Abstract
Purpose
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is overexpressed in many solid tumors. EGFR-specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), such as cetuximab and panitumumab, have been approved for the treatment of colorectal and head and neck cancer. To increase tissue penetration, we constructed single-chain fragment variable (scFv) antibodies derived from these mAbs and evaluated their potential for targeted cancer therapy. The resulting scFv-based EGFR-specific immunotoxins (ITs) combine target specificity of the full-size mAb with the cell-killing activity of a toxic effector domain, a truncated version of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (ETA′).
Methods
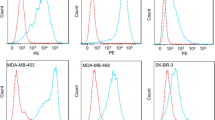
The ITs and corresponding imaging probes were tested in vitro against four solid tumor entities (rhabdomyosarcoma, breast, prostate and pancreatic cancer). Specific binding and internalization of the ITs scFv2112-ETA′ (from cetuximab) and scFv1711-ETA′ (from panitumumab) were demonstrated by flow cytometry and for the scFv-SNAP-tag imaging probes by live cell imaging. Cytotoxic potential of the ITs was analyzed in cell viability and apoptosis assays. Binding of the ITs was proofed ex vivo on rhabdomyosarcoma, prostate and breast cancer formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded biopsies.
Results
Both novel ITs showed significant pro-apoptotic and anti-proliferative effects toward the target cells, achieving IC50 values of 4 pM (high EGFR expression) to 460 pM (moderate EGFR expression). Additionally, rapid internalization and specific in vitro and ex vivo binding on patient tissue were confirmed.
Conclusions
These data demonstrate the potent therapeutic activity of two novel EGFR-specific ETA′-based ITs. Both molecules are promising candidates for further development toward clinical use in the treatment of various solid tumors to supplement the existing therapeutic regimes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad ZA, Yeap SK, Ali AM, Ho WY, Alitheen NB, Hamid M (2012) scFv antibody: principles and clinical application. Clin Dev Immunol 2012:980250. doi:10.1155/2012/980250
Allen TM (2002) Ligand-targeted therapeutics in anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2:750–763. doi:10.1038/nrc903
Alvarenga ML et al (2012) In-depth biophysical analysis of interactions between therapeutic antibodies and the extracellular domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Anal Biochem 421:138–151. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2011.10.039
Amoury M et al (2013) SNAP-tag based agents for preclinical in vitro imaging in malignant diseases. Curr Pharm Des 19:5429–5436
Antignani A, Fitzgerald D (2013) Immunotoxins: the role of the toxin. Toxins 5:1486–1502. doi:10.3390/toxins5081486
Armistead PM et al (2007) Expression of receptor tyrosine kinases and apoptotic molecules in rhabdomyosarcoma: correlation with overall survival in 105 patients. Cancer 110:2293–2303. doi:10.1002/cncr.23038
Asano R et al (2013) Multimerization of anti-(epidermal growth factor receptor) IgG fragments induces an antitumor effect: the case for humanized 528 scFv multimers. FEBS J 280:4816–4826. doi:10.1111/febs.12451
Azemar M et al (2000) Recombinant antibody toxins specific for ErbB2 and EGF receptor inhibit the in vitro growth of human head and neck cancer cells and cause rapid tumor regression in vivo. Int J Cancer 86:269–275
Bachran D et al (2010) Epidermal growth factor receptor expression affects the efficacy of the combined application of saponin and a targeted toxin on human cervical carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 127:1453–1461. doi:10.1002/ijc.25123
Barnea I, Ben-Yosef R, Karaush V, Benhar I, Vexler A (2013) Targeting EGFR-positive cancer cells with cetuximab-ZZ-PE38: results of in vitro and in vivo studies. Head Neck 35:1171–1177. doi:10.1002/hed.23093
Barth S (2002) Technology evaluation: bL22, NCI. Curr opin Mol Ther 4:72–75
Becker N, Benhar I (2012) Antibody-based immunotoxins for the treatment of cancer. Antibodies 1:39–69. doi:10.3390/antib1010039
Bruell D et al (2003) The recombinant anti-EGF receptor immunotoxin 425(scFv)-ETA′ suppresses growth of a highly metastatic pancreatic carcinoma cell line. Int J Oncol 23:1179–1186
