Abstract
Purpose
Treatment of cancer using standard chemotherapy still offers a poor prognosis combined with severe side effects. Novel antibody-based therapies have been shown to overcome low efficiency and lack of selectivity by targeting cancer-associated antigens, such as aminopeptidase CD13.
Methods
We isolated a high-affinity CD13-specific single-chain fragment variable (scFv13) from a phage display library of V-genes from mice immunized with soluble antigen. An immunotoxin comprising the scFv13 and a truncated version of the exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ETA′, scFv13–ETA′) and a bispecific scFv targeting CD13 and CD16 simultaneously (bsscFv[13xds16]) was generated and investigated for their therapeutic potential.
Results
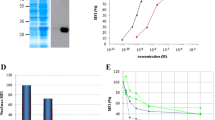
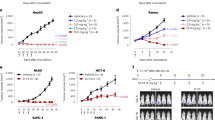
Both fusion proteins bound specifically to target cells with high affinity. Furthermore, scFv13–ETA′ inhibited the proliferation of human cancer cell lines efficiently at low concentrations (IC50 values of 408 pM–7 nM) and induced apoptosis (40–85% of target cells). The bsscFv triggered dose-dependent antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, resulting in the lysis of up to 23.9% A2058 cells, 18.0% MDA-MB-468 cells and 19.1% HL-60 cells.
Conclusion
The provided data demonstrate potent therapeutic activity of the scFv13–ETA′ and the bsscFv[13xds16]. The CD13-specific scFv is therefore suitable for the direct and specific delivery of both cytotoxic agents and effector cells to cancer-derived cells, making it ideal for further therapeutic evaluation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alewine C, Hassan R, Pastan I (2015) Advances in anticancer immunotoxin therapy. Oncologist 20:176–185. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0358
Antignani A, Fitzgerald D (2013) Immunotoxins: the role of the toxin. Toxins 5:1486–1502. doi:10.3390/toxins5081486
Asano R, Hagiwara Y, Koyama N, Masakari Y, Orimo R, Arai K, Ogata H, Furumoto S, Umetsu M, Kumagai I (2013) Multimerization of anti-(epidermal growth factor receptor) IgG fragments induces an antitumor effect: the case for humanized 528 scFv multimers. FEBS J 280:4816–4826. doi:10.1111/febs.12451
Bargou R, Leo E, Zugmaier G, Klinger M, Goebeler M, Knop S, Noppeney R, Viardot A, Hess G, Schuler M, Einsele H, Brandl C, Wolf A, Kirchinger P, Klappers P, Schmidt M, Riethmuller G, Reinhardt C, Baeuerle PA, Kufer P (2008) Tumor regression in cancer patients by very low doses of a T cell-engaging antibody. Science (New York, NY) 321:974–977. doi:10.1126/science.1158545
Barth S, Huhn M, Matthey B, Klimka A, Galinski EA, Engert A (2000) Compatible-solute-supported periplasmic expression of functional recombinant proteins under stress conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1572–1579
Bauvois B, Dauzonne D (2006) Aminopeptidase-N/CD13 (EC 3.4.11.2) inhibitors: chemistry, biological evaluations, and therapeutic prospects. Med Res Rev 26:88–130. doi:10.1002/med.20044
Benedict CA, MacKrell AJ, Anderson WF (1997) Determination of the binding affinity of an anti-CD34 single-chain antibody using a novel, flow cytometry based assay. J Immunol Methods 201:223–231
Bruenke J, Fischer B, Barbin K, Schreiter K, Wachter Y, Mahr K, Titgemeyer F, Niederweis M, Peipp M, Zunino SJ, Repp R, Valerius T, Fey GH (2004) A recombinant bispecific single-chain Fv antibody against HLA class II and FcgammaRIII (CD16) triggers effective lysis of lymphoma cells. Br J Haematol 125:167–179. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2004.04893.x
Bruenke J, Barbin K, Kunert S, Lang P, Pfeiffer M, Stieglmaier K, Niethammer D, Stockmeyer B, Peipp M, Repp R, Valerius T, Fey GH (2005) Effective lysis of lymphoma cells with a stabilised bispecific single-chain Fv antibody against CD19 and FcgammaRIII (CD16). Br J Haematol 130:218–228. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05414.x
