Abstract
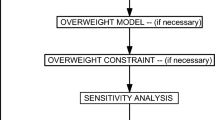
The design of mechanical microstructures having auxetic behaviour is proposed in this paper using techniques of topology optimization for compliant mechanisms. A robust hybrid algorithm based on evolutionary algorithms and local search steps is used. The result may need verification in order to accommodate needs not taken into account in the topology optimization. Therefore, a numerical homogenization scheme is used in order to show that the final design still has the wished negative Poisson’s property.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaire G., Jouve F., Maillot H.: Topology optimization for minimum stress design with the homogenization method. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 28(2–3), 87–98 (2004)
Andreassen E., Lazarov B.S., Sigmund O.: Design of manufacturable 3D extremal elastic microstructure. Mech. Mater. 69(1), 1–10 (2014)
ASME: Guide for Verification and Validation in Computational Solid Mechanics. American Society of Mechanical Engineers (2006)
Bendsøe M.P.: Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 1(4), 193–202 (1989)
Bendsøe M.P., Kikuchi N.: Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 71(2), 197–224 (1988)
Bendsøe M.P., Sigmund O.: Topology Optimization—Theory, Methods and Applications, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Bendsøe M.P., Sigmund O.: Topology Optimization. Theory, Methods and Applications, 2nd edn, pp. 94–98. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Canfield S., Frecker M.: Topology optimization of compliant mechanical amplifiers for piezoelectric actuators. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 20(4), 269–279 (2000)
Dascalu C., Bilbie G., Agiasofitou E.K.: Damage and size effects in elastic solids: a homogenization approach. Int. J. Solids Struct. 45(2), 409–430 (2008)
Drosopoulos, G.A., Wriggers, P., Stavroulakis, G.E.: Contact analysis in multi-scale computational homogenization. In: Jirásek, M., Allix, O., Moës, N., Oliver, J. (eds.) Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Computational Modeling of Fracture and Failure of Materials and Structures (CFRAC), p. 226. Prague, Czech Republic (2013)
Drosopoulos, G.A., Wriggers, P., Stavroulakis, G.E.: Incorporation of contact mechanics in multi-level computational homogenization for the study of composite materials. In: Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Computational Contact Mechanics (ICCCM). Lecce, Italy (2013)
Eberhart, R., Kennedy, J.: A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: Micro Machine and Human Science, 1995. MHS ’95, Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on, pp. 39–43 (1995)
Frecker M., Kikuchi N., Kota S.: Topology optimization of compliant mechanisms with multiple outputs. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 17(4), 269–278 (1999)
Geers M.G.D., Kouznetsova V., Brekelmans W.A.M.: Multi-scale computational homogenization: trends and challenges. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 234(7), 2175–2182 (2010)
Herakovich C.T.: Composite laminates with negative through-the-thickness Poisson’s ratios. J. Compos. Mater. 18(5), 447–455 (1984)
Hill R.: Elastic properties of reinforced solids: some theoretical principles. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 11(5), 357–372 (1963)
Holland J.H.: Outline for a logical theory of adaptive systems. J. ACM 9(3), 297–314 (1962)
Holland J.H.: Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems: An Introductory Analysis with Applications to Biology, Control and artificial Intelligence. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA (1992)
Kaminakis N.T., Stavroulakis G.E.: Topology optimization for compliant mechanisms, using evolutionary-hybrid algorithms and application to the design of auxetic materials. Compos. Part B Eng. 43(6), 2655–2668 (2012)
Kanouté P., Boso D., Chaboche J., Schrefler B.: Multiscale methods for composites: a review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 16(1), 31–75 (2009)
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.: Particle swarm optimization. In: Neural Networks, 1995. Proceedings, IEEE International Conference on, vol. 4, pp. 1942–1948 (1995)
Kouznetsova, V.: Computational Homogenization for the Multi-Scale Analysis of Multi-Phase materials. PhD thesis. Technical University Eindhoven, The Netherlands (2002)
Krishnan, G., Ananthasuresh, G.K.: Evaluation and design of displacement-amplifying compliant mechanisms for sensor applications. J. Mech. Des. 130(10), 102304 (2008)
