Abstract
Background
To compare intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements obtained by the Icare ONE rebound tonometer (RTONE) and the Goldmann applanation tonometer (GAT) in healthy persons and glaucoma patients in a prospective study, and to investigate the influence of central corneal thickness (CCT).
Methods
Measurements on 126 right eyes were obtained by three equally skilled ophthalmologists with each of the above-mentioned tonometers. In addition, patients measured their own IOP with the RTONE (RTONE(p)). The means and standard deviation for all tonometers were compared. Agreement between the tonometers was calculated using the Bland–Altman method.
Results
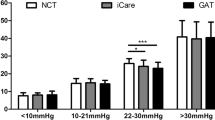
A total of 95 (75.3%) patients were able to perform correct self-tonometry. Mean IOPs obtained were 17.1 ± 5.9 mmHg (RTONE performed by ophthalmologist: RTONE (o)), 17.3 ± 5.6 mmHg (RTONE(p)) and 16.5 ± 5.1 mmHg (GAT). Correlation analysis indicated a good correlation between IOP readings obtained using RTONE(o) and RTONE(p) (ρ = 0.916; p < 0.001) and RTONE(o) and GAT (ρ = 0.901; p < 0.001). Bland–Altman analysis revealed a mean difference (bias) between RTONE(o) and RTONE(p), between RTONE(o) and GAT, and between RTONE(p) and GAT of −0.2, 0.6, and 0.8 mmHg, respectively, with 95% limits of agreement of −5.0 to 4.5, –4.4 to 5.6, and −4.6 to 6.1 mmHg, respectively. The difference between RTONE(o) and GAT significantly increased with increasing CCT (ρ = 0.004), with a 10% increase in CCT resulting in a 1.8% increase in the difference.
Conclusions
Measurements obtained with the RTONE, either by an ophthalmologist or by the patient, showed an excellent correlation with those provided by applanation tonometry. RTONE generally tends to overestimate IOP compared to GAT readings and displays a dependence on CCT.
This study was registered with the DRKS (German Clinical Trials Register; www.germanctr.de; DRKS00000478).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quigley HA (1996) Number of people with glaucoma worldwide. Br J Ophthalmol 80:389–393
Kass MA (1996) Standardizing the measurement of intraocular pressure for clinical research. Guidelines from the Eye Care Technology Forum. Ophthalmology 103:183–185
Kontiola AI (1997) A new electromechanical method for measuring intraocular pressure. Doc Ophthalmol 93:265–276
Danias J, Kontiola AI, Filippopoulos T, Mittag T (2003) Method for the noninvasive measurement of intraocular pressure in mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:1138–1141
Abraham LM, Epasinghe NCR, Selva D, Casson R (2008) Comparison of the Icare® rebound tonometer with the Goldmann applanation tonometer by experienced and inexperience tonometrists. Eye 22:503–506
Sahin A, Basmak H, Niyaz L, Yildirim N (2007) Reproducibility and tolerability of the Icare rebound tonometer in school children. J Glaucoma 16:185–188
Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Garcia-Feijoo J, Castillo A, Garcia-Sanchez J (2005) Reproducibility and clinical evaluation of rebound tonometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:4578–4580
Dielemans I, Vingerling JR, Hofman A, Grobbee DE, de Jong PT (1994) Reliability of intraocular pressure measurement with the Goldmann applanation tonometer in epidemiological studies. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 232:141–144
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1:307–310
van der Jagt LH, Jansonius LM (2005) Three portable tonometers, the TGDc-01, the Icare and the Tonopen XL, compared with each other and with Goldmann applanation tonometry. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 25:429–435
Iliev ME, Goldblum D, Katsoulis K, Amstutz C, Frueh B (2006) Comparison of rebound tonometry with Goldmann applanation tonometry and correlation with central corneal thickness. Br J Ophthalmol 90:833–835
Fernandes P, Diaz-Rey JA, Queiros A, Gonzalez-Meijome JM, Jorge J (2005) Comparison of the Icare rebound tonometer with the Goldmann tonometer in a normal population. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 25:436–440
Garcia-Resua C, Gonzalez-Meijome JM, Gilino J, Yebra-Pimentel E (2006) Accuracy of the new Icare rebound tonometer vs. other portable tonometers in healthy eyes. Optom Vis Sci 83:102–107
Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Garcia-Feijoo J, Vico E, Fernandez-Vidal A, Benitez del Castillo JM, Wasfi M, Garcia-Sanchez J (2006) Effect of corneal thickness on dynamic contour, rebound, and Goldmann tonometry. Ophthalmology 113:2156–2162
Munkwitz S, Elkarmouty A, Hoffmann EM, Pfeiffer N, Thieme H (2008) Comparison of the Icare rebound tonometer and the Goldmann applanation tonometer over a wide IOP range. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246:875–879
Poostchi A, Mitchell R, Nicholas S, Purdie G, Wells A (2009) The Icare rebound tonometer: comparisons with Goldmann tonometry, and influence of central corneal thickness. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 37:687–691
Emara B, Probst LE, Tingey DP, Kennedy DW, Willms LJ, Machat J (1998) Correlation of intraocular pressure and central corneal thickness in normal myopic eyes and after laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg 24:1320–1325
Lam AK, Wu R, Wang Z, Woo V, Chan E, Tam K, Chau R, Wong KK (2010) Effect of laser in situ keratomileusis on rebound tonometry and Goldmann applanation tonometry. J Cataract Refract Surg 36:631–636
Schipper I, Senn P, Oyo-Szerenyi K, Peter R (2000) Central and peripheral pressure measurements with the Goldmann tonometer and Tono-Pen after photorefractive keratectomy for myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg 26:929–933
Ehlers N, Bramsen T, Sperling S (1975) Applanation tonometry and central corneal thickness. Acta Ophthalmol 53:34–43
Kohlhaas M, Boehm AG, Spoerl E, Pürsten A, Grein HJ, Pillunat LE (2006) Effect of central corneal thickness, corneal curvature, and axial length on applanation tonometry. Arch Ophthalmol 124:471–476
Whitacre MM, Stein RA, Hassanein K (1993) The effect of corneal thickness on applanation tonometry. Am J Ophthalmol 115:592–596
Martinez-de-la-Casa JM, Garcia-Feijoo J, Saenz-Frances VG, Fernandez-Vidal A, Mendez-Hernandez C, Garcia-Sanchez J (2009) Comparison of rebound tonometer and Goldmann handheld applanation tonometer in congenital glaucoma. J Glaucoma 18:49–52
Pakrou N, Gray T, Mills R, Landers J, Craig J (2008) Clinical comparison of the Icare tonometer and Goldmann applanation tonometry. J Glaucoma 17:43–47
Brusini P, Salvetat ML, Zeppieri M, Tosoni C, Parisi L (2006) Comparison of Icare tonometer with Goldmann applanation tonometer in glaucoma patients. J Glaucoma 15:213–217
Sacu S, Vass C, Schemper M, Rainer G (2004) Self-tonometry with the Ocuton S: evaluation of accuracy in glaucoma patients. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 82:405–409
Leonardi M, Leuenberger P, Bertrand D, Bertsch A, Renaud P (2004) First steps toward noninvasive intraocular pressure monitoring with a sensing contact lens. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:3113–3117
Leonardi M, Pitchon EM, Bertsch A, Renaud P, Mermoud A (2009) Wireless contact lens sensor for intraocular pressure monitoring: assessment on enucleated pig eyes. Acta Ophthalmol 87:433–437
Hediger A, Kniestedt C, Zweifel S, Knecht P, Funk J, Kanngiesser H (2009) Continuous intraocular pressure measurement: first results with a pressure-sensitive contact lens. Ophthalmologe 106:1111–1115
Draeger J, Schwartz R, Deutsch C, Groenhoff S (1991) Clinical and experimental results with a new fully automatic self-tonometer. Fortschr Ophthalmol 88:304–307
Draeger J, Groenhoff S, Hock B, Klemm M (1993) Optimizing the automatic self-tonometer by an acoustic control signal and changed fixation optics. Ophthalmologe 90:54–57
Asrani S, Chatterjee A, Wallace DK, Santiago-Turla C, Stinnett S (2011) Evaluation of the Icare rebound tonometer as a home intraocular pressure monitoring device. J Glaucoma 20:74–79
Chui WS, Lam A, Chen D, Chiu R (2008) The influence of corneal properties on rebound tonometry. Ophthalmology 115:80–84
Competing interest for all authors
None to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors have full control of all primary data and agree to allow Graefes Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology to review their data upon request.
Clinical trial registration: German Clinical Trials Register; number: DRKS00000478.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosentreter, A., Jablonski, K.S., Mellein, A.C. et al. A new rebound tonometer for home monitoring of intraocular pressure. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 249, 1713–1719 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-011-1785-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-011-1785-7