Abstract
Purpose
The clinicopathological or genetic features related to the prognosis of mucinous adenocarcinoma are unknown because of its rarity. The clinicopathological or targetable features were investigated for better management of patients with mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung.
Methods
We comprehensively evaluated the clinicopathological and genetic features of 60 completely resected mucinous lung adenocarcinomas. Targetable genetic variants were explored using nCounter and polymerase chain reaction, PD-L1 and TTF-1 expression were evaluated using immunohistochemistry. We analyzed the prognostic impact using the Kaplan–Meier method and log-rank test.
Results
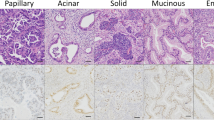
Of the 60 enrolled patients, 13 (21.7%) had adenocarcinoma in situ/minimally invasive adenocarcinoma, and 47 (78.3%) had invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma (IMA). Fifteen patients (25%) showed a pneumonic appearance on computed tomography (CT). CD74-NRG1 fusion, EGFR mutations, and BRAF mutation were detected in three (5%), four (6.7%), and one (1.7%) patient(s), respectively. KRAS mutations were detected in 31 patients (51.7%). Two patients (3.5%) showed immunoreactivity for PD-L1. No in situ or minimally invasive cases recurred. IMA patients with pneumonic appearance had significantly worse recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) (p < 0.001). Furthermore, IMA patients harboring KRAS mutations had worse RFS (p = 0.211). Multivariate analysis revealed that radiological pneumonic appearance was significantly associated with lower RFS (p < 0.003) and OS (p = 0.012). KRAS mutations served as an unfavorable status for RFS (p = 0.043).
Conclusion
Mucinous adenocarcinoma had a low frequency of targetable genetic variants and PD-L1 immunoreactivity; however, KRAS mutations were frequent. Pneumonic appearance on CT imaging and KRAS mutations were clinicopathological features associated with a worse prognosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data is original from our study. No data from public or shared database was utilized.
References
Caruso C (2019) AMG 510 first to inhibit “Undruggable” KRAS. Cancer Discov 9:988–989
Cheema PK, Doherty M, Tsao MS (2017) A case of invasive mucinous pulmonary adenocarcinoma with a CD74-NRG1 fusion protein targeted with afatinib. J Thorac Oncol 12:e200–e202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2017.07.033
Cho JH, Lim SH, An HJ, Kim KH, Park KU, Kang EJ, Choi YH, Ahn MS, Lee MH, Sun JM, Lee SH (2020) Osimertinib for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring uncommon EGFR mutations: a multicenter, open-label, phase II trial (KCSG-LU15-09). J Clin Oncol 10(38):488–495. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.00931
Drilon A, Somwar R, Mangatt BP, Edgren H, Desmeules P, Ruusulehto A, Smith RS, Delasos L, Vojnic M, Plodkowski AJ, Sabari J (2018) Response to ERBB3-directed targeted therapy in NRG1 \-rearranged cancers. Cancer Discov 8:686–695. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-1004
Gay ND, Wang Y, Beadling C, Warrick A, Neff T, Corless CL, Tolba K (2017) Durable response to afatinib in lung adenocarcinoma harboring NRG1 gene fusions. N Thorac Oncol 12:e107–e110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2017.04.025
Goldstraw P, Chansky K, Crowley J, Rami-Porta R, Asamura H, Eberhardt WE, Nicholson AG, Groome P, Mitchell A, Bolejack V, Rami-Porta R (2016) The IASLC lung cancer staging project: proposals for revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol 11:39–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2015.09.009
Guo M, Tomoshige K, Meister M, Muley T, Fukazawa T, Tsuchiya T, Karns R, Warth A, Fink-Baldauf IM, Nagayasu T, Naomoto Y (2017) Gene signature driving invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung. EMBO Mol Med 9:462–481. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201606711
Ito M, Miyata Y, Kushitani K, Yoshiya T, Kai Y, Tsutani Y, Mimura T, Konishi K, Takeshima Y, Okada M (2018) Increased risk of recurrence in resected EGFR-positive pN0M0 invasive lung adenocarcinoma. Thorac Cancer 9:1594–1602. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.12866
Ito M, Miyata Y, Hirano S, Kimura S, Irisuna F, Ikeda K, Kushitani K, Kishi N, Tsutani Y, Takeshima Y, Okada M (2019) Synchronicity of genetic variants between primary sites and metastatic lymph nodes, and prognostic impact in nodal metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 145:2325–2333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02978-0
Izar B, Zhou H, Heist RS, Azzoli CG, Muzikansky A, Scribner EE, Bernardo LA, Dias-Santagata D, Iafrate AJ, Lanuti M (2014) The prognostic impact of KRAS, its codon and amino acid specific mutations, on survival in resected stage I lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 9:1363–1369. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000266
Jinesh GG, Sambandam V, Vijayaraghavan S, Balaji K, Mukherjee S (2018) Molecular genetics and cellular events of K-Ras-driven tumorigenesis. Oncogene 37:839–846. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.377
Kim EY, Cho EN, Park HS, Hong JY, Lim S, Youn JP, Hwang SY, Chang YS (2016) Compound EGFR mutation is frequently detected with co-mutations of actionable genes and associated with poor clinical outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther 17:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2016.1139235
Kneuertz PJ, Carbone DP, D’Souza DM, Shilo K, Abdel-Rasoul M, Zhao W, Williams TM, Jones D, Merritt RE (2020) Prognostic value and therapeutic implications of expanded molecular testing for resected early stage lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 143:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.03.012
