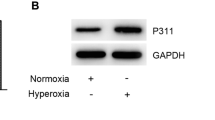
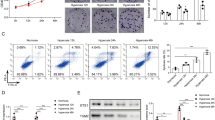
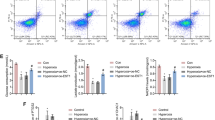
Abstract
Purpose
Hyperoxia-induced apoptosis in alveolar epithelial type II cells (AECIIs) plays a critical role in the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). Melatonin has been shown to improve BPD. However, the protective effect of melatonin on hyperoxia-induced apoptosis in AECIIs and the precise mechanisms involved remain unclear.
Methods
Human alveolar epithelial type II A549 cells were treated with hyperoxia as an in vitro model to investigate the antiapoptotic mechanism of melatonin. CCK-8 assays were performed to investigate the viability of A549 cells. Hoechst 33,258 staining was carried out to quantify apoptosis in A549 cells. The protein expression levels of E26 oncogene homolog 1 (ETS1), Bcl-2, Bax, Bim, Wnt, β-catenin, AKT and phosphorylated AKT were measured by western blotting. LY294002, SC79 and the downregulation of ETS1, melatonin receptor 1 (MT1) and MT2 with specific siRNAs were used to investigate the role of the PI3K/AKT pathway, ETS1, MT1 and MT2 in hyperoxia-induced apoptosis in A549 cells.
Results
Melatonin prevented hyperoxia-induced apoptosis in A549 cells, and the upregulation of E26 oncogene homolog 1 (ETS1) contributed to the antiapoptotic effect of melatonin. Melatonin activated the PI3K/AKT axis, which led to ETS1 upregulation and inhibited apoptosis in hyperoxia-exposed A549 cells. Furthermore, melatonin-induced activation of the PI3K/AKT axis, upregulation of ETS1 and inhibition of apoptosis were reversed by melatonin receptor 2 (MT2) siRNA in hyperoxia-exposed A549 cells.
Conclusion
Melatonin prevents hyperoxia-induced apoptosis by activating the MT2/PI3K/AKT/ETS1 axis in alveolar epithelial cells.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AECIIs:
-
Alveolar epithelial type II cells
- BPD:
-
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- ETS1:
-
E26 oncogene homolog 1
- MTs:
-
Melatonin receptors
- MT1:
-
Melatonin receptor 1
- MT2:
-
Melatonin receptor 2
- TGM2:
-
Transglutaminase 2
References
Principi N, Di Pietro GM, Esposito S (2018) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: clinical aspects and preventive and therapeutic strategies. J Transl Med 16:36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-018-1417-7
Hwang JS, Rehan VK (2018) Recent advances in bronchopulmonary dysplasia: pathophysiology, prevention, and treatment. Lung 196:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-018-0084-z
Zhang L, Zhao S, Yuan L, Wu H, Jiang H, Luo G (2016) Hyperoxia-mediated LC3B activation contributes to the impaired transdifferentiation of type II alveolar epithelial cells (AECIIs) to type I cells (AECIs). Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 43:834–843. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.12592
Hou A, Fu J, Yang H, Zhu Y, Pan Y, Xu S, Xue X (2015) Hyperoxia stimulates the transdifferentiation of type II alveolar epithelial cells in newborn rats. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 308:L861–L872. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00099.2014
Chen S, Wu Q, Zhong D, Li C, Du L (2020) Caffeine prevents hyperoxia-induced lung injury in neonatal mice through NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-kappaB pathway. Respir Res 21:140. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-020-01403-2
Wu D, Liang M, Dang H, Fang F, Xu F, Liu C (2018) Hydrogen protects against hyperoxia-induced apoptosis in type II alveolar epithelial cells via activation of PI3K/Akt/Foxo3a signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495:1620–1627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.193
Jiang J, Wang J, Li C, Mo L, Huang D (2022) Hyperoxia induces alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis by regulating mitochondrial function through small mothers against decapentaplegic 3 (SMAD3) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). Bioengineered 13:242–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.2012953
Li L, Gang X, Wang J, Gong X (2022) Role of melatonin in respiratory diseases (Review). Exp Ther Med 23:271. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2022.11197
