Abstract
Background
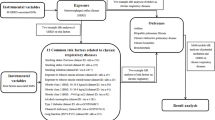
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) have been shown to be potentially closely related, but the relationship between these conditions, particularly the possibility of a causal link, is not fully understood. This study used Mendelian randomization (MR) to assess the causal relationship between these two disorders.
Methods
We extracted genome-wide association study data sets for GERD and CRS from publicly available gene summaries, and used MR to conduct a causal inference analysis. The main robustness test used in this study included MR-Egger regression, a leave-one-out sensitivity test, and multivariate MR (MVMR).
Results
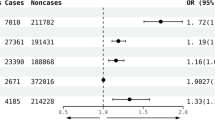
GERD increased the risk of developing CRS by 36%, based on the inverse-variance weighted method, a statistically significant association (odds ratio [OR] 1.360, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.179–1.568, P < 0.001). Other MR assessment methods, such as weighted median, simple mode, and weighted mode, similarly observed a significant increase in the risk of CRS occurrence (OR 1.434, 95% CI 1.186–1.734, P < 0.001; OR 1.927, 95% CI 1.166–3.184, P = 0.013; and OR 1.910, 95% CI 1.222–2.983, P = 0.006, respectively). No significant bias was found in the heterogeneity or pleiotropy tests (P = 0.071 and P = 0.700, respectively). Even after excluding possible mediators using MVMR, GERD appeared to significantly increase the risk of developing CRS (OR 1.013, 95% CI 1.008–1.023, P = 0.002).
Conclusions
This study provides new, significant evidence that GERD is genetically associated with a higher incidence rate of CRS. However, further research is needed to elucidate the potential underlying biological mechanisms of this relationship.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets (GWAS for GERD and CRS) for this study can be found in the UK Biobank (https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/) and the FinnGen research project (https://www.finngen.fi/en).
References
Bachert C, Marple B, Schlosser RJ, Hopkins C, Schleimer RP, Lambrecht BN, Bröker BM, Laidlaw T, Song WJ (2020) Adult chronic rhinosinusitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 6(1):86. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-020-00218-1
Bachert C, Han JK, Desrosiers M, Hellings PW, Amin N, Lee SE, Mullol J, Greos LS, Bosso JV, Laidlaw TM, Cervin AU, Maspero JF, Hopkins C, Olze H, Canonica GW, Paggiaro P, Cho SH, Fokkens WJ, Fujieda S, Zhang M et al (2019) Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (LIBERTY NP SINUS-24 and LIBERTY NP SINUS-52): results from two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group phase 3 trials. Lancet (London, England) 394(10209):1638–1650. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31881-1IF:202.731Q1
Hoggard M, Wagner Mackenzie B, Jain R, Taylor MW, Biswas K, Douglas RG (2017) Chronic rhinosinusitis and the evolving understanding of microbial ecology in chronic inflammatory mucosal disease. Clin Microbiol Rev 30(1):321–348. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00060-16
Kennedy DW (2004) Pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 193:6–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/00034894041130s503IF:1.973Q3
Ceballos Cantu JC, Alobid I, Mullol J (2022) chronic rhinosinusitis in a population of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 18(12):1253–1263. https://doi.org/10.1080/1744666X.2022.2128767
Baguley C, Brownlow A, Yeung K, Pratt E, Sacks R, Harvey R (2014) The fate of chronic rhinosinusitis sufferers after maximal medical therapy. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 4(7):525–532. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.21315
Wynn R, Har-El G (2004) Recurrence rates after endoscopic sinus surgery for massive sinus polyposis. Laryngoscope 114(5):811–813. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200405000-00004
Lal D, Brar T, Ramkumar SP, Li J, Kato A, Zhang L (2023) Genetics and epigenetics of chronic rhinosinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 151(4):848–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2023.01.004
Mehta RS, Staller K, Chan AT (2021) Review of gastroesophageal reflux disease. JAMA 325(14):1472. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.1438
DiBaise JK, Olusola BF, Huerter JV, Quigley EM (2002) Role of GERD in chronic resistant sinusitis: a prospective, open label, pilot trial. Am J Gastroenterol 97(4):843–850. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05598.x
Bergqvist J, Bove M, Andersson A, Scholer L, Hellgren J (2023) Dose-dependent relationship between nocturnal gastroesophageal reflux and chronic rhinosinusitis in a middle-aged population: results from the SCAPIS pilot. Rhinology 61(2):118–123. https://doi.org/10.4193/Rhin22.297
