Abstract
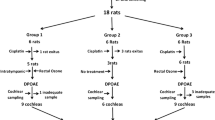
Although dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is one of the most common solvents employed in otoprotection studies, its effect on the inner ear remains unknown. Only a few in vitro studies have addressed the effect of DMSO in cochlear cells. Up to the date, no in vivo functional studies have been reported. To determine the effect of intratympanic DMSO application in the inner ear, and to evaluate its effect in combination with cisplatin in Wistar rats, twelve Wistar rats were randomly assigned into two groups. Group A received intratympanic 1 % DMSO in both ears. Group B received intraperitoneal cisplatin (10 mg/kg) and intratympanic 0.5 % DMSO in the right ear and saline solution in the left ear. Functional changes were evaluated with Auditory Steady-State Responses before and 5 days after the procedure. Morphological changes were studied by means of confocal laser scanning microscopy following the removal of the temporal bones and cochlear dissection. Hearing threshold levels in group A did not show any statistically significant changes after the treatment. In group B, significant differences between pre- and post-treatment were found, with no statistically significant variations between right (DMSO) and left ear (saline solution). We suggest that DMSO could be safely used to dissolve hydrophobic compounds in otoprotection studies without interfering with the cochlear damage produced by cisplatin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goycoolea MV (2001) Clinical aspects of round window membrane permeability under normal and pathological conditions. Acta Otolaryngol 121:437–447
Parnes LS, Sun AH, Freeman DJ (1999) Corticosteroid pharmacokinetics in the inner ear fluids: an animal study followed by clinical application. Laryngoscope 109(Suppl 9):1
Uribe PM, Mueller MA, Gleichman JS, Kramer MD, Wang Q, Sibrian-Vazquez M, Strongin RM, Steyger PS, Cotanche DA, Matsui JI (2013) Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) exacerbates cisplatin-induced sensory hair cell death in zebrafish (Danio rerio). PLoS ONE 8:e55359
Pommier RF, Woltering EA, Milo G, Fletcher WS (1988) Synergistic cytotoxicity between dimethyl sulfoxide and antineoplastic agents against ovarian cancer in vitro. Am J Obstet Gynecol 159:848–852
Schoenfeld RH, Belville WD, Jacob WH, Buck AS, Dresner ML, Insalaco SJ, Ward GS (1983) The effect of dimethyl sulfoxide on the uptake of cisplatin from the urinary bladder of the dog: a pilot study. J Am Osteopath Assoc 82:570–573
Melki SJ, Heddon CM, Frankel JK et al (2010) Pharmacological protection of hearing loss in the mouse model of endolymphatic hydrops. Laryngoscope 120:1637–1645
Canlon B, Dulon D (1993) Dissociation between the calcium-induced and voltage-driven motility in cochlear outer hair cells from the waltzing guinea pig. J Cell Sci 104:1137–1143
Szonyi M, He DZ, Ribari O, Sziklai I, Dallos P (1999) Cyclic GMP and outer hair cell electromotility. Hear Res 137:29–42
Szonyi M, He DZ, Ribari O, Sziklai I, Dallos P (2001) Intracellular calcium and outer hair cell electromotility. Brain Res 922:65–70
Qi W, Ding D, Salvi RJ (2008) Cytotoxic effects of dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) on cochlear organotypic cultures. Hear Res 236:52–60
Reynaud D, Demin PM, Sutherland M, Nigam S, Pace-Asciak CR (1999) Hepoxilin signaling in intact human neutrophils: biphasic elevation of intracellular calcium by unesterified hepoxilin A3. FEBS Lett 446:236–238
Saldanha C, Santos NC, Martins-Silva J (2002) Fluorescent probes DPH, TMA-DPH and C17-HC induce erythrocyte exovesiculation. J Membr Biol 190:75–82
Santos NC, Figueira-Coelho J, Saldanha C, Martins-Silva J (2002) Biochemical, biophysical and haemorheological effects of dimethyl-sulphoxide on human erythrocyte calcium loading. Cell Calcium 31:183–188