Bruell D et al (2005) Recombinant anti-EGFR immunotoxin 425(scFv)-ETA′ demonstrates anti-tumor activity against disseminated human pancreatic cancer in nude mice. Int J Mol Med 15:305–313
Bruns CJ, Harbison MT, Kuniyasu H, Eue I, Fidler IJ (1999) In vivo selection and characterization of metastatic variants from human pancreatic adenocarcinoma by using orthotopic implantation in nude mice. Neoplasia (New York, NY) 1:50–62
Cao Y, Mohamedali KA, Marks JW, Cheung LH, Hittelman WN, Rosenblum MG (2013) Construction and characterization of novel, completely human serine protease therapeutics targeting Her2/neu. Mol Cancer Ther 12:979–991. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0002
Carey LA et al (2012) TBCRC 001: randomized phase II study of cetuximab in combination with carboplatin in stage IV triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 30:2615–2623. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.34.5579
Cathomas R et al (2012) Efficacy of cetuximab in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer might depend on EGFR and PTEN expression: results from a phase II trial (SAKK 08/07). Clin Cancer Res 18:6049–6057. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-12-2219
Chandramohan V, Bigner DD (2013) A novel recombinant immunotoxin-based therapy targeting wild-type and mutant EGFR improves survival in murine models of glioblastoma. Oncoimmunology 2:e26852. doi:10.4161/onci.26852
Chandramohan V et al (2013) Construction of an immunotoxin, D2C7-(scdsFv)-PE38KDEL, targeting EGFRwt and EGFRvIII for brain tumor therapy. Clin Cancer Res 19:4717–4727. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-12-3891
Chaudhary VK, FitzGerald DJ, Adhya S, Pastan I (1987) Activity of a recombinant fusion protein between transforming growth factor type alpha and Pseudomonas toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:4538–4542
Cizeau J, Grenkow DM, Brown JG, Entwistle J, MacDonald GC (2009) Engineering and biological characterization of VB6-845, an anti-EpCAM immunotoxin containing a T-cell epitope-depleted variant of the plant toxin bouganin. J Immunother (Hagerstown, Md : 1997) 32:574–584. doi:10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181a6981c
de Goeij BE et al (2014) HER2 monoclonal antibodies that do not interfere with receptor heterodimerization-mediated signaling induce effective internalization and represent valuable components for rational antibody-drug conjugate design. mAbs 6:392–402. doi:10.4161/mabs.27705
de Larco JE, Todaro GJ (1978) Epithelioid and fibroblastic rat kidney cell clones: epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors and the effect of mouse sarcoma virus transformation. J Cell Physiol 94:335–342. doi:10.1002/jcp.1040940311
Faller BA, Burtness B (2009) Treatment of pancreatic cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy. Biologics 3:419–428
Freeman DJ (2009) Safety and efficacy of panitumumab in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Med 2009(1):633–645
Ganti R et al (2006) Expression and genomic status of EGFR and ErbB-2 in alveolar and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Mod Pathol 19:1213–1220. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800636
Gerber HP, Koehn FE, Abraham RT (2013) The antibody-drug conjugate: an enabling modality for natural product-based cancer therapeutics. Nat Prod Rep 30:625–639. doi:10.1039/c3np20113a
Gilabert-Oriol R et al (2013) Modified trastuzumab and cetuximab mediate efficient toxin delivery while retaining antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in target cells. Mol Pharm 10:4347–4357. doi:10.1021/mp400444q
Hristodorov D et al (2013) Microtubule-associated protein tau facilitates the targeted killing of proliferating cancer cells in vitro and in a xenograft mouse tumour model in vivo. Br J Cancer 109:1570–1578. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.457
Hussain AF, Kampmeier F, von Felbert V, Merk HF, Tur MK, Barth S (2011) SNAP-tag technology mediates site specific conjugation of antibody fragments with a photosensitizer and improves target specific phototoxicity in tumor cells. Bioconjugate Chem 22:2487–2495. doi:10.1021/bc200304k
Jakobovits A, Yang XD, Gallo M, Jia X (2001) Human monoclonal antibodies to epidermal growth factor receptor. US Patent