Bohnhorst I, Jawad S, Lange B, Kjeldsen J, Hansen JM, Kjeldsen AD (2015) Prevalence of chronic rhinosinusitis in a population of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Rhinol Allergy 29(3):e70–e74. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2015.29.4167
Katle EJ, Hart H, Kjærgaard T, Kvaløy JT, Steinsvåg SK (2012) Nose- and sinus-related quality of life and GERD. European archives of oto-rhino-laryngology: official journal of the European Federation of Oto-Rhino-Laryngological Societies (EUFOS): affiliated with the German Society for Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. Head Neck Surg 269(1):121–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-011-1675-y
Finocchio E, Locatelli F, Sanna F, Vesentini R, Marchetti P, Spiteri G, Antonicelli L, Battaglia S, Bono R, Corsico AG, Ferrari M, Murgia N, Pirina P, Olivieri M, Verlato G (2021) Gastritis and gastroesophageal reflux disease are strongly associated with non-allergic nasal disorders. BMC Pulm Med 21(1):53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-020-01364-8
Lechien JR, Saussez S, Hopkins C (2023) Association between laryngopharyngeal reflux, gastroesophageal reflux and recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis: a systematic review. Clin Otolaryngol 48(4):501–514. https://doi.org/10.1111/coa.14047
Sella GCP, Tamashiro E, Anselmo-Lima WT, Valera FCP (2017) Relation between chronic rhinosinusitis and gastroesophageal reflux in adults: systematic review. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 83(3):356–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjorl.2016.05.012
Leason SR, Barham HP, Oakley G, Rimmer J, DelGaudio JM, Christensen JM, Sacks R, Harvey RJ (2017) Association of gastro-oesophageal reflux and chronic rhinosinusitis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Rhinology 55(1):3–16. https://doi.org/10.4193/Rhino16.177
Katle EJ, Hatlebakk JG, Steinsvåg S (2013) Gastroesophageal reflux and rhinosinusitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 13(2):218–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-013-0340-5
Hanna BC, Wormald PJ (2012) Gastroesophageal reflux and chronic rhinosinusitis. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 20(1):15–18. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOO.0b013e32834e8f11
Smith GD, Ebrahim S (2004) Mendelian randomization: prospects, potentials, and limitations. Int J Epidemiol 33(1):30–42. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyh132
Ahn K, Penn RB, Rattan S, Panettieri RA Jr, Voight BF, An SS (2023) Mendelian randomization analysis reveals a complex genetic interplay among atopic dermatitis, asthma, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 207(2):130–137. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.202205-0951OC
Reynolds CJ, Del Greco MF, Allen RJ, Flores C, Jenkins RG, Maher TM, Molyneaux PL, Noth I, Oldham JM, Wain LV, An J, Ong JS, MacGregor S, Yates TA, Cullinan P, Minelli C (2023) The causal relationship between gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomisation study. Eur Respir J 61(5):2201585. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01585-2022
Sun X, Chen L, Zheng L (2022) A Mendelian randomization study to assess the genetic liability of gastroesophageal reflux disease for cardiovascular diseases and risk factors. Hum Mol Genet 31(24):4275–4285. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddac162
Zhang Z, Li G, Yu L, Jiang J, Li R, Zhou S, Jiang Y (2023) Causal relationships between potential risk factors and chronic rhinosinusitis: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Eur arch Oto-rhino-laryngol 280(6):2785–2793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-022-07798-6
Skrivankova VW, Richmond RC, Woolf BAR, Yarmolinsky J, Davies NM, Swanson SA, VanderWeele TJ, Higgins JPT, Timpson NJ, Dimou N, Langenberg C, Golub RM, Loder EW, Gallo V, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, Davey Smith G, Egger M, Richards JB (2021) Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using mendelian randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA 326(16):1614–1621. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.18236
Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Haycock PC, Burgess S (2016) Consistent estimation in mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol 40(4):304–314. https://doi.org/10.1002/gepi.21965
Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Burgess S (2015) Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol 44(2):512–525. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyv080
Davey Smith G, Hemani G (2014) Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet 23(R1):R89–R98. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddu328
Carter AR, Sanderson E, Hammerton G, Richmond RC, Davey Smith G, Heron J, Taylor AE, Davies NM, Howe LD (2021) Mendelian randomisation for mediation analysis: current methods and challenges for implementation. Eur J Epidemiol 36(5):465–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-021-00757-1
