013 consensus statement–executive summary. Endocr Pract 19(3):536–557. https://doi.org/10.4158/EP13176.CS. (PMID: 23816937)
Grilo A, Sáez-Rosas MP, Santos-Morano J, Sánchez E, Moreno-Rey C, Real LM, Ramírez-Lorca R, Sáez ME (2011) Identification of genetic factors associated with susceptibility to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors-induced cough. Pharmacogenet Genom 21(1):10–17. https://doi.org/10.1097/FPC.0b013e328341041c. (PMID: 21052031)
Hagen GA, Frawley TF (1970) Hyponatremia due to sulfonylurea compounds. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 31(5):570–576. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-31-5-570. (PMID: 5470213)
Hernandez R, Teruel T, Lorenzo M (2003) Rosiglitazone produces insulin sensitisation by increasing expression of the insulin receptor and its tyrosine kinase activity in brown adipocytes. Diabetologia 46(12):1618–1628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-003-1236-z. (Epub 2003 Nov 1 PMID: 14595539)
Hill MA, Yang Y, Zhang L, Sun Z, Jia G, Parrish AR, Sowers JR (2021) Insulin resistance, cardiovascular stiffening and cardiovascular disease. Metabolism 119:154766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154766
International Diabetes Federation (IDF) (2021) Diabetes Atlas, 7th edn. International Diabetes Federation, Brussels, Belgium. http://www.diabetesatlas.org. Accessed 13 July 2022
Inagaki N, Gonoi T, Clement JP 4th, Namba N, Inazawa J, Gonzalez G, Aguilar-Bryan L, Seino S, Bryan J (1995) Reconstitution of IKATP: an inward rectifier subunit plus the sulfonylurea receptor. Science 270(5239):1166–1170. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.270.5239.1166. (PMID: 7502040)
Jauch KW, Hartl WH, Georgieff M, Wolfe RR, Dietze GJ, Günther B (1988) Low-dose bradykinin infusion reduces endogenous glucose production in surgical patients. Metabolism 37(2):185–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0026-0495(98)90016-6. (PMID: 3123876)
Jiang S, Hsu YH, Venners SA, Zhang Y, Xing H, Wang X, Xu X (2011) Interactive effect of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AGT1R) polymorphisms and plasma irbesartan concentration on antihypertensive therapeutic responses to irbesartan. J Hypertens 29(5):890–895. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0b013e32834494f6. (PMID: 21346624)
Kang ES, Park SY, Kim HJ, Kim CS, Ahn CW, Cha BS, Lim SK, Nam CM, Lee HC (2005) Effects of Pro12Ala polymorphism of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma2 gene on rosiglitazone response in type 2 diabetes. Clin Pharmacol Ther 78(2):202–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clpt.2005.04.013. (PMID: 16084854)
Kaplan A, Abidi E, El-Yazbi A, Eid A, Booz GW, Zouein FA (2018) Direct cardiovascular impact of SGLT2 inhibitors: mechanisms and effects. Heart Fail Rev 23(3):419–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-017-9665-9. (PMID: 29322280)
Karg MV, Bosch A, Kannenkeril D, Striepe K, Ott C, Schneider MP, Boemke-Zelch F, Linz P, Nagel AM, Titze J, Uder M, Schmieder RE (2018) SGLT-2-inhibition with dapagliflozin reduces tissue sodium content: a randomised controlled trial. Cardiovasc Diabetol 17(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-017-0654-z. (PMID: 29301520)
Kario K, Okada K, Kato M, Nishizawa M, Yoshida T, Asano T, Uchiyama K, Niijima Y, Katsuya T, Urata H, Osuga JI (2019) Twenty-four-hour blood pressure–lowering effect of a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor in patients with diabetes and uncontrolled nocturnal hypertension: results from the randomized, placebo-controlled SACRA study. Circulation 139(18):2089–2097
Kashi Z, Masoumi P, Mahrooz A, Hashemi-Soteh MB, Bahar A, Alizadeh A (2015) The variant organic cation transporter 2 (OCT2)–T201M contribute to changes in insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with metformin. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 108(1):78–83
Klen J, Dolžan V, Janež A (2014) CYP2C9, KCNJ11 and ABCC8 polymorphisms and the response to sulphonylurea treatment in type 2 diabetes patients. Eur J ClinPharmacol 70(4):421–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-014-1641-x. (Epub 2014 Jan 18 PMID: 24442125)
Lago RM, Singh PP, Nesto RW (2007) Diabetes and hypertension. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 3(10):667. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpendmet0638. (PMID: 17893686)
Lehmann JM, Moore LB, Smith-Oliver TA, Wilkison WO, Willson TM, Kliewer SA (1995) An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). J Biol Chem 270(22):12953–12956. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.22.12953. (PMID: 7768881)
