Abstract
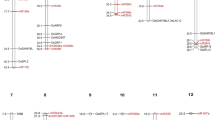
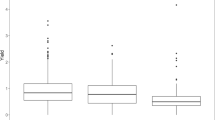
Sugarcane is an economically important commercial crop which provides raw material for the production of sugar, jaggery, bioethanol, biomass and other by-products. Sugarcane breeding till today heavily relies on conventional breeding approaches which is time consuming, laborious and costly. Integration of marker-assisted selection (MAS) in sugarcane genetic improvement programs for difficult to select traits like sucrose content, resistance to pests and diseases and tolerance to abiotic stresses will accelerate varietal development. In the present study, association mapping approach was used to identify QTLs and genes associated with sucrose and other important yield-contributing traits. A mapping panel of 110 diverse sugarcane genotypes and 148 microsatellite primers were used for structured association mapping study. An optimal subpopulation number (ΔK) of 5 was identified by structure analysis. GWAS analysis using TASSEL identified a total of 110 MTAs which were localized into 27 QTLs by GLM and MLM (Q + K, PC + K) approaches. Among the 24 QTLs sequenced, 12 were able to identify potential candidate genes, viz., starch branching enzyme, starch synthase 4, sugar transporters and G3P-DH related to carbohydrate metabolism and hormone pathway-related genes ethylene insensitive 3-like 1, reversion to ethylene sensitive1-like, and auxin response factor associated to juice quality- and yield-related traits. Six markers, NKS 5_185, SCB 270_144, SCB 370_256, NKS 46_176 and UGSM 648_245, associated with juice quality traits and marker SMC31CUQ_304 associated with NMC were validated and identified as significantly associated to the traits by one-way ANOVA analysis. In conclusion, 24 potential QTLs identified in the present study could be used in sugarcane breeding programs after further validation in larger population. The candidate genes from carbohydrate and hormone response pathway presented in this study could be manipulated with genome editing approaches to further improve sugarcane crop.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso JM, Hirayama T, Roman G et al (1999) EIN2, a bifunctional transducer of ethylene and stress responses in Arabidopsis. Science 284:2148–2152. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5423.2148
Alonso-Blanco C, El-Assal SED, Coupland G, Koornneef M (1998) Analysis of natural allelic variation at flowering time loci in the Landsberg erecta and Cape Verde Islands ecotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 149:749–764
Alwala S, Kimbeng CA, Veremis JC, Gravois KA (2009) Identification of molecular markers associated with sugar-related traits in a Saccharum interspecific cross. Euphytica 167:127–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9869-0
Arceneaux G (1967) Cultivated sugarcane of the world and their botanical derivation. Proc ISSCT 12:844–854
Banerjee N, Siraree A, Yadav S et al (2015) Marker–trait association study for sucrose and yield contributing traits in sugarcane (Saccharum spp. hybrid). Euphytica 205:185–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1422-3
Banerjee N, Khan MS, Swapna M et al (2020) Progress and prospects of association mapping in sugarcane (Saccharum species Hybrid), a complex polyploid crop. Sugar Tech 22:939–953
Barnes J, Rutherford R, Botha F, Barnes JM, Rutherford RSBF (1997) The identification of potential genetic markers in sugarcane varieties for the prediction of disease and pest resistance ratings. ProcS Afr Sug Technol Ass 71:57–61
Barreto FZ, Bachega Feijó Rosa JR, Balsalobre TWA, Pastina MM, Silva RR, Hoffman HP, de Souza AP, Garcia AAF, Carneiro MS (2019) A genome-wide association study identified loci for yield component traits in sugarcane (Saccharum spp.). PLoS ONE 14:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219843
Böttcher C, Keyzers RA, Boss PK, Davies C (2010) Sequestration of auxin by the indole-3-acetic acid–amido synthetase GH3-1 in grape berry (Vitis vinifera L.) And the proposed role of auxin conjugation during ripening. J Exp Bot 61:3615–3625. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq174
Buckler ES, Thornsberry JM (2002) Plant molecular diversity and applications to genomics. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:107–111
Cardon LR, Palmer LJ (2003) Population stratification and spurious allelic association. Lancet 361:598–604
Casu RE, Grof CPL, Rae AL et al (2003) Identification of a novel sugar transporter homologue strongly expressed in maturing stem vascular tissues of sugarcane by expressed sequence tag and microarray analysis. Plant Mol Biol 52:371–386. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023957214644
Chang KN, Zhong S, Weirauch MT et al (2013) Temporal transcriptional response to ethylene gas drives growth hormone cross-regulation in Arabidopsis. Elife 2013:675. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.00675