Costello RT, Fauriat C, Sivori S, Marcenaro E, Olive D (2004) NK cells: innate immunity against hematological malignancies? Trends Immunol 25:328–333. doi:10.1016/j.it.2004.04.005
Cremer C, Braun H, Mladenov R, Schenke L, Cong X, Jost E, Brummendorf TH, Fischer R, Carloni P, Barth S, Nachreiner T (2015) Novel angiogenin mutants with increased cytotoxicity enhance the depletion of pro-inflammatory macrophages and leukemia cells ex vivo. Cancer Immunol Immunother 64:1575–1586. doi:10.1007/s00262-015-1763-8
Daeron M (1997) Fc receptor biology. Annu Rev Immunol 15:203–234. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.15.1.203
Dondossola E, Rangel R, Guzman-Rojas L, Barbu EM, Hosoya H, St John LS, Molldrem JJ, Corti A, Sidman RL, Arap W, Pasqualini R (2013) CD13-positive bone marrow-derived myeloid cells promote angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:20717–20722. doi:10.1073/pnas.1321139110
Durocher Y, Perret S, Kamen A (2002) High-level and high-throughput recombinant protein production by transient transfection of suspension-growing human 293-EBNA1 cells. Nucleic Acids Res 30:E9
Haraguchi N, Ishii H, Mimori K, Tanaka F, Ohkuma M, Kim HM, Akita H, Takiuchi D, Hatano H, Nagano H, Barnard GF, Doki Y, Mori M (2010) CD13 is a therapeutic target in human liver cancer stem cells. J Clin Invest 120:3326–3339. doi:10.1172/jci42550
Hollevoet K, Mason-Osann E, Muller F, Pastan I (2015) Methylation-associated partial down-regulation of mesothelin causes resistance to anti-mesothelin immunotoxins in a pancreatic cancer cell line. PLoS ONE 10:e0122462. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0122462
Hristodorov D, Mladenov R, Pardo A, Pham AT, Huhn M, Fischer R, Thepen T, Barth S (2013) Microtubule-associated protein tau facilitates the targeted killing of proliferating cancer cells in vitro and in a xenograft mouse tumour model in vivo. Br J Cancer 109:1570–1578. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.457
Kellner C, Bruenke J, Stieglmaier J, Schwemmlein M, Schwenkert M, Singer H, Mentz K, Peipp M, Lang P, Oduncu F, Stockmeyer B, Fey GH (2008) A novel CD19-directed recombinant bispecific antibody derivative with enhanced immune effector functions for human leukemic cells. J Immunother (Hagerstown, Md: 1997) 31:871–884. doi:10.1097/CJI.0b013e318186c8b4
Krebber A, Bornhauser S, Burmester J, Honegger A, Willuda J, Bosshard HR, Pluckthun A (1997) Reliable cloning of functional antibody variable domains from hybridomas and spleen cell repertoires employing a reengineered phage display system. J Immunol Methods 201:35–55
Kreitman RJ (2006) Immunotoxins for targeted cancer therapy. AAPS J 8:E532–E551. doi:10.1208/aapsj080363
Mina-Osorio P (2008) The moonlighting enzyme CD13: old and new functions to target. Trends Mol Med 14:361–371. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2008.06.003
Mladenov R, Hristodorov D, Cremer C, Hein L, Kreutzer F, Stroisch T, Niesen J, Brehm H, Blume T, Brummendorf TH, Jost E, Thepen T, Fischer R, Stockmeyer B, Barth S, Stein C (2015) The Fc-alpha receptor is a new target antigen for immunotherapy of myeloid leukemia. Int J Cancer 137:2729–2738. doi:10.1002/ijc.29628
Monnier PP, Vigoroux RJ, Tassew NG (2013) In vivo applications of single chain Fv (variable domain) (scFv) fragments. Antibodies 2:193–208. doi:10.3390/antib2020193
Niesen J, Stein C, Brehm H, Hehmann-Titt G, Fendel R, Melmer G, Fischer R, Barth S (2015) Novel EGFR-specific immunotoxins based on panitumumab and cetuximab show in vitro and ex vivo activity against different tumor entities. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141:2079–2095. doi:10.1007/s00432-015-1975-5