Zhang XQ, Eyzaguirre C (1999) Effects of hypoxia induced by Na2S204 on intracellular calcium and resting potential of mouse glomus cells. Brain Res 818:118–126
Lu C, Mattson MP (2001) Dimethyl sulfoxide suppresses NMDA- and AMPA-induced ion currents and calcium influx and protects against excitotoxic death in hippocampal neurons. Exp Neurol 170:180–185
Momin SR, Melki SJ, Obokhare JO et al (2011) Hearing preservation in Guinea pigs with long-standing endolymphatic hydrops. Otol Neurotol 32:1583–1589
Salim AS (1992) Allopurinol and dimethyl sulfoxide improve treatment outcomes in smokers with peptic ulcer disease. J Lab Clin Med 119:702–709
Salim AS (1992) Oxygen-derived free-radical scavengers prolong survival in gastric cancer. Chemotherapy 38:135–144
Morassi P, Massa F, Mesesnel E, Magris D, Dagnol B (1989) Treatment of amyloidosis with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Minerva Med 80:65–70
McCammon KA, Lentzner AN, Moraiarty RP, Schellhammer PF (1998) Intravesical dimethyl sulfoxide for primary amyloidosis of the bladder. Urology 52:1136–1138
Iwasaki T, Hamano T, Aizawa K, Kobayashi K, Kakishita E (1994) A case of pulmonary amyloidosis associated with multiple myeloma successfully treated with dimethyl sulfoxide. Acta Haematol 91:91–94
Burgues JL, Hammer AP, Robertson WO (1998) Sulfhemoglobinemia after dermal application of DMSO. Vet Hum Toxicol 40:87–89
Leite MT, Gomes HC, Percario S et al (2007) Dimethyl sulfoxide as a block to the deleterious effect of nicotine in a random skin flap in the rat. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:1819–1822
Broadwell RD, Salcman M, Kaplan RS (1982) Morphologic effect of dimethyl sulfoxide on the blood-brain barrier. Science 217:164–166
Ikeda Y, Long DM (1990) Comparative effects of direct and indirect hydroxyl radical scavengers on traumatic brain oedema. Acta Neurochir Suppl 51:74–76
Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B, Nicotera P (2003) Regulation of cell death: the calcium-apoptosis link. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:552–565
Harris KC, Hu B, Hangauer D, Henderson D (2005) Prevention of noise-induced hearing loss with Src-PTK inhibitors. Hear Res 208:14–25
Guitton MJ, Caston J, Ruel J, Jonson RM, Pujol R, Puel JL (2003) Salicylate induces tinnitus through activation of cochlear NMDA receptors. J Neurosci 23:3944–3952
Lee JH, Marcus DC (2002) Nongenomic effects of corticosteroids on ion transport by stria vascularis. Audiol Neurootol 7:100–106
Ding D, Stracher A, Salvi RJ (2002) Leupeptin protects cochlear and vestibular hair cells from gentamicin ototoxicity. Hear Res 164:115–126
Kamimura T, Whitworth CA, Rybak LP (1999) Effect of 4-methylthiobenzoic acid on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in the rat. Hear Res 131:117–127
Basile AS, Huang JM, Webster D, Xie C, Berlin C, Skolnick P (1996) N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist limit aminoglycoside antibiotic-induced hearing loss. Nat Med 2:1338–1343
Simsek G, Tokgoz SA, Vuralkan E, Cliskan M, Besalti O, Akin I (2013) Protective effect of resveratrol on cisplatin-dependent inner-ear damage in rats. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270:1789–1793
Hirose Y, Simon JA, Ou HC (2011) Hair cell toxicity in anti-cancer drugs: evaluating an anti-cancer drug library for independent and synergistic toxic effects on hair cells using the zebrafish lateral line. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 12:719–728
Chin LL, Cunninghan LL, Raible DW, Rubel EW, Ou HC (2008) Using the zebrafish lateral line to screen for ototoxicity. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 9:178–190
Owens KN, Santos F, Roberts B, Linbo T, Coffin AB, Knisely AJ, Simon JA, Rubel EW, Raible DW (2008) Identification of genetic and chemical modulators of zebrafish mechanosensory hair cell death. PLoS Genet 4:c1000020
Coffin AB, Ou H, Owens KN, Santos F, Simon JA, Rubel EW, Raible DW (2010) Chemical screening for hair cell loss and protection in the zebrafish lateral line. Zebrafish 7:3–11