Larsen U., Sigmund O., Bouwstra S.: Design and fabrication of compliant micromechanisms and structures with negative Poisson’s ratio. J. Micro Electro. Mech. Syst. 6(2), 99–106 (1997)
Liu, Q.: Literature Review: Materials with Negative Poisson’s Ratios and Potential Applications to Aerospace and Defence. Technical Report DSTO-GD-0472, Air Vehicles Division, Defence Science and Technology Organisation, Department of Defence, Australian Goverment (2006)
Mankame N.D., Ananthasuresh G.K.: Synthesis of contact-aided compliant mechanisms for non-smooth path generation. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 69(12), 2564–2605 (2007)
Massart T.J., Peerlings R.H.J., Geers M.G.D.: Structural damage analysis of masonry walls using computational homogenization. Int. J. Damage Mech. 16(2), 199–226 (2007)
Mehta V., Frecker M., Lesieutre G.A.: Stress relief in contact-aided compliant cellular mechanisms. J. Mech. Des. 131(9), 091009 (2009)
Nakshatrala P.B., Tortorelli D.A., Nakshatrala K.B.: Nonlinear structural design using multiscale topology optimization. Part i: static formulation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 261–262, 167–176 (2013)
Osher S., Sethian J.A.: Fronts propagating with curvature dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton–Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 79(1), 12–49 (1988)
Pettermann H.E., Suresh S.: A comprehensive unit cell model: a study of coupled effects in piezoelectric 1–3 composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 37(39), 5447–5464 (2000)
Pindera M.J., Khatam H., Drago A.S., Bansal Y.: Micromechanics of spatially uniform heterogeneous media: a critical review and emerging approaches. Compos. Part B Eng. 40(5), 349–378 (2009)
Price K.V., Storn R.M., Lampinen J.A.: Differential Evolution—A practical Approach to Global Optimization. Natural Computing Series. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Rozvany G.I.N.: Structural Design Via Optimality Criteria. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1989)
Rozvany G.I.N.: A critical review of established methods of structural topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 37(3), 217–237 (2009)
Sanchez-Palencia E.: Non-homogeneous Media and Vibration Theory, Lecture Notes in Physics. Springer, Berlin (1980)
Sethian J.A.: Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods: Evolving Interfaces in Computational Geometry, Fluid Mechanics, Computer Vision and Materials Science. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, MA (1999)
Sigmund O.: Some Inverse Problems in Topology Design of Materials and Mechanisms, pp. 277–284. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1996)
Sigmund O.: A 99 line topology optimization code written in Matlab. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 21(2), 120–127 (2001)
Sigmund O.: On the usefulness of non-gradient approaches in topology optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 43(5), 589–596 (2011)
Sigmund O., Torquato S.: Composites with extremal thermal expansion coefficients. Appl. Phys. Lett. 69(21), 3203–3205 (1996)
Sigmund O., Torquato S.: Design of smart composite materials using topology optimization. Smart Mater. Struct. 8, 365–379 (1999)
Sokolowski J., Zochowski A.: On the topological derivative in shape optimization. SIAM J. Control Optim. 37(4), 1251–1272 (1999)
Storn R., Price K.: Differential evolution—a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J. Glob. Optim. 11(4), 341–359 (1997)
Suquet P., Sawczuk A., Bianchi G.: Local and Global Aspects in the Mathematical Theory of Plasticity, Plasticity Today: Modelling, Methods and Applications. Elsevier, London (1985)
Svanberg K.: The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 24(2), 359–373 (1987)
Theocaris P.S., Stavroulakis G.E., Panagiotopoulos P.D.: Negative Poisson’s ratios in composites with star-shaped inclusions: a numerical homogenization approach. Arch. Appl. Mech. 67(4), 274–286 (1997)
Yoon G., Kim Y., Bendsøe M., Sigmund O.: Hinge-free topology optimization with embedded translation-invariant differentiable wavelet shrinkage. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 27(3), 139–150 (2004)
Zohdi T.I., Wriggers P.: An Introduction to Computational Micromechanics. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaminakis, N.T., Drosopoulos, G.A. & Stavroulakis, G.E. Design and verification of auxetic microstructures using topology optimization and homogenization. Arch Appl Mech 85, 1289–1306 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-014-0970-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-014-0970-7