Wang W, Gao J (2021) Effects of melatonin on protecting against lung injury (Review). Exp Ther Med 21:228. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2021.9659
Yip HK, Chang YC, Wallace CG, Chang LT, Tsai TH, Chen YL, Chang HW, Leu S, Zhen YY, Tsai CY, Yeh KH, Sun CK, Yen CH (2013) Melatonin treatment improves adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy for acute lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Pineal Res 54:207–221. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12020
Li J, Liu L, Zhou X, Lu X, Liu X, Li G, Long J (2020) Melatonin attenuates sepsis-induced acute lung injury through improvement of epithelial sodium channel-mediated alveolar fluid clearance via activation of SIRT1/SGK1/Nedd4–2 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol 11:590652. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.590652
Wu GC, Peng CK, Liao WI, Pao HP, Huang KL, Chu SJ (2020) Melatonin receptor agonist protects against acute lung injury induced by ventilator through up-regulation of IL-10 production. Respir Res 21:65. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-020-1325-2
Pan L, Fu JH, Xue XD, Xu W, Zhou P, Wei B (2009) Melatonin protects against oxidative damage in a neonatal rat model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. World J Pediatr 5:216–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-009-0041-2
Gharehbaghi MM, Yeganedoust S, Shaseb E, Fekri M (2022) Evaluation of melatonin efficacy in prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm newborn infants. Turk J Pediatr 64:79–84. https://doi.org/10.24953/turkjped.2021.1334
Yang M, Gao XR, Meng YN, Shen F, Chen YP (2021) ETS1 ameliorates hyperoxia-induced alveolar epithelial cell injury by regulating the TGM2-mediated Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Lung 199:681–690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-021-00489-9
You J, Zhou O, Liu J, Zou W, Zhang L, Tian D, Dai J, Luo Z, Liu E, Fu Z, Zou L (2020) Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles alleviate lung injury in rat model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia by affecting cell survival and angiogenesis. Stem Cells Dev 29:1520–1532. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2020.0156
Tan YZ, Xu XY, Dai JM, Yin Y, He XT, Zhang YL, Zhu TX, An Y, Tian BM, Chen FM (2021) Melatonin induces the rejuvenation of long-term ex vivo expanded periodontal ligament stem cells by modulating the autophagic process. Stem Cell Res Ther 12:254. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02322-9
Gao T, Wang T, Wang Z, Cao J, Dong Y, Chen Y (2021) Melatonin-mediated MT2 attenuates colitis induced by dextran sodium sulfate via PI3K/AKT/Nrf2/SIRT1/RORalpha/NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 96:107779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107779
Li J, Wang C, Xue L, Zhang F, Liu J (2021) Melatonin suppresses apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells through inhibiting autophagy via the PI3K/Akt pathway in a high-glucose culture. Biomed Res Int 2021:4604258. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/4604258
Ray U, Roy Chowdhury S, Vasudevan M, Bankar K, Roychoudhury S, Roy SS (2017) Gene regulatory networking reveals the molecular cue to lysophosphatidic acid-induced metabolic adaptations in ovarian cancer cells. Mol Oncol 11:491–516. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12046
Hui K, Wu S, Yue Y, Gu Y, Guan B, Wang X, Hsieh JT, Chang LS, He D, Wu K (2018) RASAL2 inhibits tumor angiogenesis via p-AKT/ETS1 signaling in bladder cancer. Cell Signal 48:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.04.006
Nikolaev G, Robeva R, Konakchieva R (2021) Membrane melatonin receptors activated cell signaling in physiology and disease. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23010471
Patel A, Zhou EW, O’Brien M, Wang X, Zhou S (2021) Melatonin in neuroskeletal biology. Curr Opin Pharmacol 61:42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2021.08.016
Ding Z, Wu X, Wang Y, Ji S, Zhang W, Kang J, Li J, Fei G (2020) Melatonin prevents LPS-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human alveolar epithelial cells via the GSK-3beta/Nrf2 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 132:110827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110827
