Abstract
Monazite and magnetite are sensitive indicators of local fluid chemistry, pressure, and temperature during metasomatism. In this study, the role of fluids, during the metamorphism of a granite to metagranite, (Jiao-Liao-Ji orogenic belt, North China Craton), is explored via monazite, magnetite, and pyrite microtextures and mineral chemistry coupled with zircon and monazite Th–U–Pb dating. CL bright zircon cores (2163 ± 17 Ma) record the crystallization age of the granite. BSE dark monazite cores (1876 ± 36 Ma) are characterized by high U and Ca and low Nd contents. The surrounding BSE bright mantle (1836 ± 14 Ma) is characterized by abundant fine-grained huttonite inclusions, a high porosity, a high Th and Si content, and a low P, La, Ce, and Y content. The monazites are surrounded by a three-layered concentric corona consisting of first fluorapatite, followed by allanite, and then epidote. TiO2 in the primary magmatic magnetite (Mag1–1) has been mobilized to form a series of compositionally and texturally distinct magnetites (Mag1–2, Mag2, Mag3, Mag4, and Mag5) associated with ilmenite, rutile, and titanite reaction textures. Combined, these results suggest that external NaCl and sulphate-bearing fluids derived from a local sulphate-bearing evaporate infiltrated the granite and induced the formation of pyrite and enriched the pre-existing monazite in S at around 1904 Ma. In situ δ34S values for pyrite range from 13.03 ‰ to 13.41 ‰, which is typical of metamorphic pyrite. Sporadic synchysite-(Y) inclusions in the pyrite indicate a local CO2-rich component in the fluid. The BSE bright mantle around monazite formed from later fluids from the same local evaporite deposit during the decompression stage of the Jiao-Liao-Ji orogenic belt at around ~ 1840 Ma, which overlaps with zircon dark rims at 1849 ± 12 Ma. This same Na-bearing fluid induced the albitization of the feldspars, formation of apatite–allanite–epidote coronas around monazite, and formation of rutile–titanite–epidote alteration textures associated with magnetite and ilmenite exsolved from the magnetite. During subsequent much later greenschist facies metamorphism, muscovite, chlorite, and Mag5 were precipitated along mineral grain boundaries, mineral cleavage, micropores, and fractures and pyrite experienced partial alteration to goethite.

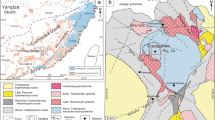
modified from Tian et al. 2017), eastern Liaoning Province, with the metagranite location (16KD67) marked by a star in a circle. Some granite and pegmatite ages are also marked









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleinikoff JN, Schenck WS, Plank MO, Srogi L, Fanning CM, Kamo SL, Bosbyshell H (2006) Deciphering igneous and metamorphic events in highgrade rocks of the Wilmington Complex, Delaware: morpholog cathodoluminescence and backscattered electron zoning, and SHRIMP U–Pb geochronology of zircon and monazite. Geol Soc Am Bull 118:39–64. https://doi.org/10.1130/B25659.1
Altree-Williams A, Pring A, Ngothai Y, Brugger J (2015) Textural and compositional complexities resulting from coupled dissolution–reprecipitation reactions in geomaterials. Earth Sci Rev 150:628–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.08.013
Bourdelle F, Parra T, Chopin C, Beyssac O (2013) A new chlorite geothermometer for diagenetic to low-grade metamorphic conditions. Contrib Miner Petrol 165:723–735
Broska I, Williams CT, Janák M, Nagy G (2005) Alteration and breakdown of xenotime-(Y) and monazite-(Ce) in granitic rocks of the Western Carpathians. Slovakia Lithos 82(1–2):71–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2004.12.007
Budzyń B, Harlov DE, Kozub-Budzyń GA, Majka J (2017) Experimental constraints on the relative stabilities of the two systems monazite-(Ce)–allanite-(Ce)–fluorapatite and xenotime-(Y)–(Y, HREE)-rich epidote–(Y, HREE)-rich fluorapatite, in high Ca and Na-Ca environments under P–T conditions of 200–1000 MPa and 450–750 °C. Miner Petrol 11:183–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-016-0464-0
Budzyń B, Harlov DE, Williams ML, Jercinovic MJ (2011) Experimental determination of stability relations between monazite, fluorapatite, allanite, and REE-epidote as a function of pressure, temperature, and fluid composition. Am Mineral 96:1547–1567. https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2011.3741
Budzyń B, Hetherington CJ, Williams ML, Jercinovic MJ, Michalik M (2010) Fluid-mineral interactions and constraints on monazite alterations during metamorphism. Mineral Mag 74(4):633–655
Cai J, Liu FL, Liu PH, Wang F, Meng E, Wang W, Yang H, Ji L, Liu LS (2017) Discovery of granulite-facies metamorphic rocks in the Ji’an area, northeastern Jiao–Liao–Ji Belt, North China Craton: Metamorphic P-T evolution and geological implications. Precambr Res 303:626–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2017.08.018