Niesen J, Hehmann-Titt G, Woitok M, Fendel R, Barth S, Fischer R, Stein C (2016) A novel fully-human cytolytic fusion protein based on granzyme B shows in vitro cytotoxicity and ex vivo binding to solid tumors overexpressing the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Lett 374:229–240. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2016.02.020
Nohara S, Kato K, Fujiwara D, Sakuragi N, Yanagihara K, Iwanuma Y, Kajiyama Y (2016) Aminopeptidase N (APN/CD13) as a target molecule for scirrhous gastric cancer. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 40:494–503. doi:10.1016/j.clinre.2015.11.003
Pasqualini R, Koivunen E, Kain R, Lahdenranta J, Sakamoto M, Stryhn A, Ashmun RA, Shapiro LH, Arap W, Ruoslahti E (2000) Aminopeptidase N is a receptor for tumor-homing peptides and a target for inhibiting angiogenesis. Can Res 60:722–727
Pastan I, Hassan R, FitzGerald DJ, Kreitman RJ (2007) Immunotoxin treatment of cancer. Annu Rev Med 58:221–237. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.58.070605.115320
Piedfer M, Dauzonne D, Tang R, N’Guyen J, Billard C, Bauvois B (2011) Aminopeptidase-N/CD13 is a potential proapoptotic target in human myeloid tumor cells. FASEB J 25:2831–2842. doi:10.1096/fj.11-181396
Qiu Y, Lv W, Xu M, Xu Y (2016) Single chain antibody fragments with pH dependent binding to FcRn enabled prolonged circulation of therapeutic peptide in vivo. J Control Release 229:37–47. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.03.017
Raghavan M, Chen MY, Gastinel LN, Bjorkman PJ (1994) Investigation of the interaction between the class I MHC-related Fc receptor and its immunoglobulin G ligand. Immunity 1:303–315
Schiffer S, Hansen HP, Hehmann-Titt G, Huhn M, Fischer R, Barth S, Thepen T (2013) Efficacy of an adapted granzyme B-based anti-CD30 cytolytic fusion protein against PI-9-positive classical Hodgkin lymphoma cells in a murine model. Blood Cancer J 3:e106. doi:10.1038/bcj.2013.4
Schubert I, Kellner C, Stein C, Kugler M, Schwenkert M, Saul D, Stockmeyer B, Berens C, Oduncu FS, Mackensen A, Fey GH (2012) A recombinant triplebody with specificity for CD19 and HLA-DR mediates preferential binding to antigen double-positive cells by dual-targeting. MAbs 4:45–56. doi:10.4161/mabs.4.1.18498
Schubert I, Saul D, Nowecki S, Mackensen A, Fey GH, Oduncu FS (2014) A dual-targeting triplebody mediates preferential redirected lysis of antigen double-positive over single-positive leukemic cells. MAbs 6:286–296. doi:10.4161/mabs.26768
Schwenkert M, Birkholz K, Schwemmlein M, Kellner C, Kugler M, Peipp M, Nettelbeck DM, Schuler-Thurner B, Schaft N, Dorrie J, Ferrone S, Kampgen E, Fey GH (2008) A single chain immunotoxin, targeting the melanoma-associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan, is a potent inducer of apoptosis in cultured human melanoma cells. Melanoma Res 18:73–84. doi:10.1097/CMR.0b013e3282f7c8f9
Scott AM, Wolchok JD, Old LJ (2012) Antibody therapy of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 12:278–287. doi:10.1038/nrc3236
Sheng W, Shang Y, Li L, Zhen Y (2014) An EGFR/CD13 bispecific fusion protein and its enediyne-energized analog show potent antitumor activity. Anticancer Drugs 25:82–91. doi:10.1097/cad.0000000000000029
Singer H, Kellner C, Lanig H, Aigner M, Stockmeyer B, Oduncu F, Schwemmlein M, Stein C, Mentz K, Mackensen A, Fey GH (2010) Effective elimination of acute myeloid leukemic cells by recombinant bispecific antibody derivatives directed against CD33 and CD16. J Immunother (Hagerstown, Md: 1997) 33:599–608. doi:10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181dda225
Singh R, Samant U, Hyland S, Chaudhari PR, Wels WS, Bandyopadhyay D (2007) Target-specific cytotoxic activity of recombinant immunotoxin scFv(MUC1)–ETA on breast carcinoma cells and primary breast tumors. Mol Cancer Ther 6:562–569. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.mct-06-0604