Ou HC, Cunningham LL, Francis SP, Brandon CS, Simon JA, Raible DW, Rubel EW (2009) Identification of FDA-approved drugs and bioactives that protect hair cells in the zebrafish (Danio rerio) lateral line and mouse (Mus musculus) utricle. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 10:191–203
Ou HC, Santos F, Raible DW, Simon JA, Rubel EW (2010) Drug screening for hearing loss: using the zebrafish lateral line to screen for drugs deal prevent and cause hearing loss. Drug Discov Today 15:265–271
Ou H, Simon JA, Rubel EW, Raible DW (2012) Screening for chemicals that affect hair cell death and survival in the zebrafish lateral line. Hear Res 288:58–66
Namdaran P, Reinhart KF, Owens KN, Raibel FW (2012) Identification of modulators of hair cell regeneration in the zebrafish lateral line. J Neurosci 32:3516–3528
Ramírez-Camacho R, Fernández DE, Verdaguer JM, Gómez MM, Trinidad A, García-Berrocal JR, Corvillo MA (2008) Cisplatin-induced hearing loss does not correlate with intracellular platinum concentration. Acta Otolaryngol 128:505–509
García-Berrocal JR, Nevado J, González-García JA, Sánchez-Rodríguez C, Sanz R, Trinidad A, España P, Citores MJ, Ramírez-Camacho R (2010) Heat shock protein 70 and cellular disturbances in cochlear cisplatin ototoxicity model. J Laryngol Otol 124:599–609
González-García JA, Nevado J, García-Berrocal JR, Sánchez-Rodríguez C, Trinidad A, Sanz R, Ramírez-Camacho R (2010) Endogenous protection against oxidative stress caused by cisplatin: role of superoxide dismutase. Acta Otolaryngol 130:453–457
Casares C, Ramírez-Camacho R, Trinidad A, Roldán A, Jorge E, García-Berrocal JR (2012) Reactive oxygen species in apoptosis induced by cisplatin: review of physiopathological mechanisms in animal models. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269:2455–2459
Viberg A, Canlon B (2004) The guide to plotting to cochleogram. Hear Res 197:1–10
Lorito G, Hatzopoulos S, Laurell G, Campbell KC, Petruccelli J, Giordano P, Kochanek K, Sliwa L, Martini A, Skarzynski H (2011) Dose-dependent protection on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity—an electrophysiological study on the effect of three antioxidants in the Sprague–Dawley rat animal model. Med Sci Monit 17:BR179–BR186
Campbell KC, Meech RP, Rybak LP, Hughes LF (2003) The effect of d-methionine on cochlear oxidative state with and without cisplatin administration: mechanisms of otoprotection. J Am Acad Audiol 14:144–156
Korver KD, Rybak LP, Whitworth CA, Campbell KC (2002) Round window application of d-methionine provides complete cisplatin otoprotection. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:683–689
Li G, Frenz DA, Brahmblastt S et al (2001) Round window membrane delivery of l-methionine provides protection from cisplatin ototoxicity without compromising chemotherapeutic efficacy. Neurotoxicology 22:163–176
Nakai Y, Konishi K, Chang KC et al (1982) Ototoxicity of the anticancer drug cisplatin. An experimental study. Acta Otolaryngol 93:227–232
Daldal A, Odabasi O, Serbetcioglu B (2007) The protective effect of intratympanic dexamethasone on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in guinea pigs. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137:747–752
Acknowledgments
Research supported by a Spanish FIS Grant EI 11/00742. The authors wish to thank Alejandro Kurtz and Cristina Martin for assisting with the English language and manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roldán-Fidalgo, A., Trinidad, A., Rodríguez-Valiente, A. et al. Effect of intratympanic dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) in an in vivo model of cisplatin-related ototoxicity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271, 3121–3126 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-2957-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-2957-y