Chakhmouradian AR, Mitchell RH (1999) Niobian ilmenite, hydroxylapatite and sulfatian monazite: alternative hosts for incompatible elements in calcite kimberlite from Internatsional’naya, Yakutia. Can Miner 37:1177–1189
Chen C, Li DT, Wu TT, Zhao Y, Zhao CQ, Yang JL, Gu YC (2019) Genesis of gold deposits in the Wulong orefield, Liaodong Peninsula, North China Craton: constraints from ore deposit geology, REE, and C-H–O–S–Pb isotopes. Geol J 55(8):5914–5933. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3661
Chen F, Deng J, Wang Q, Huizenga JM, Li G, Gu Y (2020) LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis of magnetite and pyrite from the Hetaoping Fe-Zn-Pb skarn deposit in Baoshan block, SW China: implications for ore-forming processes. Ore Geol Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103309
Chi YK (2002) Geochemical characteristics of ore-forming elements of the Qingchengzi ore field. J Precious Metallic Geol 11:109–118 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cuney M, Emetz A, Mercadier J, Mykchaylov V, Shunko V, Yuslenko A (2012) Uranium deposits associated with Na-metasomatism from central Ukraine: a review of some of the major deposits and genetic constraints. Ore Geol Rev 44:82–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.09.007
Ding TP, Jiang SY, Wan DF, Li JC, Song B, Zhao DM (1992) Stable Isotope Studies on the Proterozoic Pb-Zn Mineral Belt of northern China. Beijing Publishing House of Science and Technology, Beijing
Dong AG, Zhu XK, Li SZ, Kendall B, Wang Y, Gao ZF (2016) Genesis of a giant Paleoproterozoic strata-bound magnesite deposit: constraints from Mg isotopes. Precambr Res 281:673–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2016.06.020
Dong AG, Zhu XK, Li ZH, Kendall B, Li SZ, Wang Y, Tang C (2017) A multi-isotope approach towards constraining the origin of large-scale Paleoproterozoic B-(Fe) mineralization in NE China. Precambr Res 292:115–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2017.01.030
Drūppel K, Wagner T, Boyce AJ (2006) Evolution of sulfide mineralization in ferrocarbonatite, Swartbooidsrif, NW Namibia: constraints from mineral chemistry and sulfur isotopes. Can Miner 44(4):877–894
Duan XX, Zeng QD, Wang YB, Zhou LL, Chen B (2017) Genesis of the Pb−Zn deposits of the Qingchengzi ore field, eastern Liaoning, China: constraints from carbonate LA−ICPMS trace element analysis and C-O–S–Pb isotopes. Ore Geol Rev 89:752–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.07.012
Enami M, Suzuki K, Liou J, Bird DK (1993) Al-Fe3+ and F–OH substitutions in titanite and constraints on their P-T dependence. Eur J Mineral 5(2):219–231. https://doi.org/10.1127/EJM/5/2/0219
Finger F, Broska I, Roberts MP, Schermaier A (1998) Replacement of primary monazite by apatite-allanite-epidote coronas in an amphibolite facies granite gneiss from the eastern Alps. Am Mineral 83:248–258. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-1998-3-408
Förster HJ (2006) Composition and origin of intermediate solid solutions in the system thorite-xenotime-zircon-coffinite. Lithos 88(1–4):35–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2005.08.003
Fu JL, Hu ZC, Zhang W, Yang L, Liu YS, Li M, Zong KQ, Gao S, Hu SH (2016) In situ, sulfur isotopes (δ34S and δ33S) analyses in sulfides and elemental sulfur using high sensitivity cones combined with the addition of nitrogen by Laser Ablation MC-ICP-MS. Anal Chim Acta 911:14–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.01.026
Gasser D, Bruand E, Rubatto D, Stuwe K (2012) The behaviour of monazite from greenschist facies phyllites to anatectic gneisses: an example from the Chugach Metamorphic Complex, southern Alaska. Lithos 134–135(3–3):108–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2011.12.003
Grand’Homme A, Janots E, Seydoux-Guillaume AM, Guillaume D, Magnin V, Hövelmann J, Höschen C, Boiron MC (2018) Mass transport and fractionation during monazite alteration by anisotropic replacement. Chem Geol 484:51–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.10.008
Gratz R, Heinrich W (1997) Monazite–xenotime thermobarometry: experimental calibration of the miscibility gap in the system CePO4–YPO4. Am Mineral 82:772–780. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-1997-7-816
Gratz R, Heinrich W (1998) Monazite–xenotime thermometry. III. Experimental calibration of the partitioning of gadolinium between monazite and xenotime. Eur J Mineral 10:579–588. https://doi.org/10.1127/ejm/10/3/0579
Guillaume AMS, Montel JM, Bingen B, Bosse V, Parseval P, Paquette JL, Janots E, Wirth R (2012) Low-temperature alteration of monazite: fluid mediated coupled dissolution–precipitation, irradiation damage, and disturbance of the U–Pb and Th–Pb chronometers. Chem Geol 330–331:140–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.07.031