Kamat V et al (2008) Enhanced EGFR inhibition and distinct epitope recognition by EGFR antagonistic mAbs C225 and 425. Cancer Biol Ther 7:726–733
Kampmeier F, Ribbert M, Nachreiner T, Dembski S, Beaufils F, Brecht A, Barth S (2009) Site-specific, covalent labeling of recombinant antibody fragments via fusion to an engineered version of 6-O-alkylguanine DNA alkyltransferase. Bioconjugate Chem 20:1010–1015. doi:10.1021/bc9000257
Kampmeier F et al (2010) Rapid optical imaging of EGF receptor expression with a single-chain antibody SNAP-tag fusion protein. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37:1926–1934. doi:10.1007/s00259-010-1482-5
Kim GP, Grothey A (2008) Targeting colorectal cancer with human anti-EGFR monoclonocal antibodies: focus on panitumumab. Biologics 2:223–228
Koefoed K et al (2011) Rational identification of an optimal antibody mixture for targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. mAbs 3:584–595. doi:10.4161/mabs.3.6.17955
Kreitman RJ (2006) Immunotoxins for targeted cancer therapy. AAPS J 8:E532–E551. doi:10.1208/aapsj080363
Li S, Schmitz KR, Jeffrey PD, Wiltzius JJ, Kussie P, Ferguson KM (2005) Structural basis for inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor by cetuximab. Cancer Cell 7:301–311. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.03.003
Lukianova-Hleb EY, Belyanin A, Kashinath S, Wu X, Lapotko DO (2012) Plasmonic nanobubble-enhanced endosomal escape processes for selective and guided intracellular delivery of chemotherapy to drug-resistant cancer cells. Biomaterials 33:1821–1826. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.11.015
Madhumathi J, Verma RS (2012) Therapeutic targets and recent advances in protein immunotoxins. Curr Opin Microbiol 15:300–309. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2012.05.006
Mamot C, Ritschard R, Kung W, Park JW, Herrmann R, Rochlitz CF (2006) EGFR-targeted immunoliposomes derived from the monoclonal antibody EMD72000 mediate specific and efficient drug delivery to a variety of colorectal cancer cells. J Drug Target 14:215–223. doi:10.1080/10611860600691049
Matthey B, Engert A, Klimka A, Diehl V, Barth S (1999) A new series of pET-derived vectors for high efficiency expression of Pseudomonas exotoxin-based fusion proteins. Gene 229:145–153
Mendelsohn J (2002) Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor for cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 20:1s–13s
Monnier PP, Vigouroux RJ, Tassew NG (2013) In vivo applications of single chain Fv (variable domain) (scFv) fragments. Antibodies 2:193–208. doi:10.3390/antib2020193
Muller KM, Arndt KM, Strittmatter W, Pluckthun A (1998) The first constant domain (C(H)1 and C(L)) of an antibody used as heterodimerization domain for bispecific miniantibodies. FEBS Lett 422:259–264
Murthy U, Basu A, Rodeck U, Herlyn M, Ross AH, Das M (1987) Binding of an antagonistic monoclonal antibody to an intact and fragmented EGF-receptor polypeptide. Arch Biochem Biophys 252:549–560
Nabholtz JM et al (2012) P3-14-01: panitumumab in combination with FEC 100 (5-fluorouracile, epirubicin, cyclophosphamide) followed by docetaxel (T) in patients with operable, triple negative breast cancer (TNBC): final results of a multicentre neoadjuvant pilot phase II study. Cancer Res 71:P3-14-01–P13-14-01. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.sabcs11-p3-14-01
Nachreiner T, Kampmeier F, Thepen T, Fischer R, Barth S, Stocker M (2008) Depletion of autoreactive B-lymphocytes by a recombinant myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-based immunotoxin. J Neuroimmunol 195:28–35. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.01.001
Nicholson RI, Gee JM, Harper ME (2001) EGFR and cancer prognosis. Eur J Cancer 37(Suppl 4):S9–S15
Niesen J et al (2014) In vitro effects and ex vivo binding of an EGFR-specific immunotoxin on rhabdomyosarcoma cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. doi:10.1007/s00432-014-1884-z
Panowksi S, Bhakta S, Raab H, Polakis P, Junutula JR (2014) Site-specific antibody drug conjugates for cancer therapy. mAbs 6:34–45. doi:10.4161/mabs.27022
Pardo A, Stocker M, Kampmeier F, Melmer G, Fischer R, Thepen T, Barth S (2012) In vivo imaging of immunotoxin treatment using Katushka-transfected A-431 cells in a murine xenograft tumour model. Cancer Immunol Immunother (CII) 61:1617–1626. doi:10.1007/s00262-012-1219-3
