Abstract
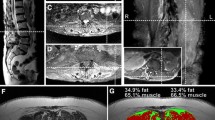
The pathophysiology of postural abnormalities in patients with Parkinson’s disease is poorly understood. In the present study, 13 patients with Pisa syndrome (PS) underwent EMG study of paraspinal lumbar (L2–L4) and thoracic (T8–T10) muscles, and of non-paraspinal muscles. Patients also underwent a whole spine X-ray and an MRI assessment of paraspinal muscles (L1–S1). The EMG evaluation disclosed two main patterns: patients with pattern I (n = 6, hyperactivity of lumbar paraspinals ipsilateral to the trunk leaning side) or pattern II (n = 7: hyperactivity of lumbar paraspinals contralateral to the trunk leaning side. In pattern I, half the patients also had ipsilateral hyperactivity of the thoracic paraspinals, the other half had contralateral thoracic hyperactivity; in pattern II, thoracic paraspinal hyperactivity was contralateral in all patients (like the lumbar paraspinal hyperactivity). Non-paraspinal muscles were hyperactive ipsilaterally in four of six patients with pattern I and in all patients with pattern II. The MRI showed mild muscular atrophy with fatty degeneration in patients with pattern I, whereas in pattern II patients this was greater and prevalent on paraspinal lumbar muscles ipsilateral to the leaning side. The present data support the hypothesis that two main patterns of muscular activation are associated with PS. In both patterns, hyperactivity of contralateral paraspinal muscles is probably compensatory for the trunk leaning.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doherty KM, van de Warrenburg BP, Peralta MC, Silveira-Moriyama L, Azulay JP, Gershanik OS, Bloem BR (2011) Postural deformities in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 10(6):538–549. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70067-9
Yokochi F (2006) Lateral flexion in Parkinson’s disease and Pisa syndrome. J Neurol 253(Suppl 7):17–20. doi:10.1007/s00415-006-7005-4
Di Matteo A, Fasano A, Squintani G, Ricciardi L, Bovi T, Fiaschi A, Barone P, Tinazzi M (2011) Lateral trunk flexion in Parkinson’s disease: EMG features disclose two different underlying pathophysiological mechanisms. J Neurol 258(5):740–745. doi:10.1007/s00415-010-5822-y
Ekbom K, Lindholm H, Ljungberg L (1972) New dystonic syndrome associated with butyrophenone therapy. Z Neurol 202(2):94–103
Colosimo C (1998) Pisa syndrome in a patient with multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord 13(3):607–609. doi:10.1002/mds.870130342
Cannas A, Solla P, Floris G, Borghero G, Tacconi P, Spissu A (2005) Reversible Pisa syndrome in Parkinson’s disease during treatment with pergolide: a case report. Clin Neuropharmacol 28(5):252 00002826-200509000-00012 [pii]
Gambarin M, Antonini A, Moretto G, Bovi P, Romito S, Fiaschi A, Tinazzi M (2006) Pisa syndrome without neuroleptic exposure in a patient with Parkinson’s disease: case report. Mov Disord 21(2):270–273. doi:10.1002/mds.20711
Harada K (2006) Pisa syndrome without neuroleptic exposure in a patient with Parkinson’s disease: a case report. Mov Disord 21(12):2264. doi:10.1002/mds.21168 author reply 2264–2265
Solla P, Cannas A, Congia S, Floris G, Aste R, Tacconi P, Marrosu MG (2008) Levodopa/carbidopa/entacapone-induced acute Pisa syndrome in a Parkinson’s disease patient. J Neurol Sci 275(1–2):154–156. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2008.07.017
Cannas A, Solla P, Floris G, Tacconi P, Serra A, Piga M, Marrosu F, Marrosu MG (2009) Reversible Pisa syndrome in patients with Parkinson’s disease on dopaminergic therapy. J Neurol 256(3):390–395. doi:10.1007/s00415-009-0072-6
Bonanni L, Thomas A, Varanese S, Scorrano V, Onofrj M (2007) Botulinum toxin treatment of lateral axial dystonia in Parkinsonism. Mov Disord 22(14):2097–2103. doi:10.1002/mds.21694
Tassorelli C, Furnari A, Buscone S, Alfonsi E, Pacchetti C, Zangaglia R, Pichiecchio A, Bastianello S, Lozza A, Allena M, Bolla M, Sandrini G, Nappi G, Martignoni E (2012) Pisa syndrome in Parkinson’s disease: clinical, electromyographic, and radiological characterization. Mov Disord 27(2):227–235. doi:10.1002/mds.23930
Susan Standring (2008) Gray’s Anatomy. 40th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Netter F (2000) Atlas der Anatomie des Menschen. 2nd edn. Novartis Thieme, Verlag