Guo S, Tang P, Su B, Chen Y, Ye K, Zhang L, Gao Y, Liu J, Yang Y (2017) Unusual replacement of Fe-Ti oxides by rutile during retrogression in amphibolite-hosted veins (Dabie UHP terrane): a mineralogical record of fluid-induced oxidation processes in exhumed UHP slabs. Am Mineral 102:2268–2283. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2017-6120
Hao LB, Zhao X, Zhao YY (2017) Stable isotope characteristics and ore genesis of the Baiyun gold deposit Liaoning province. J Jilin Univ 47:442–451
Harlov DE (1992) Comparative oxygen barometry in granulites, bamble sector. SE Norway J Geo 100(4):446–467. https://doi.org/10.1086/629597
Harlov DE (2000) Titaniferous magnetite-ilmenite thermometry and titaniferous magnetite-ilmenite-orthopyroxene-quartz oxygen barometry in granulite facies gneisses, Bamble Sector, SE Norway: implications for the role of high-grade CO2-rich fuids during granulite genesis. Contrib Mineral Petrol 1139:180–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00007670
Harlov DE, Hansen EC (2005) Oxide and sulphide isograds along a late Archean, deep-crustal profile in Tamil Nadu, south India. J Metam Geol 23:241–259
Harlov DE, Hetherington CJ (2010) Partial high-grade alteration of monazite using alkali-bearing fluids: experiment and nature. Am Mineral 95(7):1105–1108. https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2010.3525
Harlov DE, Newton RC, Hansen EC, Jarnardhan AS (1997) Oxide and sulphide minerals in highly oxidized Rb-depleted Archean granulites of the Shevaroy Hills Massif, South India: oxidation states and the role of metamorphic fluids. J Metamorph Geol 15:701–717
Harlov DE, Wirth R, Förster HJ (2005) An experimental study of dissolution-reprecipitation in fluorapatite: fluid infiltration and the formation of monazite. Contrib Miner Petrol 150(3):268–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-005-0017-8
Harlov DE, Wirth R, Hetherington CJ (2007) The relative stability of monazite and huttonite at 300–900 °C and 200–1000 MPa: metasomatism and the propagation of metastable mineral phases. Am Mineral 92(10):1652–1664. https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2007.2459
Harlov DE, Wirth R, Hetherington CJ (2011) Fluid-mediated partial alteration of monazite: the role of fluids during apparent solid state element mass transfer. Contrib Mineral Petrol 162:329–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-010-0599-7
Heinrich W, Andrehs G, Franz G (1997) Monazite–xenotime miscibility gap thermometry I An empirical calibration. J Metamorph Geol 15(1):3–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1314.1997.t01-1-00052.x
Hetherington CJ, Harlov DE (2008) Metasomatic thorite and uraninite inclusions in xenotime and monazite from granitic pegmatites, Hidra anorthosite massif, southwestern Norway: mechanics and fluid chemistry. Am Mineral 93:806–820. https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2008.2635
Hetherington CJ, Harlov DE, Budzyń B (2010) Experimental metasomatism of monazite and xenotime: mineral stability, REE mobility and fluid composition. Mineral Petrol 99:165–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-010-0110-1
Horstwood MSA, Foster GL, Parrish RR, Noble SR, Nowell GM (2003) Common-Pb corrected in situ U-Pb accessory mineral geochronology by LAMC-ICP-MS. J Anal at Spectrom 18:837–846. https://doi.org/10.1039/B304365G
Hu GY, Li YH, Fan CF, Hou KJ, Zhao Y, Zeng LS (2015a) In situ LA–MC–ICP–MS boron isotope and zircon U-Pb age determinations of Paleoproterozoic borate deposits in Liaoning Province, northeastern China. Ore Geol Rev 65:1127–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.09.005
Hu H, Lentz D, Li JW, McCarron T, Zhao XF, Hall D (2015b) Reequilibration processes in magnetite from iron skarn deposits. Econ Geol 110(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.110.1.1
Hu H, Li JW, Lentz D, Ren Z, Zhao XF, Deng XD, Hall D (2014) Dissolution–reprecipitation process of magnetite from the Chengchao iron deposit: insights into ore genesis and implication for in-situ chemical analysis of magnetite. Ore Geol Rev 57:393–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.07.008
Hu X, Chen H, Zhao L, Han J, Xia X (2017) Magnetite geochemistry of the Longqiao and Tieshan Fe–(Cu) deposits in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Belt: implications for deposit type and ore genesis. Ore Geol Rev 89:822–835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.07.019
Hu ZC, Gao S, Liu YS, Hu SH, Chen HH, Yuan HL (2008) Signal enhancementin laser ablation ICP-MS by addition of nitrogen in the central channel gas. J Anal at Spectrom 23(3):1093–1101. https://doi.org/10.1039/b804760j
