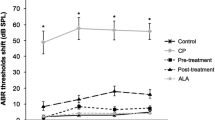
Abstract
Cisplatin is a highly effective chemotherapeutic agent but displays significant ototoxic side effects. The most prominent change seen in the cochlea after cisplatin administration consists of loss of outer hair cells. Several mechanisms are believed to mediate cisplatin-induced apoptosis: binding of cisplatin to guanine bases on DNA and the formation of inter- and intra-strand chain cross-linking, generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) with increased lipid peroxidation and Ca2+ influx and, finally, inflammation mediated by cisplatin. The aim of the present review is to analyze the role of ROS in the mechanisms causing cisplatin-mediated apoptosis in the inner ear and the contribution of the different pathways involved, emphasizing the main strategies to blockade events leading to apoptosis of cochlear cells.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- STAT1:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription-1
- TRPV1:
-
Transient receptor vanilloid-1
- siRNA:
-
Short interfering RNA
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- NOX3:
-
NADPH nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase isoform, nitro-l-arginine methyl ester
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- HSP70:
-
Heat shock protein 70
- HSP32:
-
Heat shock protein 32
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase-1
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- NF-kβ:
-
Nuclear factor-kβ
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- TRAIL:
-
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
- Cyt-c :
-
Cytochrome c
- AIF:
-
Apoptosis-inducing factor
- PARP:
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- JNK-c:
-
Jun N-terminal kinase
- RIP1:
-
Kinase receptor interacting protein-1
- TRAF2:
-
TNF receptor-associated factor-2
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- AP1:
-
Transcription activator protein-1
References
Estrem SA, Babin RW, Ryu JH, Moore KC (1981) Cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) ototoxicity in the guinea pig. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 89:638–645
Anniko M, Sobin A (1986) Cisplatin: evaluation of its ototoxic potential. Am J Otol 7:276–293
Watanabe K, Yagi T (2000) Expression of myeloperoxidase in the inner ear of cisplatin-treated guinea pigs. Anticancer Drugs 11:727–730
Lee JE, Nagakawa T, Kita T, Kim TS, Iguchi F, Endo T, Shiga A, Lee SH, Ito J (2004) Mechanisms of apoptosis induced by cisplatin in marginal cells in mouse stria vascularis. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 66:111–118
Ramírez-Camacho R, García-Berrocal JR, Trinidad A, González-García JA, Verdaguer JM, Ibáñez A, Rodríguez A, Sanz R (2006) Central role of supporting cells in cochlear homeostasis and pathology. Med Hypotheses 67:550–555
McKeage MJ (1995) Comparative adverse effect profiles of platinum drugs. Drug Saf 13:228–244
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM (1998) Death receptors: signalling and modulation. Science 281:1305–1308
Harris MH, Thompson CB (2000) The role of Bcl-2 family in the regulation of outer mitochondrial membrane permeability. Cell Death Differ 7:1182–1191
Goldstein JC, Waterhouse NJ, Juin P, Evan GI, Green DR (2000) The coordinate release of cytochrome c during apoptosis is rapid, complete and kinetically invariant. Nature Cell Biol 2:156–162
Li H, Zhu H, Xu CJ, Yuan J (1998) Cleavage of Bid by caspase 8 mediated the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell 94:491–501
Thomas JP, Lautermann J, Liedert B, Seller F, Thomale J (2006) High accumulation of platinum-DNA adducts in strial marginal cells of the cochlea is an early event in cisplatin but not in carboplatin ototoxicity. Mol Pharmacol 70:23–29
Liang F, Schulte BA, Qu C, Hu W, Shen Z (2005) Inhibition of the calcium and voltage-dependent big conductance potassium channel ameliorates cisplatin-induced apoptosis in spiral ligament fibrocytes of the cochlea. Neuroscience 135:263–271
Watanabe K, Hess A, Bloch W, Michel O (2000) Nitric oxide synthase inhibitor suppresses the ototoxic side effects of cisplatin in guinea pigs. Anticancer Drugs 11:401–406
Mukherjea D, Kaur T, Jajoo S, Sheehan KE, Ramkumar V, Rybak LP (2010) Transtympanic administration of short interfering (si)RNA for the NOX3 isoform of NADPH oxidase protects against cisplatin-induced hearing loss in the rat. Antiox Redox Signal 13(5):589–598
