Abstract
Purpose
Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR) is highly overexpressed in prostate cancer (PCa) and its transcriptional regulators include various transcription factors and CTNNB1/β-catenin. Our previous findings suggested a post-transcriptional regulation by the tumor-suppressive microRNA miR-138 in PCa. Thus, the aim of this study was to demonstrate the direct interaction of miR-138 with the 3′-UTR of AMACR. Furthermore, the influence of miR-138 on the expression of AMACR and selected AMACR regulators was investigated in PCa cells.
Methods
Using DU-145, PC-3, and LNCaP PCa cells, the effect of exogenous miR-138 on AMACR and selected AMACR regulators was determined by quantitative PCR and Western blot. Luciferase reporter assays were used to verify target and promoter interaction.
Results
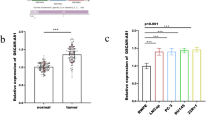
Using a luciferase reporter assay a direct interaction of miR-138 with the AMACR-3′-UTR was confirmed. Surprisingly, AMACR expression was up-regulated by up to 125% by exogenous miR-138 in PCa cells. The lack of any miR-138 binding sites within the AMACR promoter suggested an indirect mechanism of up-regulation. Therefore, the effect of miR-138 on selected AMACR regulators including CTNNB1/β-catenin, RELA, SMAD4, SP1, and TCF4 was evaluated. MiR-138 solely evoked an up-regulation of CTNNB1 mRNA expression and β-catenin protein levels by up to 75%. Further in silico analysis revealed a binding site for miR-138 within the CTNNB1 promoter. MiR-138 could enhance the activity of the CTNNB1 promoter, which in turn could contribute to the observed AMACR up-regulation.
Conclusions
The present findings suggest that miR-138 can indirectly up-regulate AMACR via transcriptional induction of CTNNB1, at least in vitro in PCa cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bracken CP, Scott HS, Goodall GJ (2016) A network-biology perspective of microRNA function and dysfunction in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 17:719–732. doi:10.1038/nrg.2016.134
Carnell AJ, Hale I, Denis S, Wanders RJ, Isaacs WB, Wilson BA, Ferdinandusse S (2007) Design, synthesis, and in vitro testing of alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase inhibitors. J Med Chem 50:2700–2707. doi:10.1021/jm0702377
Catalanotto C, Cogoni C, Zardo G (2016) MicroRNA in control of gene expression: an overview of nuclear functions. Int J Mol Sci. doi:10.3390/ijms17101712
Chang TH, Huang HY, Hsu JB, Weng SL, Horng JT, Huang HD (2013) An enhanced computational platform for investigating the roles of regulatory RNA and for identifying functional RNA motifs. BMC Bioinform 14(Suppl 2):S4. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-14-S2-S4
Chen W, Wu W, Zhao J, Yu C, Liu W, Jiang A, Zhang J (2009) Molecular cloning and preliminary analysis of the human alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase promoter. Mol Biol Rep 36:423–430. doi:10.1007/s11033-007-9196-x
Erdmann K, Kaulke K, Thomae C, Huebner D, Sergon M, Froehner M, Wirth MP, Fuessel S (2014) Elevated expression of prostate cancer-associated genes is linked to down-regulation of microRNAs. BMC Cancer 14:82. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-82
Erdmann K, Kaulke K, Rieger C, Salomo K, Wirth MP, Fuessel S (2016) MiR-26a and miR-138 block the G1/S transition by targeting the cell cycle regulating network in prostate cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142:2249–2261. doi:10.1007/s00432-016-2222-4
Freeman TJ, Smith JJ, Chen X, Washington MK, Roland JT, Means AL, Eschrich SA, Yeatman TJ, Deane NG, Beauchamp RD (2012) Smad4-mediated signaling inhibits intestinal neoplasia by inhibiting expression of beta-catenin. Gastroenterology 142(562–571):e562. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.11.026
Iorio MV, Croce CM (2012) microRNA involvement in human cancer. Carcinogenesis 33:1126–1133. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgs140
Liu X, Wang C, Chen Z, Jin Y, Wang Y, Kolokythas A, Dai Y, Zhou X (2011) MicroRNA-138 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Biochem J 440:23–31. doi:10.1042/BJ20111006