Yu N, Sun YT, Su XM, He M, Dai B, Kang J (2016) Melatonin attenuates TGFbeta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung alveolar epithelial cells. Mol Med Rep 14:5567–5572. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5950
Yang M, Chen BL, Huang JB, Meng YN, Duan XJ, Chen L, Li LR, Chen YP (2017) Angiogenesis-related genes may be a more important factor than matrix metalloproteinases in bronchopulmonary dysplasia development. Oncotarget 8:18670–18679. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14722
Chen WR, Zhou YJ, Yang JQ, Liu F, Zhao YX, Sha Y (2019) Melatonin attenuates beta-glycerophosphate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells via a wnt1/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed Res Int 2019:3139496. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3139496
Wu Y, Li J, Yuan R, Deng Z, Wu X (2021) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate hyperoxia-induced lung injury via the manipulation of microRNA-425. Arch Biochem Biophys 697:108712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2020.108712
Sidramagowda Patil S, Hernandez-Cuervo H, Fukumoto J, Krishnamurthy S, Lin M, Alleyn M, Breitzig M, Narala VR, Soundararajan R, Lockey RF, Kolliputi N, Galam L (2020) Alda-1 attenuates hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury in mice. Front Pharmacol 11:597942. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.597942
Cao H, Feng Y, Ning Y, Zhang Z, Li W, Li Q (2015) Edaravone protects rats and human pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells against hyperoxia injury: heme oxygenase-1 and PI3K/Akt pathway may be involved. Exp Lung Res 41:404–414. https://doi.org/10.3109/01902148.2015.1054053
Yang M, Li L, Chen S, Li S, Wang B, Zhang C, Chen Y, Yang L, Xin H, Chen C, Xu X, Zhang Q, He Y, Ye J (2020) Melatonin protects against apoptosis of megakaryocytic cells via its receptors and the AKT/mitochondrial/caspase pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 12:13633–13646. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103483
Zhu G, Ma B, Dong P, Shang J, Gu X, Zi Y (2020) Melatonin promotes osteoblastic differentiation and regulates PDGF/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Biol Int 44:402–411. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11240
Huang R, Xu Y, Lu X, Tang X, Lin J, Cui K, Yu S, Shi Y, Ye D, Liu Y, Liang X (2021) Melatonin protects inner retinal neurons of newborn mice after hypoxia-ischemia. J Pineal Res 71:e12716. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12716
Xu S, Ge J, Zhang Z, Zhou W (2017) MiR-129 inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting ETS1 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in prostate cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 96:634–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.037
Chen Y, Wang D, Shu T, Sun K, Zhao J, Wang M, Huang Y, Wang P, Zheng H, Cai Z, Yang Z (2021) Circular RNA_0000326 promotes bladder cancer progression via microRNA-338-3p/ETS Proto-Oncogene 1/phosphoinositide-3 kinase/Akt pathway. Bioengineered 12:11410–11422. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.2008738
Cui L, Xu F, Wang S, Jiang Z, Liu L, Ding Y, Sun X, Du M (2021) Melatonin-MT1 signal is essential for endometrial decidualization. Reproduction 162:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1530/REP-21-0159
Sasaki H, Zhang Y, Emala CW Sr, Mizuta K (2021) Melatonin MT2 receptor is expressed and potentiates contraction in human airway smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 321:L991–L1005. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00273.2021
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LPC and HYL contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by FH, QFW LL, CY, CZL, and WCW. The first draft of the manuscript was written by FH, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, F., Wang, QF., Li, L. et al. Melatonin Protects Against Hyperoxia-Induced Apoptosis in Alveolar Epithelial type II Cells by Activating the MT2/PI3K/AKT/ETS1 Signaling Pathway. Lung 201, 225–234 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-023-00610-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-023-00610-0