Hemani G, Tilling K, Davey Smith G (2017) Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data. PLoS Genet 13(11):e1007081. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1007081IF:6.020Q1
DiBaise JK, Huerter JV, Quigley EM (1998) Sinusitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Intern Med 129(12):1078. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-129-12-199812150-00029
Lupa M, DelGaudio JM (2012) Evidence-based practice: reflux in sinusitis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 45(5):983–992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2012.06.004
Flook EP, Kumar BN (2011) Is there evidence to link acid reflux with chronic sinusitis or any nasal symptoms? A review of the evidence. Rhinology 49(1):11–16. https://doi.org/10.4193/Rhino10.054
Schiöler L, Ruth M, Jõgi R, Gislason T, Storaas T, Janson C, Forsberg B, Sigsgaard T, Torén K, Hellgren J (2015) Nocturnal GERD—a risk factor for rhinitis/rhinosinusitis: the RHINE study. Allergy 70(6):697–702. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.12615
Lin YH, Chang TS, Yao YC, Li YC (2015) Increased risk of chronic sinusitis in adults with gastroesophgeal reflux disease: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Medicine 94(39):e1642. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000001642
Orlandi RR, Kingdom TT, Hwang PH, Smith TL, Alt JA, Baroody FM, Batra PS, Bernal-Sprekelsen M, Bhattacharyya N, Chandra RK, Chiu A, Citardi MJ, Cohen NA, DelGaudio J, Desrosiers M, Dhong HJ, Douglas R, Ferguson B, Fokkens WJ, Georgalas C et al (2016) International consensus statement on allergy and rhinology: rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 6(Suppl 1):S22–S209. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.21695
Wong IW, Omari TI, Myers JC, Rees G, Nair SB, Jamieson GG, Wormald PJ (2004) Nasopharyngeal pH monitoring in chronic sinusitis patients using a novel four channel probe. Laryngoscope 114(9):1582–1585. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200409000-00015
Pongdee T, Bielinski SJ, Decker PA, Kita H, Larson NB (2022) White blood cells and chronic rhinosinusitis: a Mendelian randomization study. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol 18(1):98. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-022-00739-2
Hait EJ, McDonald DR (2019) Impact of gastroesophageal reflux disease on mucosal immunity and atopic disorders. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 57(2):213–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-018-8701-4
Wong IW, Rees G, Greiff L, Myers JC, Jamieson GG, Wormald PJ (2010) Gastroesophageal reflux disease and chronic sinusitis: in search of an esophageal-nasal reflex. Am J Rhinol Allergy 24(4):255–259. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2010.24.3490
Morinaka S, Ichimiya M, Nakamura H (2003) Detection of Helicobacter pylori in nasal and maxillary sinus specimens from patients with chronic sinusitis. Laryngoscope 113(9):1557–1563. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200309000-00027
Mahdavinia M, Bishehsari F, Hayat W, Codispoti CD, Sarrafi S, Husain I, Mehta A, Benhammuda M, Tobin MC, Bandi S, LoSavio PS, Jeffe JS, Palmisano EL, Schleimer RP, Batra PS (2016) Prevalence of allergic rhinitis and asthma in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Allergy asthma Immunol 117(2):158-162.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anai.2016.05.018
Shu L, Tong X (2022) Exploring the causal relationship between gastroesophageal reflux and oral lesions: a mendelian randomization study. Front Genet 13:1046989. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.1046989
Acknowledgements
We express our gratitude to the participants and research teams who made the GWAS results publicly accessible. Thank you for the language assistance provided by Editage.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
No ethical clearance was required for this study, as no patients were involved in the formulation of the research question or outcome measures. Only secondary analysis was performed using published GWAS summary statistics available in the public domain. All authors have viewed and agreed to the submission.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Funnel plot of SNPs associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease and the risk of chronic rhinosinusitis. MR; Mendelian randomization. (TIF 2711 KB)
Fig: S2
Leave-one-out of SNPs associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease and the risk of chronic rhinosinusitis. MR; Mendelian randomization. (TIF 4259 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Guo, W., Liu, S. et al. Causal analysis between gastroesophageal reflux disease and chronic rhinosinusitis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 281, 1819–1825 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08350-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08350-w