Abstract
Background
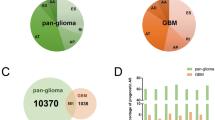
Low-grade glioma (LGG) is a crucial pathological type of glioma. The present study aimed to explore multiple RNA methylation regulator-related AS events and investigate their prognostic values in LGG.
Methods
The prognostic model for low-grade glioma was established using the LASSO regression analysis. To validate prognostic value, we performed Kaplan–Maier survival analysis, ROC curves and nomograms. The ESTIMATE algorithm, the CIBERSORT algorithm and the ssGSEA algorithm were utilized to explore the role of the immune microenvironment in LGG. Subsequently, we then used GO, KEGG and GSEA enrichment analysis to explore the functional roles of these genes. In addition, we employed the GDSC database to screen potential chemotherapeutic agents.
Results
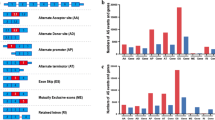
Eight RNA methylation related AS events were involved in construct a survival and prognosis model, which had good ability of independent prediction for patients with LGG. Patients in the high-risk group had shorter life expectancy and higher mortality, while patients in the low-risk group had a better prognosis. We constructed a nomogram which showed an excellent predictive performance for individual OS. The risk score exhibited a close correlation with some immune cells and expression of immune checkpoints. Patients in high-risk group were characterized by immunosuppressive microenvironment and poor response to immunotherapy, and were sensitive to more chemotherapeutic drugs. Pathway and functional enrichment analyses further confirmed that significant differences existed in immune landscape between the two subgroups.
Conclusion
The prognostic RNA methylation-related alternative splicing signature constructed could constitute a promising prognostic biomarker, which could serve to optimize treatment regimens.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets presented in this study are available in the TCGA (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov) and the TCGASpliceSeq (https://bioinformatics.mdanderson.org/TCGASpliceSeq/PSIdownload) repository.
References
Bartosovic M, Molares HC, Gregorova P, Hrossova D, Kudla G, Vanacova S (2017) N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO targets pre-mRNAs and regulates alternative splicing and 3’-end processing. Nucleic Acids Res 45:11356–11370. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx778
Bohnsack K, Höbartner C, Bohnsack M (2019) Eukaryotic 5-methylcytosine (m5C) RNA methyltransferases: mechanisms, cellular functions, and links to disease. Genes. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020102
Boland C, Goel A (2010) Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 138:2073-2087.e2073. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2009.12.064
Brooks A, Putoczki T (2020) JAK-STAT signalling pathway in cancer. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071971
Ceccarelli M et al (2016) Molecular profiling reveals biologically discrete subsets and pathways of progression in diffuse glioma. Cell 164:550–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.12.028
Chan T, Yarchoan M, Jaffee E, Swanton C, Quezada S, Stenzinger A, Peters S (2019) Development of tumor mutation burden as an immunotherapy biomarker: utility for the oncology clinic. Ann Oncol 30:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdy495
Chen D, Mellman I (2013) Oncology meets immunology: the cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 39:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.012
Chen D, Mellman I (2017) Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point. Nature 541:321–330. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21349
Chen W, Feng P, Song X, Lv H, Lin H (2019) iRNA-m7G: identifying N-methylguanosine sites by fusing multiple features. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 18:269–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2019.08.022
Chen H et al (2021) Cross-talk of four types of RNA modification writers defines tumor microenvironment and pharmacogenomic landscape in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer 20:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01322-w
Cheng W, Gao A, Lin H, Zhang W (2022) Novel roles of METTL1/WDR4 in tumor via mG methylation. Mol Ther Oncolytics 26:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2022.05.009
Chujo T, Suzuki T (2012) Trmt61B is a methyltransferase responsible for 1-methyladenosine at position 58 of human mitochondrial tRNAs. RNA (new York, NY) 18:2269–2276. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.035600.112
Courtney D et al (2019) Epitranscriptomic addition of mC to HIV-1 transcripts regulates viral gene expression. Cell Host Microbe 26:217-227.e216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2019.07.005
Delaunay S, Frye M (2019) RNA modifications regulating cell fate in cancer. Nat Cell Biol 21:552–559. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-019-0319-0