Chao Q, Rothenberg M, Solano R et al (1997) Activation of the ethylene gas response pathway in Arabidopsis by the nuclear protein ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE3 and related proteins. Cell 89:1133–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80300-1
Chaudhary RR (2001) Genetic variability and heritability in sugarcane. Nepal Agric Res J 5:56–59. https://doi.org/10.3126/narj.v4i0.4870
Chen LQ, Hou BH, Lalonde S et al (2010) Sugar transporters for intercellular exchange and nutrition of pathogens. Nature 468:527–532. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09606
Chen Qianhong G, Bleecker AB (1995) Analysis of ethylene signal-transduction kinetics associated with seedling-growth response and chitinase induction in wild-type and mutant Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 108:597–607. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.2.597
Clarke JH, Mithen R, Brown JKM, Dean C (1995) QTL analysis of flowering time in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet 248:278–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02191594
Crumpton-Taylor M, Pike M, Lu KJ et al (2013) Starch synthase 4 is essential for coordination of starch granule formation with chloroplast division during Arabidopsis leaf expansion. New Phytol 200:1064–1075. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12455
Cunha CP, Roberto GG, Vicentini R et al (2017) Ethylene-induced transcriptional and hormonal responses at the onset of sugarcane ripening. Sci Rep 7:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43364
D’Hont A (2005) Unraveling the genome structure of polyploids using FISH and GISH; examples of sugarcane and banana. Cytogenet Genome Res 109:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1159/000082378
D’Hont A, Glaszmann JC (2001) Sugarcane genome analysis with molecular markers: a first decade of research. Proc Int Soc Sugar Cane Technol 24:556–559
Daniels J, Roach BT (1987) Taxonomy and evolution. Sugarcane improvement through breeding/edited by Don. J. Heinz
Debibakas S, Rocher S, Garsmeur O et al (2014) Prospecting sugarcane resistance to sugarcane yellow leaf virus by genome-wide association. Theor Appl Genet 127:1719–1732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2334-7
Dillon SL, Shapter FM, Henry RJ et al (2007) Domestication to crop improvement: genetic resources for Sorghum and Saccharum (Andropogoneae). Ann Bot 100:975–989. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcm192
Ding X, Cao Y, Huang L et al (2008) Activation of the indole-3-acetic acid–amido synthetase GH3-8 suppresses expansin expression and promotes salicylate- and jasmonate-independent basal immunity in rice. Plant Cell 20:228–240. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.055657
Doyle J, Doyle J (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus (madison) 12:1315
Dufour P, Deu M, Grivet L et al (1997) Construction of a composite sorghum genome map and comparison with sugarcane, a related complex polyploid. Theor Appl Genet 94:409–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050430
Earl DA, vonHoldt BM (2012) Structure HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing structure output and implementing the Evanno method. Conserv Genet Resour 4:359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02553.x
Fickett N, Gutierrez A, Verma M et al (2019) Genome-wide association mapping identifies markers associated with cane yield components and sucrose traits in the Louisiana sugarcane core collection. Genomics 111:1794–1801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2018.12.002
Gale MD, Devos KM (1998) Comparative genetics in the grasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:1971–1974. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.5.1971
Garsmeur O, Charron C, Bocs S et al (2011) High homologous gene conservation despite extreme autopolyploid redundancy in sugarcane. New Phytol 189:629–642. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03497.x
Garsmeur O, Droc G, Antonise R et al (2018) A mosaic monoploid reference sequence for the highly complex genome of sugarcane. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05051-5
Gouy M, Rousselle Y, Thong Chane A et al (2014) Genome wide association mapping of agro-morphological and disease resistance traits in sugarcane. Euphytica 202:269–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1294-y
Govindaraj P, Natarajan U, Balasundaram NP, M., et al (2005) Development of new microsatellite markers for the identification of interspecific hybrids in sugarcane. Sugar Cane Int 23:30
Govindaraj P, Sindhu R, Balamurugan A, Appunu C (2011) Molecular diversity in sugarcane hybrids (Saccharum spp. Complex) grown in Peninsular and East Coast Zones of Tropical India. Sugar Tech 13:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-011-0095-z
Grivet L, Arruda P (2002) Sugarcane genomics: depicting the complex genome of an important tropical crop. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:122–127
Grivet L, D’Hont A, Dufour P et al (1994) Comparative genome mapping of sugar cane with other species within the Andropogoneae tribe. Heredity (edinb) 73:500–508. https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1994.148