Pastan I, Hassan R, FitzGerald DJ, Kreitman RJ (2007) Immunotoxin treatment of cancer. Annu Rev Med. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.58.070605.115320
Pedersen MW, Jacobsen HJ, Koefoed K, Hey A, Pyke C, Haurum JS, Kragh M (2010) Sym004: a novel synergistic anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody mixture with superior anticancer efficacy. Cancer Res 70:588–597. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1417
Pines G, Kostler WJ, Yarden Y (2010) Oncogenic mutant forms of EGFR: lessons in signal transduction and targets for cancer therapy. FEBS Lett 584:2699–2706. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2010.04.019
Reichert JM (2014) Antibodies to watch in 2014: mid-year update. MAbs 6(4):799–802. doi:10.4161/mabs.29282
Ricci C et al (2000) Expression of HER/erbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases and induction of differentiation by glial growth factor 2 in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Int J Cancer 87:29–36
Sandvig K, van Deurs B (2005) Delivery into cells: lessons learned from plant and bacterial toxins. Gene Ther 12:865–872. doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3302525
Sasaki T, Hiroki K, Yamashita Y (2013) The role of epidermal growth factor receptor in cancer metastasis and microenvironment. BioMed Res Int 2013:546318. doi:10.1155/2013/546318
Schiffer S et al (2013) Species-dependent functionality of the human cytolytic fusion proteins granzyme B-H22(scFv) and H22(scFv)-angiogenin in macrophages. Antibodies 2:9–18. doi:10.3390/antib2010009
Schlessinger J Givol D, Bellot F, Kris R, Ricca G, Cheadle C, South V (2001) Monoclonal antibodies specific to human epidermal growth factor receptor an therapeutic methods employing same. US Patent
Schmidt M, Vakalopoulou E, Schneider DW, Wels W (1997) Construction and functional characterization of scFv(14E1)-ETA—a novel, highly potent antibody-toxin specific for the EGF receptor. Br J Cancer 75:1575–1584
Schneider MR, Yarden Y (2014) Structure and function of epigen, the last EGFR ligand. Semin Cell Dev Biol. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2013.12.011
Schrama D, Reisfeld RA, Becker JC (2006) Antibody targeted drugs as cancer therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:147–159. doi:10.1038/nrd1957
Schwenkert M et al (2008) A single chain immunotoxin, targeting the melanoma-associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan, is a potent inducer of apoptosis in cultured human melanoma cells. Melanoma Res 18:73–84. doi:10.1097/CMR.0b013e3282f7c8f9
Scott AM, Wolchok JD, Old LJ (2012) Antibody therapy of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 12:278–287. doi:10.1038/nrc3236
Shim H (2011) One target, different effects: a comparison of distinct therapeutic antibodies against the same targets. Exp Mol Med 43:539–549. doi:10.3858/emm.2011.43.10.063
Singh R, Samant U, Hyland S, Chaudhari PR, Wels WS, Bandyopadhyay D (2007) Target-specific cytotoxic activity of recombinant immunotoxin scFv(MUC1)-ETA on breast carcinoma cells and primary breast tumors. Mol Cancer Ther 6:562–569. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0604
Sliwkowski MX, Mellman I (2013) Antibody therapeutics in cancer. Science 341:1192–1198. doi:10.1126/science.1241145
Stahnke B et al (2008) Granzyme B-H22(scFv), a human immunotoxin targeting CD64 in acute myeloid leukemia of monocytic subtypes. Mol Cancer Ther 7:2924–2932. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0554
Stein C et al (2010) Novel conjugates of single-chain Fv antibody fragments specific for stem cell antigen CD123 mediate potent death of acute myeloid leukaemia cells. Br J Haematol 148:879–889. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2009.08033.x
Stocker M, Tur MK, Sasse S, Krussmann A, Barth S, Engert A (2003) Secretion of functional anti-CD30-angiogenin immunotoxins into the supernatant of transfected 293T-cells. Protein Expr Purif 28:211–219
Tebbutt N, Pedersen MW, Johns TG (2013) Targeting the ERBB family in cancer: couples therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 13:663–673. doi:10.1038/nrc3559
Thorpe SJ, Turner C, Heath A, Feavers I, Vatn I, Natvig JB, Thompson KM (2003) Clonal analysis of a human antimouse antibody (HAMA) response. Scand J Immunol 57:85–92