Dominissini D et al (2016) The dynamic N(1)-methyladenosine methylome in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature 530:441–446. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16998
Freud A, Mundy-Bosse B, Yu J, Caligiuri M (2017) The broad spectrum of human natural killer cell diversity. Immunity 47:820–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2017.10.008
Grover A, Sanseviero E, Timosenko E, Gabrilovich D (2021) Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: a propitious road to clinic. Cancer Discov 11:2693–2706. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-21-0764
He R, Man C, Huang J, He L, Wang X, Lang Y, Fan Y (2022) Identification of RNA methylation-related lncRNAs signature for predicting hot and cold tumors and prognosis in colon cancer. Front Genet 13:870945. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.870945
Jensen K, Cseh O, Aman A, Weiss S, Luchman H (2017) The JAK2/STAT3 inhibitor pacritinib effectively inhibits patient-derived GBM brain tumor initiating cells in vitro and when used in combination with temozolomide increases survival in an orthotopic xenograft model. PLoS ONE 12:e0189670. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189670
Jiang P et al (2018) Signatures of T cell dysfunction and exclusion predict cancer immunotherapy response. Nat Med 24:1550–1558. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0136-1
Jiang X et al (2019) Role of the tumor microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-mediated tumor immune escape. Mol Cancer 18:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0928-4
Jin H, Huo C, Zhou T, Xie S (2022) mA RNA modification in gene expression regulation. Genes. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050910
Lawrie T et al (2019) Long-term neurocognitive and other side effects of radiotherapy, with or without chemotherapy, for glioma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 8:013047. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD013047.pub2
Liao Y, Han P, Zhang Y, Ni B (2021) Physio-pathological effects of m6A modification and its potential contribution to melanoma. Clin Trans Oncol 23:2269–2279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-021-02644-3
Lim M, Xia Y, Bettegowda C, Weller M (2018) Current state of immunotherapy for glioblastoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 15:422–442. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-018-0003-5
Lin K, Krainer A (2019) PSI-Sigma: a comprehensive splicing-detection method for short-read and long-read RNA-seq analysis. Bioinformatics (oxford, England) 35:5048–5054. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz438
Liu F et al (2016) ALKBH1-mediated tRNA demethylation regulates translation. Cell 167:1897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.045
Liu E et al (2022) Development and validation of an MRI-based nomogram for the preoperative prediction of tumor mutational burden in lower-grade gliomas. Quant Imaging Med Surg 12:1684–1697. https://doi.org/10.21037/qims-21-300
Mao S, Chen Z, Wu Y, Xiong H, Yuan X (2022) Crosstalk of eight types of RNA modification regulators defines tumor microenvironments, cancer hallmarks, and prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma. J Oncol 2022:1285632. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/1285632
Michaud-Levesque J, Bousquet-Gagnon N, Béliveau R (2012) Quercetin abrogates IL-6/STAT3 signaling and inhibits glioblastoma cell line growth and migration. Exp Cell Res 318:925–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.02.017
Murciano-Goroff Y, Warner A, Wolchok J (2020) The future of cancer immunotherapy: microenvironment-targeting combinations. Cell Res 30:507–519. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-0337-2
Owen K, Brockwell N, Parker B (2019) JAK-STAT signaling: a double-edged sword of immune regulation and cancer progression. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11122002
Pandolfini L et al (2019) METTL1 promotes let-7 microRNA processing via m7G methylation. Mol Cell 74:1278-1290.e1279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.03.040
Ping X et al (2014) Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell Res 24:177–189. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2014.3
Poh H, Mirza A, Pickering B, Jaffrey S (2022) Alternative splicing of METTL3 explains apparently METTL3-independent m6A modifications in mRNA. PLoS Biol 20:e3001683. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3001683
Qi L et al (2022) Cross-talk of multiple types of RNA Modification regulators uncovers the tumor microenvironment and immune infiltrates in soft tissue sarcoma. Front Immunol 13:921223. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.921223
Rah B et al (2022) JAK/STAT signaling: molecular targets, therapeutic opportunities, and limitations of targeted inhibitions in solid malignancies. Front Pharmacol 13:821344. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.821344