Guilfoyle TJ, Hagen G (2007) Auxin response factors. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:453–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2007.08.014
Guimarães CT, Sills GR, Sobral BWS (1997) Comparative mapping of Andropogoneae: Saccharum L. (sugarcane) and its relation to sorghum and maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:14261–14266. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.26.14261
Hirschhorn JN, Daly MJ (2005) Genome-wide association studies for common diseases and complex traits. Nat Rev Genet 6:95–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1521
Hoang NV, Furtado A, O’Keeffe AJ et al (2017) Association of gene expression with biomass content and composition in sugarcane. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0183417
Hoarau JY, Grivet L, Offmann B et al (2002) Genetic dissection of a modern sugarcane cultivar (Saccharum spp.). II. detection of QTLs for yield components. Theor Appl Genet 105:1027–1037. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1047-5
Indian Sugar Mills Association (ISMA) (2020) Press release: 1st advance estimates of sugar production in 2020–2021. Indian Sugar Mills Assoc
Jackson P, Hogarth D (1992) Genotype × environment interactions in sugarcane. I. Patterns of response across sites and crop-years in north Queensland. Aust J Agric Res 43:1447. https://doi.org/10.1071/ar9921447
Jannoo N, Grivet L, Chantret N et al (2007) Orthologous comparison in a gene-rich region among grasses reveals stability in the sugarcane polyploid genome. Plant J 50:574–585. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03082.x
Ju C, Chang C (2015) Mechanistic insights in ethylene perception and signal transduction. Plant Physiol 169:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00845
Kang MS, Miller JD, Tai PYP et al (1987) Implications of confounding of genotype × year and genotype × crop effects in sugarcane. F Crop Res 15:349–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-4290(87)90022-0
Le Cunff L, Garsmeur O, Raboin LM et al (2008) Diploid/polyploid syntenic shuttle mapping and haplotype-specific chromosome walking toward a rust resistance gene (Bru1) in highly polyploid sugarcane (2n ∼ 12× ∼ 115). Genetics 180:649–660. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.108.091355
Li F, Xie J, Zhu X et al (2018) Genetic basis underlying correlations among growth duration and yield traits revealed by GWAS in rice (Oryza sativa L). Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00650
Liu K, Kang BC, Jiang H et al (2005) A GH3-like gene, CcGH3, isolated from Capsicum chinense L. fruit is regulated by auxin and ethylene. Plant Mol Biol 58:447–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-005-6505-4
Lu YH, D’Hont A, Paulet F et al (1994) Molecular diversity and genome structure in modern sugarcane varieties. Euphytica 78:217–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00027520
Marconi T, Costa E, Miranda H et al (2011) Functional markers for gene mapping and genetic diversity studies in sugarcane. BMC Res Notes. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-4-264
Martin F (1996) Survey of germplasm needs for saccharum species in the United States
McIntyre CL, Whan VA, Croft B et al (2005) Identification and validation of molecular markers associated with Pachymetra root rot and brown rust resistance in sugarcane using map- and association-based approaches. Mol Breed 16:151–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-005-7492-5
McIntyre CL, Goode ML, Cordeiro G et al (2015) Characterisation of alleles of the sucrose phosphate synthase gene family in sugarcane and their association with sugar-related traits. Mol Breed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0286-5
Ming R, Liu SC, Lin YR et al (1998) Detailed alignment of Saccharum and Sorghum chromosomes: comparative organization of closely related diploid and polyploid genomes. Genetics 150:1663–1682
Ming R, Liu SC, Moore PH et al (2001) QTL analysis in a complex autopolyploid: genetic control of sugar content in sugarcane. Genome Res 11:2075–2084. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.198801
Ming R, Wang YW, Draye X et al (2002) Molecular dissection of complex traits in autopolyploids: mapping QTLs affecting sugar yield and related traits in sugarcane. Theor Appl Genet 105:332–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-001-0861-5
Moore P (1995) Temporal and spatial regulation of sucrose accumulation in the sugarcane stem. Funct Plant Biol 22:661. https://doi.org/10.1071/pp9950661
Moore PH (2005) Integration of sucrose accumulation processes across hierarchical scales: towards developing an understanding of the gene-to-crop continuum. F Crop Res 92:119–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2005.01.031
Msomi N, Botha FC (1994) Identification of molecular markers linked to fibre using bulk segregant analysis. In: Proc Annu Congr S Afr Sugar Technol Assoc, pp 41–45