Gelb DJ, Oliver E, Gilman S (1999) Diagnostic criteria for Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 56(1):33–39
Mercuri E, Counsell S, Allsop J, Jungbluth H, Kinali M, Bonne G, Schwartz K, Bydder G, Dubowitz V, Muntoni F (2002) Selective muscle involvement on magnetic resonance imaging in autosomal dominant Emery–Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Neuropediatrics 33(1):10–14. doi:10.1055/s-2002-23593
Fasano A, Di Matteo A, Vitale C, Squintani G, Ferigo L, Bombieri F, Santangelo G, Amboni M, Barone P, Tinazzi M (2011) Reversible Pisa syndrome in patients with Parkinson’s disease on rasagiline therapy. Mov Disord 26(14):2578–2580. doi:10.1002/mds.23918
Floyd WF, Silver PH (1955) The function of the erectores spinae muscles in certain movements and postures in man. J Physiol 129(1):184–203
Quirk JA, Sheean GL, Marsden CD, Lees AJ (1996) Treatment of nonoccupational limb and trunk dystonia with botulinum toxin. Mov Disord 11(4):377–383. doi:10.1002/mds.870110405
Comella CL, Shannon KM, Jaglin J (1998) Extensor truncal dystonia: successful treatment with botulinum toxin injections. Mov Disord 13(3):552–555. doi:10.1002/mds.870130330
Wunderlich S, Csoti I, Reiners K, Gunthner-Lengsfeld T, Schneider C, Becker G, Naumann M (2002) Camptocormia in Parkinson’s disease mimicked by focal myositis of the paraspinal muscles. Mov Disord 17(3):598–600. doi:10.1002/mds.10110
Gomez-Puerta JA, Peris P, Grau JM, Martinez MA, Guanabens N (2007) Camptocormia as a clinical manifestation of mitochondrial myopathy. Clin Rheumatol 26(6):1017–1019. doi:10.1007/s10067-006-0259-5
Ozer F, Ozturk O, Meral H, Serdaroglu P, Yayla V (2007) Camptocormia in a patient with Parkinson disease and a myopathy with nemaline rods. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 86(1):3–6
Margraf NG, Wrede A, Rohr A, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Raethjen J, Eymess A, Volkmann J, Mehdorn MH, Jansen O, Deuschl G (2010) Camptocormia in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a focal myopathy of the paravertebral muscles. Mov Disord 25(5):542–551. doi:10.1002/mds.22780
Spuler S, Krug H, Klein C, Medialdea IC, Jakob W, Ebersbach G, Gruber D, Hoffmann KT, Trottenberg T, Kupsch A (2010) Myopathy causing camptocormia in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a multidisciplinary approach. Mov Disord 25(5):552–559. doi:10.1002/mds.22913
Wrede A, Margraf NG, Goebel HH, Deuschl G, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ (2012) Myofibrillar disorganization characterizes myopathy of camptocormia in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 123(3):419–432. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0927-7
Ng JK, Richardson CA (1996) Reliability of electromyographic power spectral analysis of back muscle endurance in healthy subjects. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 77(3):259–264 S0003-9993(96)90108-2 [pii]
Danneels LA, Cagnie BJ, Cools AM, Vanderstraeten GG, Cambier DC, Witvrouw EE, De Cuyper HJ (2001) Intra-operator and inter-operator reliability of surface electromyography in the clinical evaluation of back muscles. Man Ther 6(3):145–153. doi:10.1054/math.2001.0396
Schwerthoffer D, Fatke B, Bauml J, Forstl H (2012) Senile anorexia: three cases with complicated treatment and two occurrences of a Pisa syndrome. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 27(7):765–768. doi:10.1002/gps.2778
Vitale C, Marcelli V, Furia T, Santangelo G, Cozzolino A, Longo K, Allocca R, Amboni M, Marciano E, Barone P (2011) Vestibular impairment and adaptive postural imbalance in parkinsonian patients with lateral trunk flexion. Mov Disord 26(8):1458–1463. doi:10.1002/mds.23657
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
This study has been approved by the appropriate ethics committee and has therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tinazzi, M., Juergenson, I., Squintani, G. et al. Pisa syndrome in Parkinson’s disease: an electrophysiological and imaging study. J Neurol 260, 2138–2148 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-6945-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-6945-8