Rapino F et al (2018) Codon-specific translation reprogramming promotes resistance to targeted therapy. Nature 558:605–609. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0243-7
Ryan M et al (2016) TCGASpliceSeq a compendium of alternative mRNA splicing in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D1018-1022. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1288
Sakuishi K, Jayaraman P, Behar S, Anderson A, Kuchroo V (2011) Emerging Tim-3 functions in antimicrobial and tumor immunity. Trends Immunol 32:345–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2011.05.003
Shao D, Li Y, Wu J, Zhang B, Xie S, Zheng X, Jiang Z (2022) An m6A/m5C/m1A/m7G-related long non-coding RNA signature to predict prognosis and immune features of glioma. Front Genet 13:903117. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.903117
Song N et al (2022) The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer: implication for nature products anti-cancer research. Front Pharmacol 13:933332. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.933332
Tian Q et al (2019) METTL1 overexpression is correlated with poor prognosis and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma via PTEN. J Mol Med (berl) 97:1535–1545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-019-01830-9
Togashi Y, Shitara K, Nishikawa H (2019) Regulatory T cells in cancer immunosuppression—implications for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 16:356–371. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-019-0175-7
Wiener D, Schwartz S (2021) The epitranscriptome beyond mA. Nat Rev Genet 22:119–131. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-020-00295-8
Xia L, Fang C, Chen G, Sun C (2018) Relationship between the extent of resection and the survival of patients with low-grade gliomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 18:48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-017-3909-x
Xu L et al (2018) TIP: a web server for resolving tumor immunophenotype profiling. Can Res 78:6575–6580. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-18-0689
Xu R et al (2022) An alternatively spliced variant of METTL3 mediates tumor suppression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Genes. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040669
Yang Y, Hsu P, Chen Y, Yang Y (2018) Dynamic transcriptomic mA decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res 28:616–624. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-018-0040-8
Zalpoor H et al (2022) Quercetin as a JAK-STAT inhibitor: a potential role in solid tumors and neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Mol Biol Lett 27:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-022-00355-3
Zhang Y, Zhang Z (2020) The history and advances in cancer immunotherapy: understanding the characteristics of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic implications. Cell Mol Immunol 17:807–821. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-020-0488-6
Zhang M, Wang X, Chen X, Zhang Q, Hong J (2020) Novel immune-related gene signature for risk stratification and prognosis of survival in lower-grade glioma. Front Genet 11:363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00363
Zhang S, Kuang G, Huang Y, Huang X, Wang W, Wang G (2022) Cross talk between RNA modification writers and tumor development as a basis for guiding personalized therapy of gastric cancer. Hum Genomics 16:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40246-022-00386-z
Zhao X et al (2014) FTO-dependent demethylation of N6-methyladenosine regulates mRNA splicing and is required for adipogenesis. Cell Res 24:1403–1419. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2014.151
Zheng Y, Dou Y, Duan L, Cong C, Gao A, Lai Q, Sun Y (2015) Using chemo-drugs or irradiation to break immune tolerance and facilitate immunotherapy in solid cancer. Cell Immunol 294:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.02.003
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the TCGA database, GTEx database and TCGASpliceSeq database for providing the valuable gene expression matrix, the alternative splicing data and clinical information.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CM conceived and designed this work. CM conducted bioinformatic analyses. BX, YB and JX helped with data collection, analysis, and interpretation. CM, YB, JX and HL wrote the manuscript. HL and BX revised the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest in terms of the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical approval
No application.
Consent to participate
No application.
Consent for publication
No application.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, C., Bao, Y., Xu, J. et al. Identification and validation of RNA methylation-related alternative splicing gene signature for low-grade glioma to predict survival and immune landscapes. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 47–62 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04431-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04431-1