Padmanabhan TSS, Hemaprabha G (2018) Genetic diversity and population structure among 133 elite genotypes of sugarcane (Saccharum spp) for use as parents in sugarcane varietal improvement. 3 Biotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1364-2
Pan YB (2006) Highly polymorphic microsatellite DNA markers for sugarcane germplasm evaluation and variety identity testing. Sugar Tech 8:246–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02943564
Pan Y-B (2010) Databasing molecular identities of sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) clones constructed with microsatellite (SSR) DNA markers. Am J Plant Sci 01:87–94. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2010.12011
Pandey D, Singh SP, Jeena AS et al (2018) Study of genetic variability, heritability and genetic advance for various yield and quality traits in sugarcane genotypes (Saccharum officinarum). Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 7:1464–1472. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.704.165
Papini-Terzi FS, Rocha FR, Vêncio RZNN et al (2009) Sugarcane genes associated with sucrose content. BMC Genomics 10:120. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-10-120
Parthiban S, Govindaraj P, Senthilkumar S (2018) Comparison of relative efficiency of genomic SSR and EST-SSR markers in estimating genetic diversity in sugarcane. Biotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1172-8
Pastina MM, Malosetti M, Gazaffi R et al (2012) A mixed model QTL analysis for sugarcane multiple-harvest-location trial data. Theor Appl Genet 124:835–849. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-011-1748-8
Paterson A, Bowers J, Bruggmann R et al (2009) The Sorghum bicolor genome and the diversification of grasses. Nature.com
Pimenta RJG, Aono AH, Burbano RCV et al (2021) Genome-wide approaches for the identification of markers and genes associated with sugarcane yellow leaf virus resistance. Sci Rep 11:15730. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-95116-1
Pinto LR, Leite DC, Fávero TM et al (2010) Identification of microsatellite markers associated with yield components and quality parameters in sugarcane. Proc ISSCT 27:1–7
Piperidis N, Jackson PA, D’Hont A et al (2008) Comparative genetics in sugarcane enables structured map enhancement and validation of marker–trait associations. Mol Breed 21:233–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-007-9124-8
Pritchard J, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000a) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Rosenberg NA, Donnelly P (2000b) Association mapping in structured populations. Am J Hum Genet 67:170–181. https://doi.org/10.1086/302959
R Core Team (2019) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Found Stat Comput, Vienna
Racedo J, Gutiérrez L, Perera MF et al (2016) Genome-wide association mapping of quantitative traits in a breeding population of sugarcane. BMC Plant Biol 16:142. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0829-x
Resnick JS, Wen CK, Shockey JA, Chang C (2006) Reversion-to-ethylene sensitivity1, a conserved gene that regulates ethylene receptor function in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:7917–7922. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0602239103
Roach BT (1989) Origin and improvement of the genetic base of sugarcane. In: Proc Aust Soc Sugar Cane Technol 34–47
Roman G, Lubarsky B, Kieber JJ et al (1995) Genetic analysis of ethylene signal transduction in Arabidopsis thaliana: five novel mutant loci integrated into a stress response pathway. Genetics 139:1393–1409
Ross J, Li Y, Lim EK, Bowles DJ (2001) Higher plant glycosyltransferases. Genome Biol 2:R3004
Sawitri WD, Afidah SN, Nakagawa A et al (2018) Identification of UDP-glucose binding site in glycosyltransferase domain of sucrose phosphate synthase from sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum) by structure-based site-directed mutagenesis. Biophys Rev 10:293–298
Selvi A, Nair NV (2010) Molecular breeding in sugarcane. Int J Agric Enviorn Biotechnol 3:115–127
Sheoran OP, Tonk DS, Kaushik LS et al (1998) Statistical software package for agricultural research workers. Recent Adv Inf Theory, Stat Comput Appl by Hooda, DS Hasija, RC, Dep Math Stat CCS HAU, Hisar 139–143
Singh RBK, Singh RBK, Singh SP, Sharma ML (2011) Identification of sugarcane microsatellites associated to sugar content in sugarcane and transferability to other cereal genomes. Euphytica 182:335–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0484-0
Singh RK, Singh SP, Tiwari DK et al (2013) Genetic mapping and QTL analysis for sugar yield-related traits in sugarcane. Euphytica 191:333–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-012-0841-7
Singh RK, Banerjee N, Khan MS et al (2016) Identification of putative candidate genes for red rot resistance in sugarcane (Saccharum species hybrid) using LD-based association mapping. Mol Genet Genomics 291:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-016-1190-3