Hu ZC, Zhang W, Liu YS, Gao S, Li M, Zong KQ, Chen HH, Hu SH (2015c) “Wave” signal-smoothing and mercury-removing device for laser ablation quadrupole and multiple collector icpms analysis: application to lead isotope analysis. Anal Chem 87(2):1152–1157. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac503749k
Imayama T, Takeshita T, Yi K, Cho D-L, Kitajima K, Tsutsumi Y, Kayama M, Nishido H, Okumura T, Yagi K, Itaya T, Sano Y (2012) Two-stage partial melting and contrasting cooling history within the higher himalayan crystalline sequence in the far-eastern Nepal Himalaya. Lithos 134–135:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2011.12.004
Itano K, Iizuka T, Chang Q, Kimura JI, Maruyama S (2016) U–Pb chronology and geochemistry of detrital monazites from major African rivers: constraints on the timing and nature of the Pan-African Orogeny. Precambr Res 282:139–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2016.07.008
Jamtveit B, Malthesorenssen A, Kostenko O (2008) Reaction enhanced permeability during retrogressive metamorphism. Earth Planet Sci Lett 267(3–4):620–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2007.12.016
Jiang SY, Palmer MR, Peng QM, Yang JH (1997) Chemical and stable isotopic compositions of Proterozoic metamorphosed evaporites and associated tourmalines from the Houxianyu borate deposit, eastern Liaoning. China Chem Geol 135(3–4):189–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(96)00115-5
Kelsey DE, Clark C, Hand M (2008) Thermobarometric modelling of zircon and monazite growth in melt-bearing systems: examples using model metapelitic and metapsammitic granulites. J Metamorph Geol 26(2):199–212. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1314.2007.00757.x
Kimura JI, Chang Q, Tani K (2011) Optimization of ablation protocol for 200 nm UV femtosecond laser in precise U–Pb age dating coupled to multi-collector ICP mass spectrometry. Geochem J 45:283–296. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.1.0120
Kirkland CL, Erickson TM, Johnson TE, Danišík M, Evans NJ, Bourdet J, McDonald BJ (2016) Discriminating prolonged, episodic or disturbed monazite age spectra: an example from the Kalak Nappe Complex, Arctic Norway. Chem Geol 424:96–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.01.009
Laurent AT, Seydoux-Guillaume A-M, Duchene S, Bingen B, Bosse V, Datas L (2016) Sulphate incorporation in monazite lattice and dating the cycle of sulphur in metamorphic belts. Contrib Mineral Petrol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-016-1301-5
Li J, Cai WY, Li B, Wang KY, Liu HL, Konare Y, Qian Y, Lee GJ, Yoo BC (2019) Paleoproterozoic SEDEX type stratiform mineralization overprinted by Mesozoic vein-type mineralization in the Qingchengzi Pb Zn deposit Northeastern China. J of Asian Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104009
Li SZ, Zhao GC (2007) SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Liaoji granitoids: constraints on the evolution of the Paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji belt in the Eastern Block of the North China Craton. Precambr Res 158(1–2):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.001
Li SZ, Zhao GC, Sun M, Han ZZ, Luo Y, Hao DF, Xia XP (2005) Deformation history of the Paleoproterozoic Liaohe assemblage in the eastern block of the North China Craton. J Asian Earth Sci 24(5):659–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.11.008
Li WT, Audétat A, Zhang J (2015) The role of evaporites in the formation of magnetite–apatite deposits along the Middle and Lower Yangtze River, China: evidence from LA-ICP-MS analysis of fluid inclusions. Ore Geol Rev 67:264–278
Li YH, Duan C, Han D, Chen XW, Wang CL, Yang BY, Zhang C, Liu F (2014) Effect of sulfate evaporate salt layer for formation of porphyrite iron ores in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River area. Acta Petrol Sin 30:1355–1368 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li Z, Chen B, Wei CJ (2017) Is the Paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt (North China Craton) a rift? Int J Earth Sci 106:355–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-016-1323-2
Liu FL, Liu CH, Itano K, Iizuka T, Cai J, Wang F (2017a) Geochemistry, U–Pb dating, and Lu–Hf isotopes of zircon and monazite of porphyritic granites within the Jiao-Liao-Ji orogenic belt: implications for petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Precambr Res 300:78–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2017.08.007
Liu FL, Liu LS, Cai J, Liu PH, Wang F, Liu CH, Liu JH (2019a) A widespread Paleoproterozoic partial melting event within the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt, North China Craton: zircon U-Pb dating of granitic leucosomes within pelitic granulites and its tectonic implications. Precambr Res 326:155–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2017