Lloyd MD, Yevglevskis M, Lee GL, Wood PJ, Threadgill MD, Woodman TJ (2013) alpha-Methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR): metabolic enzyme, drug metabolizer and cancer marker P504S. Prog Lipid Res 52:220–230. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2013.01.001
Majid S, Dar AA, Saini S, Yamamura S, Hirata H, Tanaka Y, Deng G, Dahiya R (2010) MicroRNA-205-directed transcriptional activation of tumor suppressor genes in prostate cancer. Cancer 116:5637–5649. doi:10.1002/cncr.25488
Mathelier A, Fornes O, Arenillas DJ, C-y Chen, Denay G, Lee J, Shi W, Shyr C, Tan G, Worsley-Hunt R, Zhang AW, Parcy F, Lenhard B, Sandelin A, Wasserman WW (2016) JASPAR 2016: a major expansion and update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D110–D115. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv1176
Matsui M, Chu Y, Zhang H, Gagnon KT, Shaikh S, Kuchimanchi S, Manoharan M, Corey DR, Janowski BA (2013) Promoter RNA links transcriptional regulation of inflammatory pathway genes. Nucleic Acids Res 41:10086–10109. doi:10.1093/nar/gkt777
Paugh SW, Coss DR, Bao J, Laudermilk LT, Grace CR, Ferreira AM, Waddell MB, Ridout G, Naeve D, Leuze M, LoCascio PF, Panetta JC, Wilkinson MR, Pui CH, Naeve CW, Uberbacher EC, Bonten EJ, Evans WE (2016) MicroRNAs form triplexes with double stranded DNA at sequence-specific binding sites; a eukaryotic mechanism via which micrornas could directly alter gene expression. PLoS Comput Biol 12:e1004744. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004744
Place RF, Li LC, Pookot D, Noonan EJ, Dahiya R (2008) MicroRNA-373 induces expression of genes with complementary promoter sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:1608–1613. doi:10.1073/pnas.0707594105
Qu H, Zheng L, Pu J, Mei H, Xiang X, Zhao X, Li D, Li S, Mao L, Huang K, Tong Q (2015) miRNA-558 promotes tumorigenesis and aggressiveness of neuroblastoma cells through activating the transcription of heparanase. Hum Mol Genet 24:2539–2551. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddv018
Requenez-Contreras JL, Lopez-Castillejos ES, Hernandez-Flores R, Moreno-Eutimio MA, Granados-Riveron JT, Martinez-Ruiz GU, Aquino-Jarquin G (2017) MiR-138 indirectly regulates the MDR1 promoter by NF-kappaB/p65 silencing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 484:648–655. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.168
Robinson D, Van Allen EM, Wu YM, Schultz N, Lonigro RJ, Mosquera JM, Montgomery B, Taplin ME, Pritchard CC, Attard G, Beltran H, Abida W, Bradley RK, Vinson J, Cao X, Vats P, Kunju LP, Hussain M, Feng FY, Tomlins SA, Cooney KA, Smith DC, Brennan C, Siddiqui J, Mehra R, Chen Y, Rathkopf DE, Morris MJ, Solomon SB, Durack JC, Reuter VE, Gopalan A, Gao J, Loda M, Lis RT, Bowden M, Balk SP, Gaviola G, Sougnez C, Gupta M, Yu EY, Mostaghel EA, Cheng HH, Mulcahy H, True LD, Plymate SR, Dvinge H, Ferraldeschi R, Flohr P, Miranda S, Zafeiriou Z, Tunariu N, Mateo J, Perez-Lopez R, Demichelis F, Robinson BD, Schiffman M, Nanus DM, Tagawa ST, Sigaras A, Eng KW, Elemento O, Sboner A, Heath EI, Scher HI, Pienta KJ, Kantoff P, de Bono JS, Rubin MA, Nelson PS, Garraway LA, Sawyers CL, Chinnaiyan AM (2015) Integrative clinical genomics of advanced prostate cancer. Cell 161:1215–1228. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.001
Salmanidis M, Pillman K, Goodall G, Bracken C (2014) Direct transcriptional regulation by nuclear microRNAs. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 54:304–311. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2014.03.010
Sander S, Bullinger L, Klapproth K, Fiedler K, Kestler HA, Barth TF, Moller P, Stilgenbauer S, Pollack JR, Wirth T (2008) MYC stimulates EZH2 expression by repression of its negative regulator miR-26a. Blood 112:4202–4212. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-03-147645
Schneider JA, Logan SK (2017) Revisiting the role of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in prostate cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2017.02.008
Seidl CI, Martinez-Sanchez A, Murphy CL (2016) Derepression of microRNA-138 contributes to loss of the human articular chondrocyte phenotype. Arthritis Rheumatol 68:398–409. doi:10.1002/art.39428
