Abstract
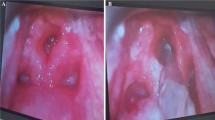
Deep neck abscesses are life-threatening conditions, in early stages preferably treated by intravenous antibiotic therapy; in advanced stages, surgical drainage is mandatory. We report two cases of retro-parapharyngeal abscess with prevalent retronasopharyngeal extension in two men aged 60 and 82, both of whom underwent transnasal endoscopic drainage. The main surgical steps were incision of the posterior pharyngeal mucosal wall, widening of the incision, drainage of purulent collection and careful dissection and removal of the necrotic tissue. The first patient, with an abscess associated with chronic otitis media and presenting hypoglossal nerve palsy, quickly recovered from pharyngodinia, otalgia and trismus. Twenty-six months after surgery, he is symptom-free, with hemitongue atrophy due to denervation as the only residual sign. The second patient, affected by skull base osteomyelitis secondary to malignant external otitis, after a first successful drainage, underwent a second endoscopic procedure for the reoccurrence of an abscess in the contralateral retroparapharyngeal space. Twelve months after the first surgery, the patient reported an improvement of symptoms, except for persistent dysphonia related to vagal nerve palsy. At follow-up MR, another abscess was detected in the left retro-parapharyngeal space. In selected cases of abscess, transnasal endoscopic drainage may be an effective alternative to external approaches. Minimal morbidity, the absence of cervical or palatal scars and a short hospitalization time can be considered as important advantages in comparison to external approaches. Patients with abscess secondary to skull base osteomyelitis require close imaging surveillance because of the difficulty of definitive control of the disease.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baatenburg de Jong RJ, Rongen RJ, Lameris JS, Knegt P, Verwoerd CD (1990) Ultrasound-guided percutaneous drainage of deep neck abscesses. Clin Otolaryngol 15:159–166
Bach MC, Roediger JH, Rinder HM (1988) Septic anaerobic jugular phlebitis with pulmonary embolism: problems in management. Rev Infect Dis 10:424–427
Batsakis JG, Sneige N (1998) Parapharyngeal and retropharyngeal space diseases. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 98:320–321
Benoit BG, Russell NA, Cole CW, Clark AJ, McIntyre RW (1983) Meningitis secondary to retropharyngeal abscess. Report of a case occurring in association with cervical spine fracture. Spine 8:438–439
Cappiello J, Piazza C, Berlucchi M, Peretti G, De Zinis LO, Maroldi R, Nicolai P (2002) Internal jugular vein patency after lateral neck dissection: a prospective study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 259:409–412
Chang PC, Fischbein NJ, Holliday RA (2003) Central skull base osteomyelitis in patients without otitis externa: imaging findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 24:1310–1316
Davis WL, Harnsberger HR, Smoker WR, Watanabe AS (1990) Retropharyngeal space: evaluation of normal anatomy and diseases with CT and MR imaging. Radiology 174:59–64
Elden LM, Grundfast KM, Vezina G (2001) Accuracy and usefulness of radiographic assessment of cervical neck infections in children. J Otolaryngol 30:82–89
Eliachar I, Peleg H, Joachims HZ (1981) Mediastinitis and bilateral pyopneumothorax complicating a parapharyngeal abscess. Head Neck Surg 3:438–442
Farina D, Hermans R, Lemmerling M, Op Beeck K (1999) Imaging of the parapharyngeal space. JBR-BTR 82:234–239
Gidley PW, Ghorayeb BY, Stiernberg CM (1997) Contemporary management of deep neck space infections. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 116:16–22
Goldenberg D, Golz A, Joachims HZ (1997) Retropharyngeal abscess: a clinical review. J Laryngol Otol 111:546–50
Hadlock FP, Wallace RJ Jr, Rivera M (1979) Pulmonary septic emboli secondary to parapharyngeal abscess; postanginal sepsis. Radiology 130:29–33
Harnsberger HR, Swartz JD (1998) Temporal bone vascular anatomy, anomalies and diseases, emphasizing the clinical-radiological problem of pulsatile tinnitus. In: Harnsberger HR, Swartz JD (eds) Imaging of the temporal bone. Thieme, New York, pp 178–180
Kao CH, Wang SJ (1992) Spread of infectious complications of odontogenic abscess detected by technetium-99m-HMPAO-labeled WBC scan of occult sepsis in the intensive care unit. J Nucl Med 33:254–255
Langenbrunner DJ, Dajani S (1971) Pharyngomaxillary space abscess with carotid artery erosion. Arch Otolaryngol 94:447–457
Lazor JB, Cunningham MJ, Eavey RD, Weber AL (1994) Comparison of computed tomography and surgical findings in deep neck infections. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 111:746–750
Lee DJ, Little JP, Tunkel DE (2000) Otorrhea from lateral extension of a retropharyngeal abscess. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 123:639–640
Leiberman A, Tovi F, Barki Y, Alkan M (1991) Salmonella neck abscess associated with jugular vein thrombosis. J Laryngol Otol 105:966–967
Magliulo G, Varacalli S, Ciofalo A (2000) Osteomyelitis of the skull base with atypical onset and evolution. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 109:326–330
Malone DG, O’Boynick PL, Ziegler DK, Batnitzky S, Hubble JP, Holladay FP (1992) Osteomyelitis of the skull base. Neurosurgery 30:426–431
Marty-Ane CH, Alauzen M, Alric P, Serres-Cousine O, Mary H (1994) Descending necrotizing mediastinitis. Advantage of mediastinal drainage with thoracotomy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 107:55–61
Murray ME, Britton J (1994) Osteomyelitis of the skull base: the role of high resolution CT in diagnosis. Clin Radiol 49:408–411
Parhiscar A, Har-El G (2001) Deep neck abscesses: a retrospective study of 210 cases. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110:1051–1054
Poe LB, Petro GR, Matta I (1996) Percoutaneous CT-guided aspiration of deep neck abscesses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17:1359–1363
Ridder GJ, Eglinger CF, Technau-Ihling K, Laszig R (2000). Deep neck abscess masquerading hypopharyngeal carcinoma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 123:659–660
Rubin Grandis J, Branstetter BF 4th, Yu VL (2004) The changing face of malignant (necrotising) external otitis: clinical, radiological, and anatomic correlations. Lancet Infect Dis 4:34–39
Sakaguchi M, Sato S, Asawa S, Taguchi K (1995) Computed tomographic findings in peritonsillar abscess and cellulitis. J Laryngol Otol 109:449–451
Sethi DS, Stanley RE (1991) Parapharyngeal abscesses. J Laryngol Otol 105:1025–1030
Sethi DS, Stanley RE (1994) Deep neck abscesses-changing trends. J Laryngol Otol 108:138–143
Sichel JY, Dano I, Hocwald E, Biron A, Eliashar R (2002) Nonsurgical management of parapharyngeal space infections: a prospective study. Laryngoscope 112:906–910
Slattery WH 3rd, Brackmann DE (1996) Skull base osteomyelitis. Malignant external otitis. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 29:795–806
Som PM, Curtin HD (1996) Parapharyngeal space. In: Som PM, Curtin HD (eds) Head and neck imaging. Mosby, New York, pp 915–951
Yamasaki T, Moritake K, Hatta J, Nagai H (1996) Intraoperative monitoring with pulse Doppler ultrasonography in transsphenoidal surgery: technique application. Neurosurgery 38:95–97
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nicolai, P., Lombardi, D., Berlucchi, M. et al. Drainage of retro-parapharyngeal abscess: an additional indication for endoscopic sinus surgery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 262, 722–730 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-004-0890-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-004-0890-1