Liu FL, Robinson PT, Liu PH (2012) Multiple partial melting events in the Sulu UHP terrane: zircon U-Pb dating of granitic leucosomes within amphibolite and gneiss. J Metam Geol 30(8):887–906. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1314.2012.01005.x
Liu J, Zhang LJ, Wang SL, Li TG, Yang Y, Liu FX, Li SH, Duan C (2019b) Formation of the Wulong gold deposit, Liaodong gold Province, NE China: constraints from zircon U-Pb age, sericite Ar–Ar age, and H–O–S–He isotopes. Ore Geol Rev 109:130–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.04.013
Liu PH, Cai J, Zou L (2017b) Metamorphic P-T-t path and its geological implications of the Sanjiazi garnet amphibolites from the northern Liaodong Penisula, Jiao-Liao-Ji belt: constraints on phase equilibria and zircon U–Pb dating. Acta Petrol Sin 33(9):2649–2674 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu PH, Liu FL, Tian ZH, Cai J, Ji L, Wang F (2019c) Petrological and geochronological evidence for Paleoproterozoic granulite-facies metamorphism of the South Liaohe Group in the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt, North China Craton. Precambr Res 327:121–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2019.03.002
Lo Pò D, Braga R, Massonne HJ, Molli G, Montanini A, Theye T (2016) Fluid-induced breakdown of monazite in medium-grade metasedimentary rocks of the Pontremoli basement (Northern Apennines, Italy). J Metamorph Geol 34:63–84
Lu XP, Wu FY, Guo JH, Wilde SA, Yang JH, Liu XM, Zhang XO (2006) Zircon U-Pb geochronological constraints on the Paleoproterozoic crustal evolution of the Eastern block in the North China Craton. Precambr Res 146(3–4):138–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2006.01.009
Liu YS, Gao S, Hu ZC, Gao CG, Zong KQ, Wang DB (2010) Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons of mantle xenoliths. J Petrol 51(1–2):537–571. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egp082
Ludwig KR (2003) User’s Manual for Isoplot/EX Version 3.00. A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication
Ma YB, Bagas L, Xing SW, Zhang ST, Wang RJ, Li N, Zhang ZJ, Zou YF, Yang XQ, Wang Y, Zhang Y (2016) Genesis of the stratiform Zhenzigou Pb Zn deposit in the North China Craton: Rb Sr and C O S Pb isotope constraints. Ore Geol Rev 79:88–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.05.009
Majka J, Budzyń B (2006) Monazite breakdown in metapelites from Wedel Jarlsberg Land Svalbard preliminary report. Mineral Pol 37(1):61–68. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10002-007-0006-9
Melo MG, Stevens G, Lana C, Pedrosa-Soares AC, Frei D, Alkmim FF, Alkmin LA (2017) Two cryptic anatectic events within a syn-collisional granitoid from the Araçuaí orogen (southeastern Brazil): evidence from the polymetamorphic Carlos Chagas batholith. Lithos 277:51–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2016.10.012
Misch D, Pluch H, Mali H, Ebner F, Huang H (2018) Genesis of giant Early Proterozoic magnesite and related talc deposits in the Mafeng area, Liaoning Province, NE China. J Asian Earth Sci 160:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.04.005
Nadoll P, Angerer T, Mauk JL, French D, Walshe J (2014a) The chemistry of hydrothermal magnetite: a review. Ore Geol Rev 61:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.12.013
Nadoll P, Mauk JL, Hayes TS, Koenig AE, Box SE (2012) Geochemistry of magnetite from hydrothermal ore deposits and host rocks of the Mesoproterozoic Belt Supergroup. United States Econ Geol 107(6):1275–1292. https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.107.6.1275
Nadoll P, Mauk JL, Leveille RA, Koenig AE (2014b) Geochemistry of magnetite from porphyry Cu and skarn deposits in the southwestern United States. Mineral Deposita 50:493–515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-014-0539-y
Ondrejka M, Uher P, Putiš M, Broska I, Bačík P, Konečný P, Schmiedt I (2012) Two-stage breakdown of monazite by post-magmatic and metamorphic fluids: an example from the Veporic orthogneiss, Western Carpathians, Slovakia. Lithos 142–143:245–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2012.03.012
Parrish RR (1990) U–Pb dating of monazite and its application to geological problems. Can J Earth Sci 27:1435–1450. https://doi.org/10.1139/e90-152
Peng QM, Palmer MR (1995) The Palaeoproterozoic boron deposits in eastern Liaoning China: a metamorphosed evaporate. Precambr Res 72(3–4):185–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-9268(94)00087-8
Peng QM, Palmer MR (2002) The paleoproterozoic Mg and Mg–Fe borate deposits of Liaoning and Jilin provinces. Northeast China Econ Geol 97(1):93–108. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.97.1.93