Rybak LP, Husain K, Whitworth C, Somani SM (1999) Dose dependent protection by lipoic acid against cisplatin ototoxicity in rats: antioxidant defense system. Toxicol Sci 47:195–202
Rybak LP (2007) Mechanisms of cisplatin ototoxicity and progress in otoprotection. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 15:364–369
González-García JA, Nevado J, García-Berrocal JR, Sánchez-Rodríguez C, Sanz R, Ramírez-Camacho R (2010) Endogenous protection against oxidative stress caused by cisplatin: role of superoxide dismutase. Acta Otolaryngol 130:453–457
Mukherjea D, Jajoo S, Whitworth C, Bunch JR, Turner JG, Rybak LP, Ramkumar B (2008) Short interfering (si)RNA against transient receptor potential Vanilloid-1 (TRPV1) attenuates cisplatin-induced hearing loss in the rat. J Neurosci 28(49):13056–13065
Rybak LP, Whitworth CA, Mukherjea D, Ramkumar V (2007) Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity and prevention. Hear Res 226(1–2):157–167
Xu Y, Huang S, Liu ZG, Han J (2006) Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 signalling to mitochondria in necrotic cell death requires RIP1/TRAF2-mediated JNK1 activation. J Biol Chem 281(13):8788–8795
Francis SP, Kramarenko II, Brandon CS, Lee FS, Baker TG, Cunningham LL (2011) Celastrol inhibits aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity via heat shock protein 32. Cell Death Dis 2:e195
Kim HJ, So HS, Lee JH, Park C, Park SY, Kim YH, Youn MJ, Kim SJ, Chung SY, Lee KM, Park R (2006) Heme oxygenase-1 attenuates the cisplatin-induced apoptosis of auditory cells via down-regulation of reactive oxygen species generation. Free Radic Biol Med 40:1810–1819
Choi BM, Chen XY, Gao SS, Zhu R, Kim BR (2011) Anti-apoptotic effect of phloretin on cisplatin-induced apoptosis in HEI-OC1 auditory cells. Pharmacol Rep 63(3):708–716
Cunningham LL, Brandon CS (2006) Heat shock inhibits both aminoglycoside- and cisplatin induced sensory hair cell death. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 7:299–307
García-Berrocal JR, Nevado J, González-García JA, Sánchez-Rodríguez C, Sanz R, Trinidad A, España P, Citores MJ, Ramírez-Camacho R (2010) Heat shock protein 70 and cellular disturbances in cochlear cisplatin ototoxicity model. J Laryngol Otol 124:599–609
García-Berrocal JR, Nevado J, Ramírez-Camacho R, Sanz R, González-García JA, Sánchez-Rodríguez C, Cantos B, España P, Verdaguer JM, Trinidad Cabezas A (2007) Antitumoral drug cisplatin induces an intrinsic apoptotic pathway inside the inner ear. British J Pharmacol 152:1012–1020
Wang J, Ladrech S, Pujol R, Brabet P, Van de Water RT, Puel JL (2004) Caspase inhibitors, but not c-Jun NH-N-terminal kinase inhibitor treatment, prevent cisplatin-induced hearing loss. Cancer Res 64:9217–9224
Jeong HJ, Choi Y, Kim MH, Kang IC, Lee JH, Park C, Park R, Kim HM (2011) Rosmarinic acid, active component of Dansam-Eum attenuates ototoxicity of cochlear hair cells through blockage of caspase-1 activity. PLoS ONE 6(4):e18815
So H, Kim H, Kim Y, Kim E, Pae HO, Chung HT, Kim HJ, Kwon KB, Lee KM, Lee HY, Moon SK, Park R (2008) Evidence that cisplatin-induced auditory damage is attenuated by downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines via Nrf2/HO-1. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 9:290–306
Watanabe K, Inai S, Jinnouchi K, Bada S, Hess A, Michel O, Yagi T (2002) Nuclear-factor kappa B (NF-kB)-inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS/NOS II) pathway damages the stria vascularis in cisplatin-treated mice. Anticancer Res 22:4081–4085
So H, Kim H, Lee JH, Park C, Kim Y, Kim E, Kim JK, Yun KJ, Lee KM, Lee HY, Moon SK, Lim DJ, Park R (2007) Cisplatin cytotoxicity of auditory cells requires secretions of proinflammatory cytokines via activation of ERK and NF-kB. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 8:338–355
Kaur T, Mukherjea D, Sheehan K, Jajoo S, Rybak LP, Ramkumar V (2011) Short interfering RNA against STAT1 attenuates cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in the rat by suppressing inflammation. Cell Death Dis 2:e180
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casares, C., Ramírez-Camacho, R., Trinidad, A. et al. Reactive oxygen species in apoptosis induced by cisplatin: review of physiopathological mechanisms in animal models. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269, 2455–2459 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2029-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2029-0