Lee HY, Cha MJ, Lee KS, Lee HY, Kwon OJ, Choi JY, Kim HK, Choi YS, Kim J, Shim YM (2016) Prognosis in resected invasive mucinous adenocarcinomas of the lung: related factors and comparison with resected nonmucinous adenocarcinomas. J Thorac Oncol 11:1064–1073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.03.011
Maeda Y, Tsuchiya T, Hao TDH, Xu Y, Mucenski ML, Du L, Keiser AR, Fukazawa T, Naomoto Y, Nagayasu T (2012) Kras(G12D) and Nkx2-1 haploinsufficiency induce mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Clin Invest 122:4388–4400. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI64048
Nakaoku T, Tsuta K, Ichikawa H, Shiraishi K, Sakamoto H, Enari M, Furuta K, Shimada Y, Ogiwara H, Watanabe SI, Nokihara H (2014) Druggable oncogene fusions in invasive mucinous lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 20:3087–3093. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0107
Reguart N, Teixido C, Gimenez-Capitan A, Pare L, Galvan P, Viteri S, Rodriguez S, Peg V, Aldeguer E, Vinolas N, Remon J (2017) Identification of ALK, ROS1, and RET fusions by a multiplexed mRNA-based assay in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples from advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Clin Chem 63:751–760. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2016.265314
Russell PA, Wainer Z, Wright GM, Daniels M, Conron M, Williams RA (2011) Does lung adenocarcinoma subtype predict patient survival?: A clinicopathologic study based on the new International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary lung adenocarcinoma classification. J Thorac Oncol 6:1496–1504. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e318221f701
Shim HS, Kenudson M, Zheng Z, Cha YJ, Ho QH, Onozato M, Le LP, Heist RS, Iafrate AJ (2015) Uniquegenetic and survival characteristics of invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Thorac Oncol 10:1156–1162. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000579
Takahashi Y, Eguchi T, Kameda K, Lu S, Vaghjiani RG, Tan KS, Travis WD, Jones DR, Adusumilli PS (2018) Histologic subtyping in pathologic stage I-IIA lung adenocarcinoma provides risk-based stratification for surveillance. Oncotarget 9:35742–35751. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.26285
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, Nicholson AG, Geisinger KR, Yatabe Y, Beer DG, Powell CA, Riely GJ, Van Schil PE, Garg K (2011) International Association for the Study of Lung cancer/American Thoracic society/European Respiratory Society International multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 6:244–285. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e318206a221
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG, Yatabe Y, Austin JH, Beasley MB, Chirieac LR, Dacic S, Duhig E, Flieder DB, Geisinger K (2015) WHO Panel. The 2015 World Health Organization classification of lung tumors: impact of genetic, clinical and radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J Thorac Oncol 10:1243–1260. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000630
Trombetta D, Graziano P, Scarpa A, Sparaneo A, Rossi G, Rossi A, Di Maio M, Antonello D, Mafficini A, Fabrizio FP, Manzorra MC (2018) Frequent NRG1 fusions in Caucasian pulmonary mucinous adenocarcinoma predicted by Phospho-ErbB3 expression. Oncotarget 9:9661–9671. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.23800
Warth A, Muley T, Meister M et al (2012) The novel histologic International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society classification system of lung adenocarcinoma is a stage-independent predictor of survival. J Clin Oncol 30:1438–1446. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.37.2185
Watanabe H, Saito H, Yokose T, Sakuma Y, Murakami S, Kondo T, Oshita F, Ito H, Nakayama H, Yamada K, Iwazaki M (2015) Relation between thin-section computed tomography and clinical findings of mucinous adenocarcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg 9:975–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2014.10.065
Yoda S, Lin JJ, Lawrence MS, Burke BJ, Friboulet L, Langenbucher A, Dardaei L, Prutisto-Chang K, Dagogo-Jack I, Timofeevski S, Hubbeling H (2018) Sequential ALK inhibitors can select for lorlatinib-resistant compound ALK mutations in ALK-positive lung cancer. Cancer Discov 8:714–729. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-1256
Yoshizawa A, Sumiyoshi S, Sonobe M, Kobayashi M, Fujimoto M, Kawakami F, Tsuruyama T, Travis WD (2013) Validation of the IASLC/ATS/ERS lung adenocarcinoma classification for prognosis and association with EGFR and KRAS gene mutations: analysis of 440 Japanese patients. J Thorac Oncol 8:52–61. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182769aa8
Acknowledgements
This work was conducted in part at the Analysis Center of Life Science, Natural Science Center for Basic Research and Development, Hiroshima University, Hiroshima, Japan. The authors thank Editage (www.editage.jp) for English language editing.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and Data Curation: DU, MI, YaT, and YM. Formal analysis: DU, MI, AGC, CA, and MMV. Investigation: DU, MI, AGC, RRL, APR, CA, KK, KA, and YuT. Supervision: MO and RR. Visualization: DU, MI, RRL, and MMV. Writing: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study protocol was approved by the institutional review board at Hiroshima University (no. E–1546).
Consent to participate
Informed Consent was obtained from patients to stock tissues for research.
Consent for publication
Informed Consent was obtained from patients to for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueda, D., Ito, M., Tsutani, Y. et al. Comprehensive analysis of the clinicopathological features, targetable profile, and prognosis of mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147, 3709–3718 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03609-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03609-3