Poujol M, Pitra P, Van Den Driessche J, Tartèse R, Ruffet G, Paquette J-L, Poilvet J-C (2016) Two-stage partial melting during the Variscan extensional tectonics (Montagne Noire, France). Int J Earth Sci 106(2):477–500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-016-1369-1
Putnis A (2002) Mineral replacement reactions: from macroscopic observations to microscopic mechanisms. Mineral Mag 66:689–708
Putnis A (2009) Mineral replacement reactions. Rev Mineral Geochem 70(1):87–124. https://doi.org/10.2138/rmg.2009.70.3
Putnis A, Austrheim H (2010) Fluid induced processes: metasomatism and metamorphism. Geofluids 10:254–269. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-8123.2010.00285.x
Pyle JM, Spear FS, Rudnick RL, McDonough WF (2001) Monazite–xenotime–garnet equilibrium in metapelites and a new monazite–garnet thermometer. J Petrol 42(11):2083–2107. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/42.11.2083
Rasmussen B, Muhling JR (2007) Monazite begets monazite: evidence for dissolution of detrital monazite and reprecipitation of syntectonic monazite during low-grade regional metamorphism. Contrib Mineral Petrol 154(6):675–689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-007-0216-6
Rasmussen B, Muhling JR (2009) Reactions destroying detrital monazite in greenschist-facies sandstones from the Witwatersrand basin. South Africa Chem Geol 264(1–4):311–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.03.017
Richard A, Montel J-M, Leborgne R, Peiffert C, Cuney M, Cathelineau M (2015) Monazite alteration in H2O ± HCl ± NaCl ± CaCl2 fluids at 150 °C and psat: implications for uranium deposits. Minerals 5(4):693–706. https://doi.org/10.3390/min5040518
Ruiz-Agudo E, Putnis CV, Putnis A (2014) Coupled dissolution and precipitation at mineral–fluid interfaces. Chem Geol 383:132–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.06.007
Shrestha S, Larson KP, Duesterhoeft E, Soret M, Cottle JM (2019) Thermodynamic modelling of phosphate minerals and its implications for the development of P-T-t histories: a case study in garnet–monazite bearing metapelites. Lithos 334–335:141–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2019.03.021
Simonetti A, Heaman LM, Chacko T, Banerjee NR (2006) In situ petrographic thin section U–Pb dating of zircon, monazite, and titanite using laser ablation–MC–ICP-MS. Int J Mass Spectrom 253:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijms.2006.03.003
Song YH, Yang FC, Yan GL, Wei MH, Shi SS (2017) Characteristics of mineralization fluids and tracers of mineralization material sources of the Qingchengzi lead-zinc deposit in Liaoning Province. Geol Explor 53(2):0259–0269 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Spear FS (2010) Monazite–allanite phase relations in metapelites. Chem Geol 279(1–2):55–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.10.004
Stepanov AS, Rubatto HJ, RappRP D (2012) Experimental study of monazite/melt partitioning with implications for the REE, Th and U geochemistry of crustal rocks. Chem Geol 300–301:200–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.01.007
Sun GT, Zeng QD, Zhou LL, Wang YB, Chen PW (2020) Trace element contents and in situ sulfur isotope analyses of pyrite in the Baiyun gold deposit, NE China: implication for the genesis of intrusion-related gold deposits. Ore Geol Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103330
Symington NJ, Weinberg RF, Hasalova P, Wolfram LC, Raveggi M, Armstrong RA (2014) Multiple intrusions and remelting-remobilization events in a magmatic arc The St. Peter Suite South Australia. Geol Soc Am Bull 126:1200–1218. https://doi.org/10.1130/b30975.1
Tam PY, Zhao GC, Liu FL, Zhou XW, Sun M, Li SZ (2011) Timing of metamorphism in the paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt: New SHRIMP U–Pb zircon dating of granulites, gneisses and marbles of the Jiaobei massif in the North China Craton. Gondwana Res 19:150–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2010.05.007
Tam PY, Zhao GC, Sun M, Li SZ, Iizuka Ki Ma YGS, Yin CQ, He YH, Wu ML (2012a) Metamorphic P–T path and tectonic implications of medium-pressure pelitic granulites from the Jiaobei massif in the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt, North China Craton. Precambr Res 220–221:177–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2012.08.008
Tam PY, Zhao GC, Sun M, Li SZ, Wu ML, Yin CQ (2012b) Petrology and metamorphic P–T path of high-pressure mafic granulites from the Jiaobei massif in the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt, North China Craton. Lithos 155:94–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2012.08.018
Tam PY, Zhao GC, Zhou X, Sun M, Guo JH, Li S, Yin CQ, Wu ML, He YH (2012c) Metamorphic P–T path and implications of high-pressure pelitic granulites from the Jiaobei massif in the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt. North China Craton Gondwana Res 22(1):104–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2011.09.006