Tur MK et al (2003) Recombinant CD64-specific single chain immunotoxin exhibits specific cytotoxicity against acute myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Res 63:8414–8419
Voigt M, Braig F, Gothel M, Schulte A, Lamszus K, Bokemeyer C, Binder M (2012) Functional dissection of the epidermal growth factor receptor epitopes targeted by panitumumab and cetuximab. Neoplasia (New York, NY) 14:1023–1031
von Minckwitz G et al (2005) Phase I clinical study of the recombinant antibody toxin scFv(FRP5)-ETA specific for the ErbB2/HER2 receptor in patients with advanced solid malignomas. Breast Cancer Res (BCR) 7:R617–R626. doi:10.1186/bcr1264
Weidle UH, Georges G, Brinkmann U (2012) Fully human targeted cytotoxic fusion proteins: new anticancer agents on the horizon. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 9:119–133
Weldon JE, Pastan I (2011) A guide to taming a toxin–recombinant immunotoxins constructed from Pseudomonas exotoxin A for the treatment of cancer. FEBS J 278:4683–4700. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08182.x
Wilkins DK, Mayer A (2006) Development of antibodies for cancer therapy. Exp Opin Biol Therapy 6:787–796. doi:10.1517/14712598.6.8.787
Wolf P, Gierschner D, Buhler P, Wetterauer U, Elsasser-Beile U (2006) A recombinant PSMA-specific single-chain immunotoxin has potent and selective toxicity against prostate cancer cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother (CII) 55:1367–1373. doi:10.1007/s00262-006-0131-0
Wolf P et al (2010) Preclinical evaluation of a recombinant anti-prostate specific membrane antigen single-chain immunotoxin against prostate cancer. J Immunother (Hagerstown, Md: 1997). doi:10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181c5495c
Yewale C, Baradia D, Vhora I, Patil S, Misra A (2013) Epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in cancer: a review of trends and strategies. Biomaterials 34:8690–8707. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.07.100
Acknowledgments
Christoph Stein was supported by the INTERREG IV A project Microbiomed. This work was funded in part by a grant from the German province NRW from EFRE “European Fund for Regional Development” under the theme “Europe—Investment in our Future.” We would like to thank Radoslav Mladenov and Nina Berges (Department of Experimental Medicine and Immunotherapy, Institute of Applied Medical Engineering, RWTH Aachen University Clinic, Aachen, Germany) for their help with immunohistochemistry and confocal microscopy. For obtaining the tissue sections, we want to thank Dr. Mehmet Kemal Tur (Department of Pathology, Justus-Liebig University, Giessen, Germany). We also thank Dr. Richard M. Twyman for critical reading of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Georg Melmer is a stakeholder of Pharmedartis GmbH and Grit Hehmann-Titt is employed by Pharmedartis. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standard
In accordance with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, primary tissue samples were obtained during routine clinical practice at the University Hospital Giessen approved by the appropriate ethics committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
The scFv2112-SNAP construct labeled with BG-Alexa Fluor® 488 incubated with the EGFR- cell line U937. Hoechst-stained nucleoli are shown in the left image. No unspecific binding of the ITs to U937 cells was detected (middle image). The right picture shows the white light channel. (TIFF 278 kb)
Fig. S2
The scFv-SNAP constructs, scFv2112-SNAP and scFv1711-SNAP, the parental mAbs cetuximab and panitumumab and a non-binding mock-ETA’ construct were used as controls in XTT assays. Unspecific effects were not observed up to the highest starting concentration used for the ITs (80 nM). As before the experiments were carried out at least four times in triplicate or quadruplicate, GraphPad Prism software was used for calculation of potential reduction in protein synthesis. (TIFF 271 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niesen, J., Stein, C., Brehm, H. et al. Novel EGFR-specific immunotoxins based on panitumumab and cetuximab show in vitro and ex vivo activity against different tumor entities. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141, 2079–2095 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-1975-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-1975-5