Masuda T, Ogura MN, Moriya T, Takahira N, Matsumoto T, Kutsuna T, Hara M, Aiba N, Noda C, Izumi T (2011) Beneficial effects of L- and N-type calcium channel blocker on glucose and lipid metabolism and renal function in patients with hypertension and type II diabetes mellitus. CardiovascTher 29(1):46–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-5922.2009.00126.x. (PMID: 20337636)
Messerli FH, Bangalore S, Bavishi C, Rimoldi SF (2018) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in hypertension: to use or not to use? J Am CollCardiol 71(13):1474–1482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.01.058. (PMID: 29598869)
Mukae S, Itoh S, Aoki S, Iwata T, Nishio K, Sato R, Katagiri T (2002) Association of polymorphisms of the renin-angiotensin system and bradykinin B2 receptor with ACE-inhibitor-related cough. J Hum Hypertens 16(12):857–863. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001486. (PMID: 12522467)
Mustafa HA, Albkrye AMS, AbdAlla BM, Khair MAM, Abdelwahid N, Elnasri HA (2020) Computational determination of human PPARG gene: SNPs and prediction of their effect on protein functions of diabetic patients. ClinTransl Med 9(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40169-020-0258-1. (PMID: 32064572)
Nam YH, Brensinger CM, Bilker WB, Flory JH, Leonard CE, Hennessy S (2021) Association between serious hypoglycemia and calcium-channel blockers used concomitantly with insulin secretagogues. JAMA Netw Open 4(9):e2124443. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.24443. (PMID: 34473261)
Palleria C, Di Paolo A, Giofrè C, Caglioti C, Leuzzi G, Siniscalchi A, De Sarro G, Gallelli L (2013) Pharmacokinetic drug-drug interaction and their implication in clinical management. J Res Med Sci 18(7):601–610 (PMID: 24516494)
Parameshappa B, Rao NV, Gouda TS, Sen S, Chakraborty R, Basha MA, Reddy AS, Kumar SS (2010) A study on drug-drug interaction between anti-hypertensive drug (propranolol) and anti-diabetic drug (glipizide). Ann Biol Res 1(3):35–40
Pei Q, Huang Q, Yang GP, Zhao YC, Yin JY, Song M, Zheng Y, Mo ZH, Zhou HH, Liu ZQ (2013) PPAR-γ2 and PTPRD gene polymorphisms influence type 2 diabetes patients’ response to pioglitazone in China. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34(2):255–261. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2012.144. (Epub 2012 Nov 12 PMID: 23147557)
Pershadsingh HA, Kurtz TW (2004) Insulin-sensitizing effects of telmisartan: implications for treating insulin-resistant hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care 27(4):1015. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.27.4.1015. (PMID: 15047668)
Petrie JR, Guzik TJ, Touyz RM (2018) Diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: clinical insights and vascular mechanisms. Can J Cardiol 34(5):575–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjca.2017.12.005
Prudente S, Di Paola R, Pezzilli S, Garofolo M, Lamacchia O, Filardi T, Mannino GC, Mercuri L, Alberico F, Scarale MG, Sesti G, Morano S, Penno G, Cignarelli M, Copetti M, Trischitta V (2018) Pharmacogenetics of oral antidiabetes drugs: evidence for diverse signals at the IRS1 locus. Pharmacogenomics J 18(3):431–435. https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2017.32. (Epub 2017 Jul 11 PMID: 28696414)
Rizvi AA, Abbas M, Verma S, Verma S, Khan A, Raza ST, Mahdi F (2022) Determinants in tailoring antidiabetic therapies: a personalized approach. Glob Med Genet 21:63
Rosen ED, Spiegelman BM (2000) Molecular regulation of adipogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:145–171. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.16.1.145. (PMID: 11031233)
Scheen AJ (2015) Pharmacodynamics, efficacy and safety of sodium–glucose co-transporter type 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs 75(1):33–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-014-0337-y. (PMID: 25488697)
Schinner S, Dellas C, Schroder M, Heinlein CA, Chang C, Fischer J, Knepel W (2002) Repression of glucagon gene transcription by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma through inhibition of Pax6 transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem 277(3):1941–1948. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109718200. (Epub 2001 Nov 13 PMID: 11707457)
Schoonjans K, Martin G, Staels B, Auwerx J (1997) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors, orphans with ligands and functions. CurrOpinLipidol 8(3):159–166. https://doi.org/10.1097/00041433-199706000-00006. (PMID: 9211064)
Shiuchi T, Cui TX, Wu L, Nakagami H, Takeda-Matsubara Y, Iwai M, Horiuchi M (2002) ACE inhibitor improves insulin resistance in diabetic mouse via bradykinin and NO. Hypertension 40(3):329–334. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.hyp.0000028979.98877.0c. (PMID: 12215475)