Tian ZH, Liu FL, Windley BF, Liu PH, Wang F, Liu CH, Wang W, Cai J, Xiao WJ (2017) Polyphase structural deformation of low- to medium-grade metamorphic rocks of the Liaohe Group in the Jiao-Liao-Ji Orogenic Belt, North China Craton: correlations with tectonic evolution. Precambr Res 303:641–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2017.08.017
Upadhyay D, Pruseth KL (2012) Fluid-induced dissolution breakdown of monazite from TsoMorari complex, NW Himalayas: evidence for immobility of trace elements. Contrib Mineral Petrol 164:303–316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-012-0739-3
Wan YS, Song B, Liu DY, Wilde SA, Wu JS, Shi YL, Yin XY, Zhou HY (2006) SHRIMP U–Pb zircon geochronology of Paleoproterozoic metasedimentary rocks in the North China Craton: evidence for a major late paleoproterozoic tectonothermal event. Precambr Res 149(3–4):249–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2006.06.006
Wang AJ, Peng QM, Palmer MR (1998) Salt dome-controlled sulfide precipitation of paleoproterozoic Fe–Cu sulfide deposits eastern Liaoning Northeastern China. Econ Geol 93:1–14. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.93.1.1
Wang F, Liu FL, Liu PH, Cai J, Schertl HP, Ji L, Liu LS, Tian ZH (2017) In situ zircon U–Pb dating and whole-rock geochemistry of metasedimentary rocks from South Liaohe Group, Jiao-Liao-Ji orogenic belt: constraints on the depositional and metamorphic ages, and implications for tectonic setting. Precambr Res 303:764–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2017.10.002
Weinberg RF, Wolfram LC, Nebel O, Hasalová P, Závada P, Kylander-Clark ARC, Becchio R (2020) Decoupled U-Pb date and chemical zonation of monazite in migmatites: the case for disturbance of isotopic systematics by coupled dissolution-reprecipitation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 269:398–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2019.10.024
Wen G, Bi SJ, Li JW (2016) Role of evaporitic sulfates in iron skarn mineralization: a fluid inclusion and sulfur isotope study from the Xishimen deposit, Handan-Xingtai district. North China Craton Miner Deposita 52(4):495–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-016-0674-8
Wen G, Li JW, Hofstra AH, Koenig AE, Lowers HA, Adams D (2017) Hydrothermal reequilibration of igneous magnetite in altered granitic plutons and its implications for magnetite classification schemes: insights from the Handan-Xingtai iron district, North China Craton. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 213:255–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2017.06.043
Whitney JA (1984) Fugacities of sulfurous gases in pyrrhotite-bearing silicic magmas. Am Mineral 69:69–78
Williams ML, Jercinovic MJ, Harlov DE, Budzyń B, Hetherington CJ (2011) Resetting monazite ages during fluid-related alteration. Chem Geol 283(3–4):218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.01.019
Williams ML, Jercinovic MJ, Hetherington CJ (2007) Microprobe monazite geochronology: understanding geologic processes by integrating composition and chronology. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 35:137–175. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.earth.35.031306.140228
Xie Q, Zhang Z, Hou T, Jin Z, Santosh M (2017) Geochemistry and oxygen isotope composition of magnetite from the Zhangmatun deposit, North China Craton: implications for the magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of Cornwall-type iron mineralization. Ore Geol Rev 88:57–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.04.014
Xing L, Trail D, Watson EB (2013) Th and U partitioning between monazite and felsic melt. Chem Geol 358:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.07.009
Xu DR, Kusiak MA, Wang ZL, Chen HY, Bakun-Czubarow N, Wu CJ, Konečný P, Hollings P (2015) Microstructural observation and chemical dating on monazite from the Shilu Group, Hainan Province of South China: implications for origin and evolution of the Shilu Fe–Co–Cu ore district. Lithos 216–217:158–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2014.12.017
Xu W, Liu FL, Wang F, Santosh M, Dong YS (2019) Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt North China Craton: geochemical and isotopic evidence from ca. 2.17 Ga felsic tuff. Geol J. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3380
Yan XL, Chen B (2014) Chemical and boron isotopic compositions of tourmaline from the paleoproterozoic Houxianyu borate deposit, NE China: implications for the origin of borate deposit. J Asian Earth Sci 94:252–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.05.021
Yang H, Wang W, Liu JH (2017) Zircon U–Pb dating and its geological significance of granitic pegmatites from the Kuandian and Sanjiazi area in eastern Liaoning province. Acta Petrol Sin 33:2675–2688 (In Chinese with English abs)