Stein C, Kellner C, Kugler M, Reiff N, Mentz K, Schwenkert M, Stockmeyer B, Mackensen A, Fey GH (2010) Novel conjugates of single-chain Fv antibody fragments specific for stem cell antigen CD123 mediate potent death of acute myeloid leukaemia cells. Br J Haematol 148:879–889. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.08033.x
Stewart BW, Wild CP (2014) World Cancer Report 2014. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon
Thorpe SJ, Turner C, Heath A, Feavers I, Vatn I, Natvig JB, Thompson KM (2003) Clonal analysis of a human antimouse antibody (HAMA) response. Scand J Immunol 57:85–92
Tur MK, Huhn M, Thepen T, Stocker M, Krohn R, Vogel S, Jost E, Osieka R, van de Winkel JG, Fischer R, Finnern R, Barth S (2003) Recombinant CD64-specific single chain immunotoxin exhibits specific cytotoxicity against acute myeloid leukemia cells. Can Res 63:8414–8419
Tur MK, Huhn M, Jost E, Thepen T, Brummendorf TH, Barth S (2011) In vivo efficacy of the recombinant anti-CD64 immunotoxin H22(scFv)–ETA′ in a human acute myeloid leukemia xenograft tumor model. Int J Cancer 129:1277–1282. doi:10.1002/ijc.25766
Wang WW, Das D, Tang XL, Budzynski W, Suresh MR (2005) Antigen targeting to dendritic cells with bispecific antibodies. J Immunol Methods 306:80–92. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2005.07.023
Weidle UH, Tiefenthaler G, Schiller C, Weiss EH, Georges G, Brinkmann U (2014) Prospects of bacterial and plant protein-based immunotoxins for treatment of cancer. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 11:25–38
Wels W, Moritz D, Schmidt M, Jeschke M, Hynes NE, Groner B (1995) Biotechnological and gene therapeutic strategies in cancer treatment. Gene 159:73–80
Wickstrom M, Larsson R, Nygren P, Gullbo J (2011) Aminopeptidase N (CD13) as a target for cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Sci 102:501–508. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01826.x
Yang F, Wen W, Qin W (2016) Bispecific antibodies as a development platform for new concepts and treatment strategies. Int J Mol Sci. doi:10.3390/ijms18010048
Zhang Q, Wang J, Zhang H, Zhao D, Zhang Z, Zhang S (2015) Expression and clinical significance of aminopeptidase N/CD13 in non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer Res Ther 11:223–228. doi:10.4103/0973-1482.138007
Acknowledgements
We thank Reinhard Rosinke, Severin Schmies, Kai Fuhrmann, Anh-Tuan Pham and Nicole Kündgen-Redding (Fraunhofer IME, Aachen) for technical support and Dr. Richard M Twyman for critically reading the manuscript. The plasmids pAK100 and pAK400 were kindly provided through a material transfer agreement (Krebber et al. 1997). Mira Woitok was supported by the RWTH Aachen University scholarship of Young Researchers at RWTH Aachen University (RFwN). BHK-21 and CD16+ BHK-21 cells were kindly provided by Dr. Christian Kellner (Christian-Albrechts-University Kiel). This work was funded by the Fraunhofer MAVO-project MultiNaBeL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Mira Woitok was supported by the RWTH Aachen University scholarship of Young Researchers at RWTH Aachen University (RFwN).
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
In accordance with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and its later amendments, primary blood samples were obtained during routine clinical practice at the University Hospital Aachen after receiving informed consent and with the approval of the Clinical Research Ethics Board of the University of Aachen. The experimental use of mice was approved by the responsible local authorities and all European guidelines for the protection of laboratory animals were followed.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grieger, E., Gresch, G., Niesen, J. et al. Efficient targeting of CD13 on cancer cells by the immunotoxin scFv13–ETA′ and the bispecific scFv [13xds16]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 143, 2159–2170 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2468-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2468-5