Silva PS, Fontana V, Luizon MR, Lacchini R, Silva WA Jr, Biagi C, Tanus-Santos JE (2013) eNOS and BDKRB2 genotypes affect the antihypertensive responses to enalapril. Eur J ClinPharmacol 69(2):167–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-012-1326-2. (Epub 2012 Jun 17 PMID: 22706620)
Soccio RE, Chen ER, Rajapurkar SR, Safabakhsh P, Marinis JM, Dispirito JR, Emmett MJ, Briggs ER, Fang B, Everett LJ, Lim HW, Won KJ, Steger DJ, Wu Y, Civelek M, Voight BF, Lazar MA (2015) Genetic Variation Determines PPARγ Function and Anti-diabetic Drug Response In Vivo. Cell 162(1):33–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.025. (PMID: 26140591)
Sonalker PA, Tofovic SP, Jackson EK (2004) Increased expression of the sodium transporter BSC-1 in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J PharmacolExpTher 311(3):1052–1061. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.104.071209. (Epub 2004 Aug 30 PMID: 15340004)
Sonalker PA, Tofovic SP, Jackson EK (2007) Cellular distribution of the renal bumetanide-sensitive Na-K-2Cl cotransporter BSC-1 in the inner stripe of the outer medulla during the development of hypertension in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. ClinExpPharmacol Physiol 34(12):1307–1312. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04747.x. (PMID: 17973873)
Sunder M, Chang AR, Henry RR (2003) Thiazolidinediones, peripheral edema, and type 2 diabetes: incidence, pathophysiology, and clinical implications. Endocr Pract 9(5):406–416
Takahashi E, Ito M, Miyamoto N, Nagasu T, Ino M, Tanaka I (2005) Increased glucose tolerance in N-type Ca2+ channel alpha(1B)-subunit gene-deficient mice. Int J Mol Med 15(6):937–944 (PMID: 15870896)
Uehara M, Kishikawa H, Isami S, Kisanuki K, Ohkubo Y, Miyamura N, Miyata T, Yano T, Shichiri M (1994) Effect on insulin sensitivity of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors with or without a sulphydryl group: bradykinin may improve insulin resistance in dogs and humans. Diabetologia 37(3):300–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00398058. (PMID: 8174845)
Verma S, Abbas M, Verma S, Khan FH, Raza ST, Siddiqi Z, Ahmad I, Mahdi F (2021) Impact of I/D polymorphism of angiotensin-converting enzyme 1 (ACE1) gene on the severity of COVID-19 patients. Infect Genet Evol 1(91):104801
White M, Racine N, Ducharme A, de Champlain J (2001) Therapeutic potential of angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Expert OpinInvestig Drugs 10(9):1687–1701. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543784.10.9.1687. (PMID: 11772278)
Wilcox CS (2020) Antihypertensive and renal mechanisms of SGLT2 (sodium–glucose linked transporter 2) Inhibitors. Hypertension 75(4):894–901. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.11684. (Epub 2020 Mar 2 PMID: 32114848)
Yagi S, Goto S, Yamamoto T, Kurihara S, Katayama S (2003) Effect of cilnidipine on insulin sensitivity in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertens Res 26(5):383–387. https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.26.383. (PMID: 12887129)
Young PW, Buckle DR, Cantello BC, Chapman H, Clapham JC, Coyle PJ, Haigh D, Hindley RM, Holder JC, Kallender H, Latter AJ, Lawrie KW, Mossakowska D, Murphy GJ, Roxbee Cox L, Smith SA (1998) Identification of high-affinity binding sites for the insulin sensitizer rosiglitazone (BRL-49653) in rodent and human adipocytes using a radioiodinated ligand for peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor gamma. J PharmacolExpTher 284(2):751–759 (PMID: 9454824)
Zhou Y, Ye W, Wang Y, Jiang Z, Meng X, Xiao Q, Zhao Q, Yan J (2015) Genetic variants of OCT1 influence glycemic response to metformin in Han Chinese patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus in Shanghai. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(8):9533
Zou H, Wu G, Lv J, Xu G (2017) Relationship of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) and bradykinin B2 receptor (BDKRB2) polymorphism with diabetic nephropathy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1863(6):1264–1272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.04.002. (Epub 2017 Apr 5. Erratum in: BiochimBiophysActa. 2017 Dec 26;: PMID: 28390948)
Acknowledgements
We are cordially grateful to ERA’s Lucknow Medical College and Hospital, ERA University, for providing intramural funding support (ELMC&H/RCell/2022/81) and laboratory space for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Shuhua Xu.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ansari, A.I., Rizvi, A.A., Verma, S. et al. Interactions between diabetic and hypertensive drugs: a pharmacogenetics approach. Mol Genet Genomics 298, 803–812 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-02011-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-02011-7