Singh RB, Mahenderakar MD, Jugran AK et al (2020) Assessing genetic diversity and population structure of sugarcane cultivars, progenitor species and genera using microsatellite (SSR) markers. Gene 753:144800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.144800
Siraree A, Banerjee N, Kumar S et al (2017) Identification of marker–trait associations for morphological descriptors and yield component traits in sugarcane. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23:185–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-016-0403-x
Slewinski TL (2011) Diverse functional roles of monosaccharide transporters and their homologs in vascular plants: a physiological perspective. Mol Plant 4:641–662
Solovyev V, Kosarev P, Seledsov I, Vorobyev D (2006) Automatic annotation of eukaryotic genes, pseudogenes and promoters. Genome Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2006-7-s1-s10
Sreekumar K, Kurokose J, Mathew T (1994) Variability, heritability and correlation studies on the yield and quality characters of sugarcane. Indian Sugar Assoc 44:243–249
Sreenivasan TV, Ahloowalia BS (1987) Sugarcane improvement through breeding In DJ Heinz (ed). Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 211–253
Swapna M, Srivastava S (2012) Molecular marker applications for improving sugar content in sugarcane. SpringerBriefs Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-2257-0
Tena E, Mekbib F, Ayana A (2016) Heritability and correlation among sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) yield and some agronomic and sugar quality traits in Ethiopia. Am J Plant Sci 07:1453–1477. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2016.710139
Thippeswamy S, Kajjidoni ST, Salimath PM, Goud JV (2003) Correlation and path analysis for cane yield, juice quality and their component traits in sugarcane. Sugar Tech 5:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02943767
Thirugnanasambandam PP, Hoang NV, Furtado A et al (2017) Association of variation in the sugarcane transcriptome with sugar content. BMC Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-4302-5
Ukoskit K, Posudsavang G, Pongsiripat N et al (2019) Detection and validation of EST-SSR markers associated with sugar-related traits in sugarcane using linkage and association mapping. Genomics 111:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2018.03.019
Wang J, Roe B, Macmil S et al (2010) Microcollinearity between autopolyploid sugarcane and diploid sorghum genomes. BMC Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-11-261
Wei X, Jackson PA, McIntyre CL et al (2006) Associations between DNA markers and resistance to diseases in sugarcane and effects of population substructure. Theor Appl Genet 114:155–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0418-8
Yang X, Luo Z, Todd J et al (2020) Genome-wide association study of multiple yield traits in a diversity panel of polyploid sugarcane (Saccharum spp.). Plant Genome 13:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/tpg2.20006
Zan F, Zhang Y, Wu Z et al (2020) Genetic analysis of agronomic traits in elite sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) germplasm. PLoS ONE 15:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0233752
Zhang SW, Li CH, Cao J et al (2009) Altered architecture and enhanced drought tolerance in rice via the down-regulation of Indole-3-acetic acid by TLD1/OsGH3.13 activation. Plant Physiol 151:1889–1901. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.146803
Zhang J, Zhang X, Tang H et al (2018) Allele-defined genome of the autopolyploid sugarcane Saccharum spontaneum L. Nat Genet 50:1565–1573. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0237-2
Zhou X, Liu Q, Xie F, Wen CK (2007) RTE1 is a Golgi-associated and ETR1-dependent negative regulator of ethylene responses. Plant Physiol 145:75–86. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.104299
Funding
The research work was funded and supported by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research -Sugarcane Breeding Institute, Coimbatore, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS: carried out field and laboratory experiments, data analysis, interpretation of results and writing the manuscript. KKV and LPT contributed to statistical analysis and manuscript correction. NB and PT contributed to conducting bioinformatics experiments and interpretation of results. SP and SPTS contributed to conducting the field and laboratory experiments. PG conceptualized the work, contributed to data analysis, interpretation of results and manuscript correction.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest between the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Bing Yang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Senthilkumar, S., Vinod, K.K., Parthiban, S. et al. Identification of potential MTAs and candidate genes for juice quality- and yield-related traits in Saccharum clones: a genome-wide association and comparative genomic study. Mol Genet Genomics 297, 635–654 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-022-01870-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-022-01870-w