Yavuz F, Yıldırım DK (2018) A Windows program for calculation and classification of epidote-supergroup minerals. Periodico Di Mineralogia 87:269–285. https://doi.org/10.2451/2018PM7808
Yin A, Nie S (1996) Phanerozoic palinspastic reconstruction of China and its neighboring regions. In: Yin A, Harrison TM (eds) The tectonic evolution of asia. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 285–442
Yu B, Zeng Q, Frimmel HE, Wang Y, Guo W, Sun G, Zhou T, Li J (2018) Genesis of the Wulong gold deposit, northeastern North China Craton: constraints from fluid inclusions, H-O-S-Pb isotopes, and pyrite trace element concentrations. Ore Geol Rev 102:313–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.09.016
Zhang P, Kou L, Zhao Y, Bi Z, Sha D, Han R, Li Z (2020) Genesis of the Wulong gold deposit, Liaoning Province, NE China: constrains from noble gases, radiogenic and stable isotope studies. Geosci Front 11(2):547–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2019.05.012
Zhang QS (1988) Early Proterozoic tectonic styles and associated mineral deposits of the North China platform. Precambr Res 39(1–2):1–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-9268(88)90047-2
Zhao GC, Cawood PA, Li SZ, Wilde SA, Sun M, Zhang J, He YH, Yin CQ (2012) Amalgamation of the North China Craton: key issues and discussion. Precambr Res 222–223:55–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2012.09.016
Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA, Li SZ (2005) Late Archean to paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: key issues revisited. Precambr Res 136(2):177–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002
Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Cawood PA, Lu LZ (1998) Thermal evolution of archean basement rocks from the eastern part of the North China Craton and its bearing on tectonic setting. Int Geol Rev 40:706–721. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206819809465233
Zhao HZ, Yang SS, Li H (2009) Geologic features of Baiyun gold ore deposit and discussion of the genesis. Non-Ferrous Mining Metal 25(3):4–7 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhong JR, Guo ZT (1988) The geological characteristics and metallogenetic control factors of the Liangshanguan uranium deposit, northeast China. Precambr Res 39:51–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-9268(88)90050-2
Zhu XK, O’Nions RK (1999) Zonation of monazite in metamorphic rocks and its implications for high temperature thermochronology: a case study from the Lewisian terrain. Earth Planet Sci Lett 171(2):209–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-821X(99)00146-6
Zou Y, Zhai MG, Santosh M, Zhou LG, Zhao L, Lu JS, Shan HX (2017) High-pressure pelitic granulites from the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt, North China Craton: a complete P–T path and its tectonic implications. J Asian Earth Sci 134:103–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.10.015
Zou Y, Zhai MG, Santosh M, Zhou LG, Zhao L, Lu JS, Liu B, Shan HX (2018) Contrasting P–T–t paths from a Paleoproterozoic metamorphic orogen: petrology, phase equilibria, zircon and monazite geochronology of metapelites from the Jiao-Liao-Ji belt, North China Craton. Precambr Res 311:74–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2018.04.010
Zou Y, Zhai MG, Zhou LG, Zhao L, Lu JS, Wang YQ, Shan HX (2019) Relics of a paleoproterozoic orogen: New petrological, phase equilibria and geochronological studies on high-pressure pelitic granulites from the Pingdu-Laiyang areas, southwest of the Jiaobei terrane, North China Craton. Precambr Res 322:136–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2018.12.01
Acknowledgements
We thank professor Andrew Putnis, researcher Shuai Guo, Zhonghua Tian, Pinghua Liu and Jia Cai for their helpful discussion. Two anonymous reviewers’ constructive comments and reviews are gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
This research is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Projects 92062214, 41890833, 41430210), the Chinese Geological Survey Bureau project (Grant nos. DD20160121) and Basic Scientific Research Foundation of the Institute of Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (J2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Daniela Rubatto.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, L., Liu, F., Harlov, D. et al. Fluid-induced alteration of monazite, magnetite, and sulphides during the albitization of a Palaeoproterozoic granite from the Jiao-Liao-Ji orogenic belt, North China Craton. Contrib Mineral Petrol 176, 81 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-021-01835-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-021-01835-z