Abstract
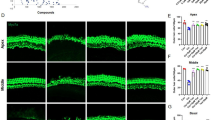
Cisplatin is a common chemotherapeutic agent used in many solid and hematologic malignancies. The main unwanted effect of cisplatin is ototoxicity, for which no standard treatment has been reported. The present study examined the protective efficacy of resveratrol on cisplatin-dependent ototoxicity through an experimental model. Fifteen rats were randomized into three groups. Group 1 (control group) (n = 5) received intraperitoneal (i.p.) 15 mg/kg cisplatin; group 2 (resveratrol group) (n = 5) received i.p. 100 mg/kg resveratrol, followed by i.p. 15 mg/kg cisplatin; group 3 (n = 5) served as a vehicle group and received i.p. 1 ml dimethyl sulfoxide. All rats underwent the auditory brainstem response (ABR) test before and 72 h after the treatment. Pretreatment ABR values of the groups were not significantly different. The pretreatment hearing threshold values of the groups were 30 ± 6.60 and 28.5 ± 5.29 dB in groups 1 and 2, respectively (p > 0.05). The post-ABR-I and post-ABR-IV values were, respectively, 1.41 ± 0.18 and 5.83 ± 0.16 ms in the control subjects and 1.19 ± 0.22 and 4.58 ± 0.27 ms in the study group. The ABR-I and ABR-IV durations in rats treated with resveratrol were significantly shorter (p < 0.01). A comparison of threshold values shows that the resveratrol-treated rats had significantly lower values than the control rats. After cisplatin injection, ABR I–IV intervals were compared among the groups. The ABR I–IV interval duration was 4.42 ± 0.16 ms in the control group, while the resveratrol-treated rats showed a significantly shorter ABR I–IV interval duration of 3.49 ± 0.27 ms (p < 0.001). Resveratrol attenuated cisplatin-dependent inner-ear damage, as shown by the ABR-I, ABR-IV, ABR I–IV interval, and hearing threshold values. Our results suggest that this natural antioxidant may be effectively used in reducing the unwanted effects of cisplatin on the ear physiology of patients, particularly those undergoing chemotherapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boulikas T, Vougiouka M (2004) Recent clinical trail using sisplatin, karboplatin and their combination chemotherapy drugs. Oncol Rep 11:559–595
Meech RP, Campbell KC, Hughes LP et al (1998) A semiquantitative analysis of the effects of sisplatin on the rat stria vascularis. Hear Res 124:44–59
Ravi R, Somani SM, Rybak LP (1995) Mechanism of sisplatin ototoxicity: antioxidant system. Pharmacol Toxicol 76:386–394
Rybak LP, Whitworth C, Somani S (1999) Satu: application of antioxidants and other agents to prevent sisplatin ototoxicity. Laryngoscope 109:1740–1744
Vidavalur R, Otani H, Singal PK, Maulik N (2006) Significance of wine and resveratrol in cardiovascular disease: French paradox revisited. Exp Clin Cardiol 11(3):217–225
Rodrigo R, Bosco C (2006) Oxidative stress and protective effects of polyphenols: comparative studies in human and rodent kidney. A review. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 142(3–4):317–327
Bonabi S, Caelers A, Monge A, Huber A, Bodmer D (2008) Resveratrol protects auditory hair cells from gentamicin toxicity. Ear Nose Throat J 87(10):570–573
Seidman M, Babu S, Tang W, Naem E, Quirk WS (2003) Effects of resveratrol on acoustic trauma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129(5):463–470
Derin A, Agirdir B, Derin N, Dinc O, Guney K, Ozcaglar H et al (2004) The effects of l-carnitine on presbyacusis in the rat model. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 29:238–241
Ozcaglar HU, Agirdir B, Dinc O, Turhan M, Kilinçarslan S, Oner G (2001) Effects of cadmium on the hearing system. Acta Otolaryngol 121:393–397
Muldoon LL, Pagel MA, Kroll RA, Brummett RE, Doolittle ND, Zuhowski EG, Egorin MJ, Neuwelt EA (2000) Delayed administration of sodium thiosulfate in animal models reduces platinum ototoxicity without reduction of antitumor activity. Clin Cancer Res 6(1):309–315
Campbell KCM, Meech RP, Rybak LP, Hughes LF (1999) d-Methionine protects against sisplatin damage to the stria vascularis. Hear Res 138:13–28
Feghali JG, Liu W, Van De Water TR et al (2001) l-n-Acetyl-cysteine protection against sisplatin-induced auditory neuronal and hair cell toxicity. Laryngoscope 111:1147–1155
Riggs LC, Matz GJ, Ryback RP (1998) Ototoxicity. In: Bailey BJ, Calhoun KH (eds) Head and neck surgery: otolaryngology, 2nd edn. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, pp 2165–2170
Rybak LP, Husain K, Morris C et al (2000) Effect of protective agents against sisplatin ototoxicity. Am J Otol 21:513–520
Rubiolo JA, Mithieux G, Vega FV (2008) Resveratrol protects primary rat hepatocytes against oxidative stress damage: activation of the Nrf2 transcription factor and augmented activities of antioxidant enzymes. Eur J Pharmacol 591:66–72
Li Y, Cao Z, Zhu H (2006) Upregulation of endogenous antioxidants and phase 2 enzymes by the red wine polyphenol, resveratrol in cultured aortic smooth muscle cells leads to cytoprotection against oxidative and electrophilic stress. Pharmacol Res 53:6–15
Di Franco R, Calvanese M, Murino P et al (2012) Skin toxicity from external beam radiation therapy in breast cancer patients: protective effects of Resveratrol, Lycopene, Vitamin C and anthocianin (Ixor®). Radiat Oncol 30(7):12
Peters RC, Mommersteeg PMC, Heijmen PS (1999) The electroreceptor organ of the catfish, Ictalurus melas, as a model for sisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Neuroscience 91:745–751
Dehne N, Lautermann J, Petrat F et al (2001) Sisplatin ototoxicity: involvement of iron and enhanced formation of superoxide anion radicals. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 174:27–34
Yumusakhuylu AC, Yazici M, Sari M, Binnetoglu A, Kosemihal E, Akdas F, Sirvanci S, Yuksel M, Uneri C, Tutkun A (2012) Protective role of resveratrol against cisplatin induced ototoxicity in guinea pigs. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76(3):404–408
Erdem T, Bayindir T, Filiz A, Iraz M, Selimoglu E (2011) The effect of resveratrol on the prevention of cisplatin ototoxicity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(10):2185–2188 (Epub ahead of print)
Acknowledgments
The authors in this manuscript indicate that they do not have any financial relationship with the organization that sponsored the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şimşek, G., Tokgoz, S.A., Vuralkan, E. et al. Protective effects of resveratrol on cisplatin-dependent inner-ear damage in rats. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270, 1789–1793 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2183-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2183-4