Sekine S, Ogawa R, Ojima H, Kanai Y (2011) Overexpression of alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase is associated with CTNNB1 mutations in hepatocellular carcinomas. Histopathology 58:712–719. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2011.03798.x
Sha HH, Wang DD, Chen D, Liu SW, Wang Z, Yan DL, Dong SC, Feng JF (2017) MiR-138: a promising therapeutic target for cancer. Tumour Biol 39:1010428317697575. doi:10.1177/1010428317697575
Takahara K, Azuma H, Sakamoto T, Kiyama S, Inamoto T, Ibuki N, Nishida T, Nomi H, Ubai T, Segawa N, Katsuoka Y (2009) Conversion of prostate cancer from hormone independency to dependency due to AMACR inhibition: involvement of increased AR expression and decreased IGF1 expression. Anticancer Res 29:2497–2505
Toscano-Garibay JD, Aquino-Jarquin G (2014) Transcriptional regulation mechanism mediated by miRNA-DNA*DNA triplex structure stabilized by Argonaute. Biochim Biophys Acta 1839:1079–1083. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.07.016
Wang C, Chen Z, Ge Q, Hu J, Li F, Hu J, Xu H, Ye Z, Li LC (2014) Up-regulation of p21(WAF1/CIP1) by miRNAs and its implications in bladder cancer cells. FEBS Lett 588:4654–4664. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2014.10.037
Williams JL, Greer PA, Squire JA (2014) Recurrent copy number alterations in prostate cancer: an in silico meta-analysis of publicly available genomic data. Cancer Genet 207:474–488. doi:10.1016/j.cancergen.2014.09.003
Wilson BA, Wang H, Nacev BA, Mease RC, Liu JO, Pomper MG, Isaacs WB (2011) High-throughput screen identifies novel inhibitors of cancer biomarker alpha-methylacyl coenzyme A racemase (AMACR/P504S). Mol Cancer Ther 10:825–838. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.mct-10-0902
Yu D, An F, He X, Cao X (2015) Curcumin inhibits the proliferation and invasion of human osteosarcoma cell line MG-63 by regulating miR-138. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:14946–14952
Zha S, Ferdinandusse S, Denis S, Wanders RJ, Ewing CM, Luo J, De Marzo AM, Isaacs WB (2003) Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase as an androgen-independent growth modifier in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 63:7365–7376
Zhang X, Leav I, Revelo MP, Deka R, Medvedovic M, Jiang Z, Ho SM (2009) Deletion hotspots in AMACR promoter CpG island are cis-regulatory elements controlling the gene expression in the colon. PLoS Genet 5:e1000334. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000334
Zhang Y, Fan M, Zhang X, Huang F, Wu K, Zhang J, Liu J, Huang Z, Luo H, Tao L, Zhang H (2014) Cellular microRNAs up-regulate transcription via interaction with promoter TATA-box motifs. RNA 20:1878–1889. doi:10.1261/rna.045633.114
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Wilhelm Sander-Foundation (Grant Number: 2010.041.1). Intramural funding (MeDDriveGrant 2013) was provided by the Medizinische Fakultät Carl Gustav Carus (TU Dresden, Germany). Kati Erdmann also received financial support from the Förderverein Hilfe bei Prostatakrebs e.V. (Movember Campaign; Grant Number: MOV-2013-06) and was supported by the Medizinische Fakultät Carl Gustav Carus (TU Dresden, Germany) within the framework of the postdoctoral habilitation program for women. Furthermore, the authors are grateful to Andrea Lohse-Fischer and Ulrike Lotzkat for their excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was funded by the Wilhelm Sander-Foundation (Grant Number: 2010.041.1). Intramural funding (MeDDriveGrant 2013) was provided by the Medizinische Fakultät Carl Gustav Carus (TU Dresden, Germany). Kati Erdmann also received financial support from the Förderverein Hilfe bei Prostatakrebs e.V. (Movember Campaign; Grant Number: MOV-2013-06) and was supported by the Medizinische Fakultät Carl Gustav Carus (TU Dresden, Germany) within the framework of the postdoctoral habilitation program for women.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erdmann, K., Kaulke, K., Rieger, C. et al. Induction of alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase by miR-138 via up-regulation of β-catenin in prostate cancer cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 143, 2201–2210 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2484-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2484-5